Comprehensive Guide to Blood Sugar Testing: Types, Importance, and Tips for Better Health
This comprehensive guide explores the main types of blood sugar tests, their significance in health management, and practical tips for maintaining optimal glucose levels. Understanding these testing methods helps individuals prevent and manage diabetes effectively, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring and lifestyle choices to promote overall wellness.

Comprehensive Guide to Blood Sugar Testing: Types, Importance, and Tips for Better Health
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar testing, also known as blood glucose testing, is an essential diagnostic and monitoring tool used worldwide to evaluate the amount of glucose present in your bloodstream. Glucose, a primary source of energy derived from the food we consume, needs to be closely monitored, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing it. Proper understanding of blood sugar levels and the various testing methods available can empower you to better manage your health and prevent future complications.
The regulation of blood sugar hinges on insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin facilitates the conversion of glucose into energy, allowing cells in your body to function optimally. When the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin, or the body becomes resistant to insulin, blood sugar levels rise uncontrollably, leading to conditions such as diabetes mellitus. Diabetes is a persistent autoimmune disease that affects millions globally, and if left unmanaged, it can precipitate severe complications including cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, blindness, and impaired wound healing. Hence, understanding and regularly monitoring blood sugar levels are vital for both diabetics and healthy individuals aiming to maintain wellness.
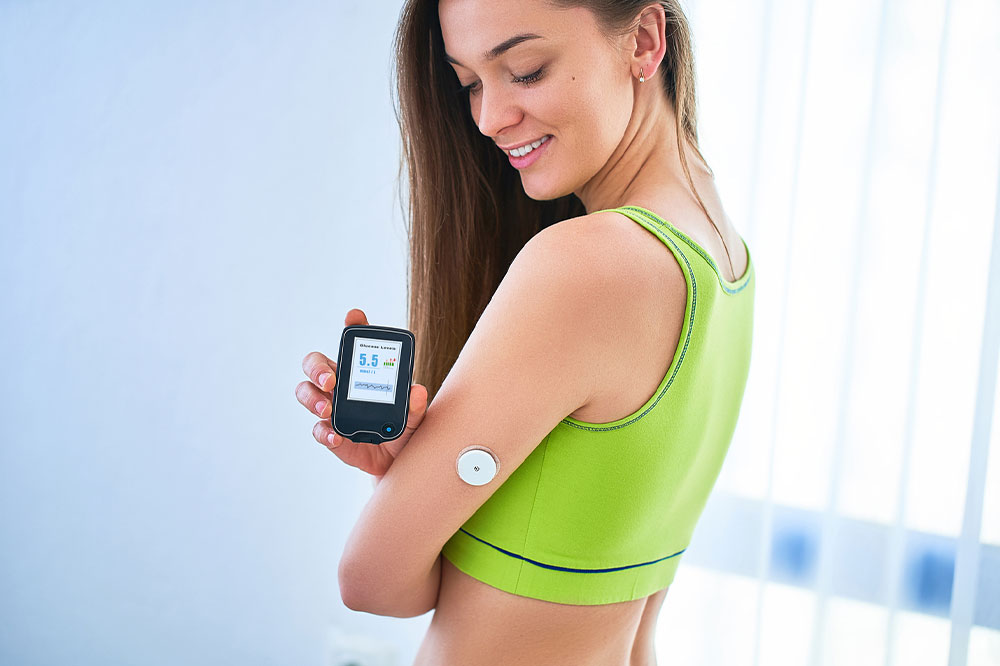
Blood glucose testing isn't solely for individuals diagnosed with diabetes. It serves as a preventative health measure, enabling early detection of abnormal blood sugar patterns even before symptoms manifest. Regular testing can provide valuable insights that guide lifestyle modifications and influence dietary choices, potentially delaying or preventing the progression to diabetes. Additionally, for those already managing insulin therapy or other medications, consistent monitoring helps in fine-tuning treatment plans for better control.
Preoperative blood sugar assessment is equally critical. Elevated blood glucose levels before surgery can increase the risk of complications, including infections and poor wound healing. Therefore, surgical teams often conduct fasting blood sugar tests prior to procedures to ensure optimal patient readiness. Your healthcare professional may recommend a combination of tests based on your medical history, lifestyle, and risk profile to provide a comprehensive picture of your glucose health.
Each blood sugar test offers unique insights into your metabolic health. Understanding these methods helps you communicate effectively with healthcare providers and make informed decisions about your health management strategies.
