Comprehensive Guide to Nutrition Plans for a Healthier, More Vibrant Life
Discover effective nutrition strategies to enhance your health and vitality. This comprehensive guide covers low carbohydrate diets, high fiber intake, and personalized dietary plans designed to optimize your well-being. Learn how to balance nutrients, manage weight, and improve digestion through scientifically backed approaches tailored for a healthier lifestyle.
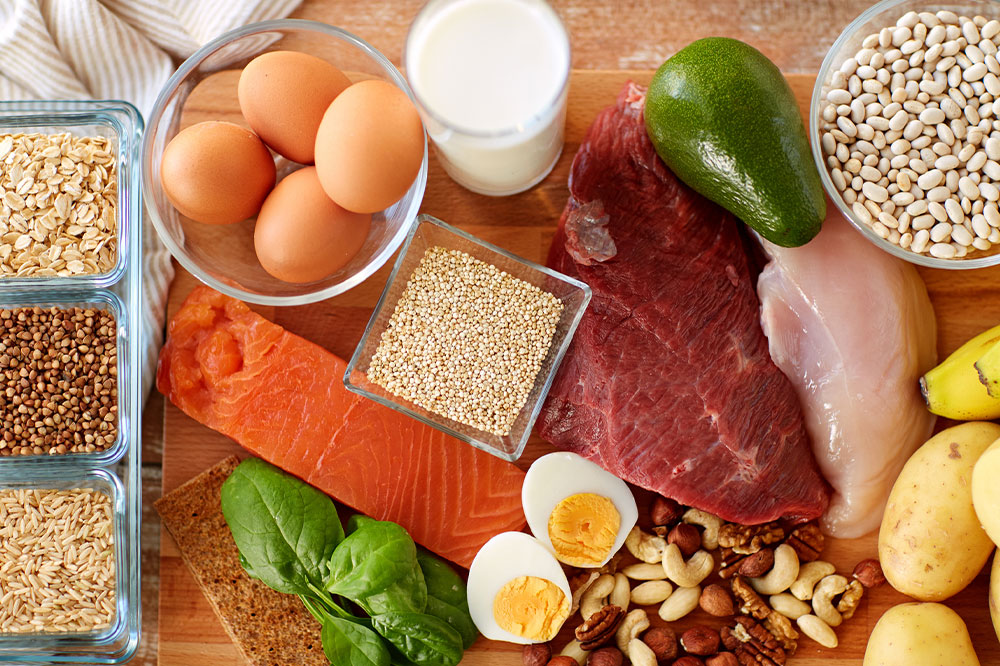

Optimized Nutrition Strategies to Boost Your Wellness and Vitality
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is fundamental to achieving optimal health and well-being. Essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, healthy fats, and phytonutrients play pivotal roles in supporting physical growth, mental clarity, immune resilience, organ function, and sustained energy levels. A well-rounded diet, when integrated with regular physical activity and sufficient restorative sleep, helps promote metabolic balance and overall vitality. Disruptions in these processes can lead to energy shortages, excess fat accumulation, oxidative stress, and sluggish bodily functions, which may predispose to chronic diseases. Therefore, establishing effective nutrition habits is critical for a thriving, wholesome lifestyle.
In today’s fast-paced world, many individuals encounter health challenges stemming from modern lifestyles, including poor dietary choices, insufficient sleep, and limited physical activity. To combat these issues, adopting a personalized nutrition plan tailored to one’s specific health needs can make a significant difference. Whether aiming for weight management, blood sugar control, or overall vitality, there are various diet strategies to consider. Below, we explore some of the most effective dietary approaches to help you select the right path toward a healthier life.
