Comprehensive Guide to Naturally Boost Testosterone Levels for Better Health
Discover effective natural methods to boost testosterone levels, including resistance training, healthy eating, stress management, and lifestyle changes. These scientifically-backed strategies help improve vitality, muscle growth, and overall health naturally and sustainably.

Effective Natural Strategies to Increase Testosterone Levels Naturally
Testosterone is a vital hormone predominantly associated with male health, but it also plays an important role in women's overall well-being. Produced mainly in the testes in men and the ovaries in women, testosterone influences various bodily functions including sexual desire, muscle mass, energy levels, mood stability, and bone density. As men age, testosterone production gradually declines, often leading to reduced vitality, muscle weakness, and other health issues. Women experience a similar but less pronounced decrease over time.
Maintaining balanced testosterone levels is crucial for overall health, and the good news is that there are numerous natural methods to support and enhance testosterone production without resorting to pharmaceutical supplements or synthetic drugs. Adopting specific lifestyle habits and dietary adjustments can help optimize your hormone levels, promote vitality, and improve quality of life. Below, we explore detailed, scientifically-supported strategies that you can integrate into your daily routine to naturally boost testosterone levels effectively and sustainably.
Practice Heavy Resistance Training: Engaging in strength training with heavy weights is one of the most effective ways to stimulate testosterone production. Exercises such as squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups activate large muscle groups, prompting your body to produce more testosterone to support muscle repair and growth. Consistent resistance workouts, especially when performed with adequate intensity and proper form, can lead to significant hormonal benefits, regardless of age or fitness level.
Incorporate Varied Workout Routines: While heavy lifting is key, combining different types of workouts can enhance hormonal responses further. Incorporate high-intensity interval training (HIIT), circuit training, and compound movements to maximize muscle recruitment and promote more testosterone release. Changing routines helps prevent plateaus, keeps workouts engaging, and stimulates various muscle groups, all contributing to healthier hormone levels over time.
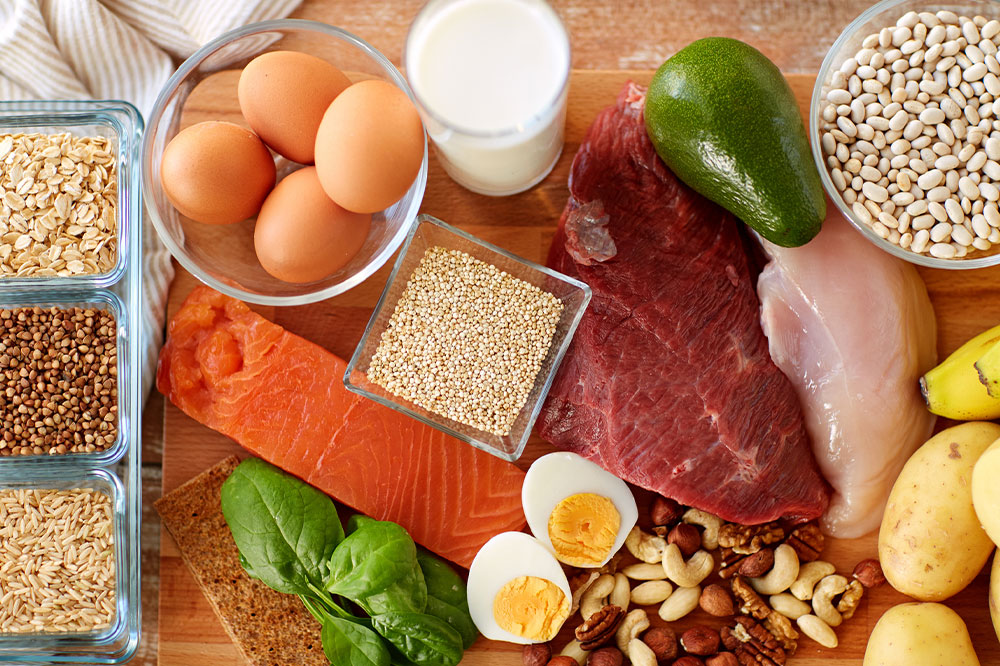
Manage Dietary Fats Wisely: Dietary fats are essential for testosterone synthesis, but moderation and quality matter. Focus on healthy fats from sources like avocados, olive oil, and nuts, while limiting excessive intake of saturated and trans fats found in processed foods. Balancing omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids supports hormonal health, with omega-3s from fatty fish like salmon and mackerel providing anti-inflammatory benefits that positively influence testosterone.