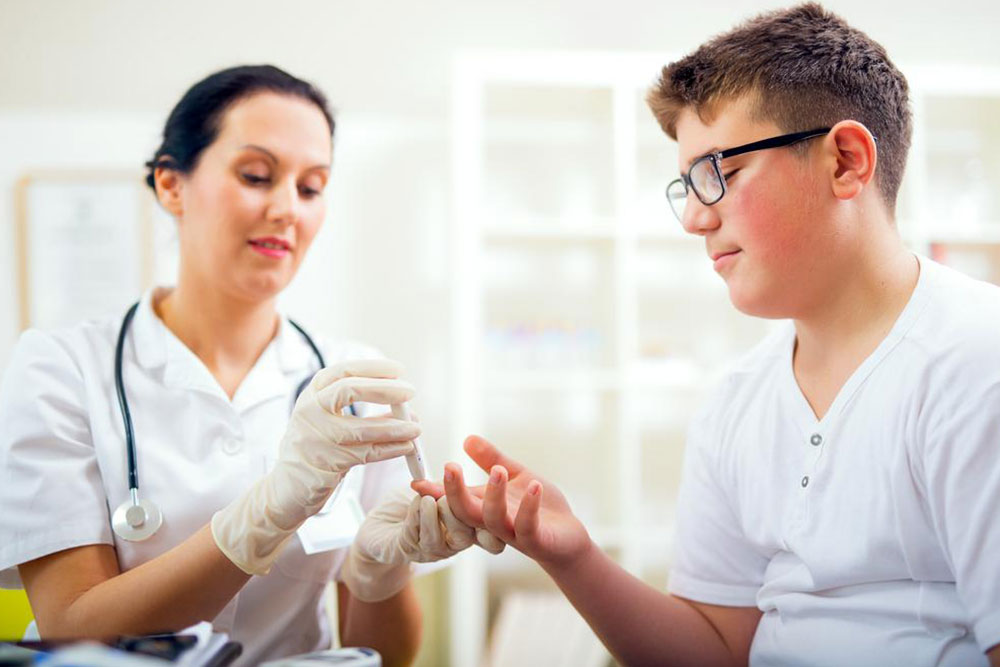
Fasting Blood Glucose Test – This test requires fasting, typically for at least eight hours, often performed early in the morning. It is a foundational test used to detect early signs of abnormal blood sugar levels, including prediabetes and diabetes. A reading below 100mg/dL is considered normal. Values between 100 and 125mg/dL suggest prediabetes, warranting further investigation. Readings exceeding 126mg/dL on two separate occasions usually confirm diabetes, requiring ongoing management and monitoring.
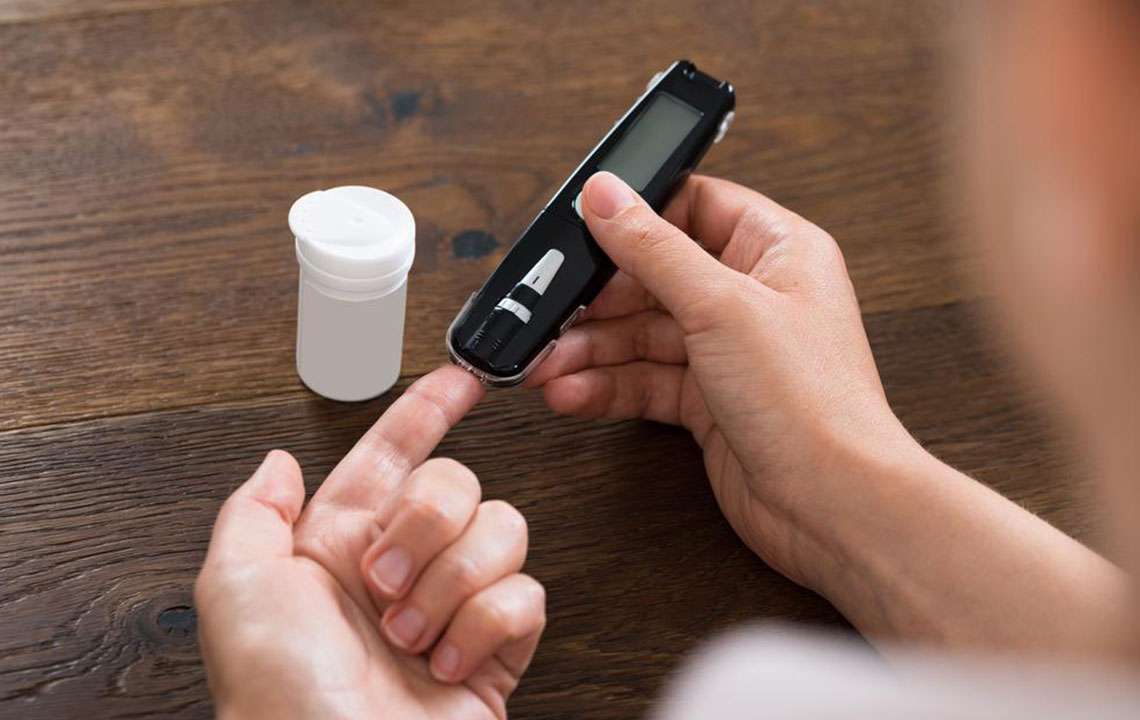
Random Blood Glucose Test – Unlike fasting tests, a random blood glucose test can be performed at any time regardless of when you last ate. It provides a snapshot of your current blood sugar level, helping to identify abnormal fluctuations throughout the day. Large variations may serve as early indicators of diabetes or other metabolic issues, prompting additional testing and evaluation.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test – Frequently used to diagnose gestational diabetes in pregnant women, this test involves drinking a sugary solution after an overnight fast. Blood samples are taken before consuming the solution and at intervals afterward, typically 1-2 hours, to track how your body processes glucose. It provides detailed insight into your body's ability to handle sugar and is instrumental in identifying insulin resistance and prediabetic states.
Hemoglobin A1c Test – This test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in your blood with attached glucose, reflecting your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months. An A1c below 5.7% indicates healthy blood sugar levels. Results between 5.7% and 6.4% suggest prediabetes, and levels of 6.5% or higher confirm diabetes. Regular A1c testing is crucial for individuals with diagnosed diabetes to monitor long-term control and adjust treatments accordingly.
Incorporating these tests into your regular health routine, along with lifestyle modifications such as balanced nutrition, regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol, can significantly enhance your ability to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent disease progression.