Low Carbohydrate Diets: A Path to Better Blood Sugar and Weight Control
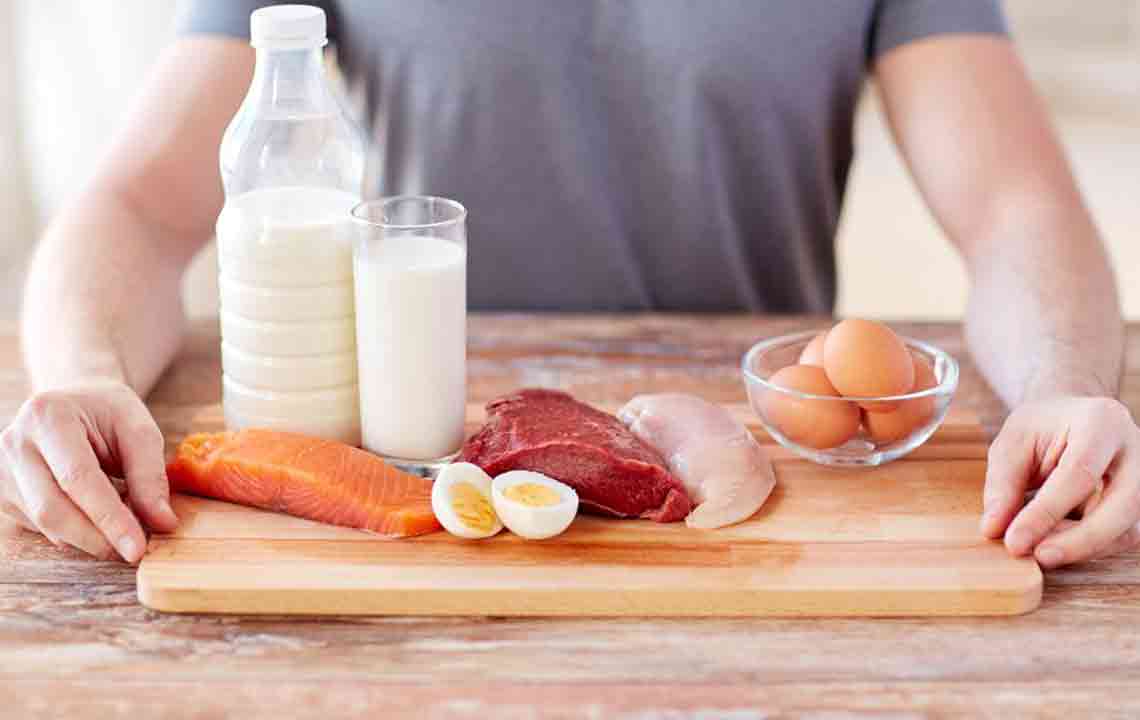
Low carbohydrate diets have gained popularity among individuals seeking to manage conditions like diabetes, obesity, and hypertension. These diets focus on reducing carbohydrate intake, mainly from simple sugars and refined starches, while emphasizing protein and healthy fats. The reduction in carbs leads to improved blood sugar levels and supports fat loss. Carbohydrates are found abundantly in foods such as wheat, rice, potatoes, cereals, bread, candies, chocolates, legumes, fruits, soft drinks, caffeine, and alcohol. It’s important to note that moderation is key—completely eliminating carbs is neither practical nor sustainable for many.
To effectively implement a low carb diet, aim to limit your daily carbohydrate consumption to approximately 30 grams initially, adjusting based on your weight-loss goals and health status. Focus on increasing your intake of lean proteins—such as chicken, fish, eggs, and plant-based options—and incorporate raw, organic foods to maximize nutrient absorption. Hydration is essential; strive to drink 8-12 glasses of water daily to support metabolic functions. Prioritize healthy fats, including olive oil, nuts, avocados, and seeds, over saturated fats like butter or cheese, to enhance cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
High Fiber Diet Strategies for Digestive and Heart Health
Dietary fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health, regulating weight, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Found exclusively in plant-based foods, fiber is divided into two main types: insoluble and soluble. Both types provide unique benefits and should be included in your daily diet to promote comprehensive health benefits.
Insoluble Fiber: Promoting Healthy Bowel Movements
This type of fiber absorbs water and adds bulk to stool, facilitating smooth and regular bowel movements. Sources rich in insoluble fiber include whole wheat products like bread and cereals, bran, nuts, seeds, and the skins of fruits and vegetables. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help prevent constipation and promote gastrointestinal health.
Soluble Fiber: Supporting Heart and Blood Sugar Health
Soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, assisting in lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels and stabilizing blood sugar levels. Common sources of soluble fiber include oats, barley, fruits such as bananas and apples, vegetables like carrots and potatoes, and legumes including beans and lentils. Increasing soluble fiber intake can contribute to reducing the risk of heart disease and managing blood glucose.
For optimal health benefits, aim to consume at least 30 grams of dietary fiber daily. Adjust this intake based on age, gender, and specific health conditions—starting gradually to prevent bloating or gas. A high-fiber diet enhances satiety, making it easier to control appetite and support weight loss efforts. Remember, consistency is key, and balancing fiber intake with adequate hydration ensures optimal digestive function.