Reduce Chronic Stress Levels: Prolonged stress elevates cortisol, a hormone that can suppress testosterone production. Incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or leisure activities to lower stress levels. Adequate rest, mindfulness, and social connections also contribute to a balanced hormonal environment, ensuring your body's stress response doesn't negatively impact testosterone levels.
Eat Eggs and Healthy Protein Sources: Egg yolks are a good source of saturated fats and nutrients like vitamin D, which are linked to higher testosterone levels. Include moderate amounts of eggs, lean meats, and seafood in your diet. Oysters, in particular, are rich in zinc, a mineral critically involved in testosterone synthesis. Ensuring sufficient protein intake supports testosterone production and overall muscle health.
Prioritize High-Quality Sleep: Adequate sleep is fundamental for optimal hormonal function. Aim for 7 to 8 hours of restful, uninterrupted sleep each night to allow your body to naturally produce and regulate testosterone levels. Poor sleep patterns have been linked to decreased testosterone production, lowered energy, and impaired recovery, so establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a sleep-friendly environment are essential.
Limit Sugar and Processed Foods: Excessive sugar intake can lead to obesity and metabolic disturbances, which negatively affect testosterone levels. Reduce consumption of sugary snacks, beverages, and processed foods. Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that support hormonal health and metabolic efficiency.
Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Obesity, especially abdominal fat, is associated with increased estrogen levels, which can suppress testosterone. Combining regular physical activity with a balanced diet to achieve and maintain a healthy weight helps restore hormonal balance and enhances overall vitality.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and heavy alcohol intake are detrimental to testosterone production. Smoking damages blood vessels and interrupts hormone signaling, while alcohol in excess can reduce testosterone levels and impair testicular function. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake are vital for maintaining hormonal health.
Limit Phytoestrogen-Rich Foods like Soy: Soy contains phytoestrogens—plant-derived compounds similar to estrogen—that can interfere with testosterone production when consumed in large quantities. If concerned about testosterone levels, it’s advisable to moderate soy-based foods such as soy milk, tofu, and soy protein isolates, focusing instead on a diversified diet rich in whole foods.
Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet with Nuts and Seeds: Nuts like walnuts, almonds, and hazelnuts are excellent sources of healthy fats, zinc, magnesium, and other micronutrients beneficial for testosterone synthesis. Incorporate a variety of nuts and seeds into your diet for sustained hormonal support and overall health benefits.
Monitor Thyroid Function and Health: The thyroid gland influences many hormonal pathways, including testosterone production. Regular health checkups and thyroid function assessments can help identify and manage imbalances that might affect testosterone levels.
Consume Lean Meats and Seafood: Foods rich in zinc, such as lean beef, chicken, and oysters, are crucial for testosterone production. Zinc deficiency is a common cause of low testosterone, so including zinc-rich foods in your diet is an effective natural booster.
Increase Sunlight Exposure for Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a vital role in hormone health and is associated with higher testosterone levels. Aim for daily sunlight exposure of about 15-20 minutes, or consider vitamin D supplementation if sunlight is limited. Ensure adequate levels to support healthy hormonal regulation.
Implementing these natural strategies can significantly improve your testosterone levels over time. They are safe, cost-effective, and sustainable ways to enhance your health and vitality. By making conscious choices concerning exercise, diet, sleep, and stress management, you can foster a hormonal environment conducive to optimal functioning and overall well-being.