Comprehensive Guide to Achieving Optimal Health Through Balanced Nutrition
This comprehensive guide emphasizes the importance of balanced nutrition for a healthier lifestyle. It covers essential nutrients, practical diet tips, and how to incorporate healthy foods into daily routines. Combining good eating habits with physical activity can improve immunity, support weight management, and promote overall wellbeing for a longer, healthier life.

Achieving Optimal Health with Balanced Nutrition: The Ultimate Dietary Guide
Maintaining a balanced diet is fundamental to leading a healthy lifestyle. It involves the careful selection and preparation of meals that provide all necessary nutrients in the right proportions. While adopting healthy eating habits can seem challenging amidst busy schedules and tempting processed foods, implementing structured dietary strategies can make a significant difference to your health and wellbeing. A well-rounded diet encompasses a variety of nutrients including carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats, each playing a vital role in supporting bodily functions, promoting vitality, and preventing disease. Contrary to popular myths, adopting a nutritious diet doesn’t mean sacrificing flavor or living in deprivation; instead, it’s about making intelligent choices that align taste with health benefits, leading to sustainable and enjoyable eating routines.
Whether you have a specific body type or simply want to improve overall wellbeing, maintaining an optimal diet is essential. Proper nutrition isn’t just about weight management; it’s about fueling your body with the right nutrients to support a robust immune system, improve mental clarity, and enhance overall quality of life. An unbalanced diet can lead to deficiencies, health conditions, and reduced energy levels, so understanding the core nutritional components and how to incorporate them effectively is crucial for everyone.
Main Nutritional Components for a Healthy Diet
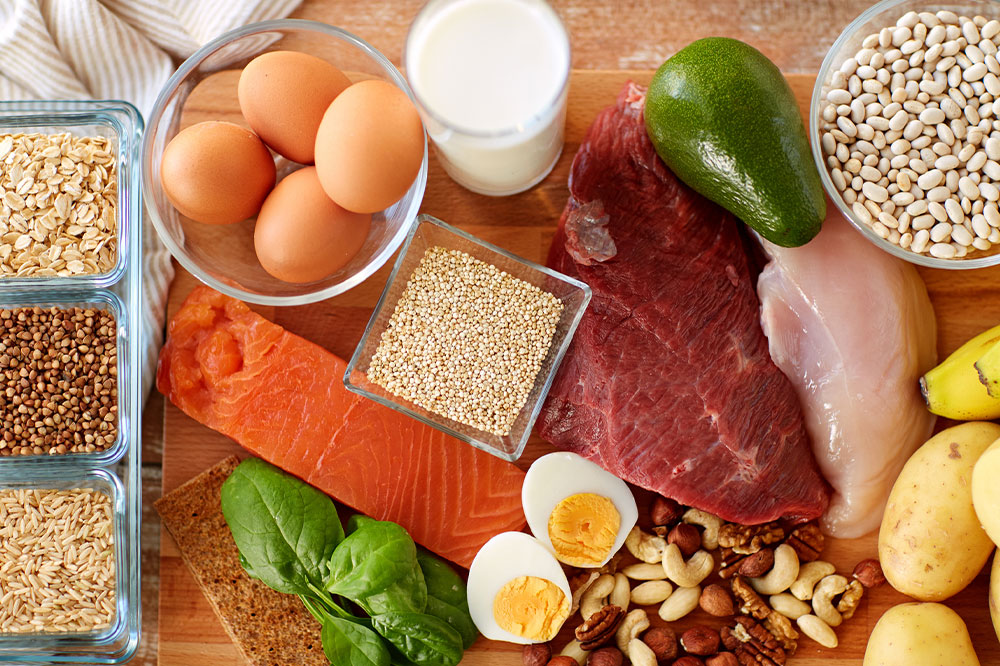
Achieving a balanced diet means combining all vital nutrients—vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, and fats—in appropriate proportions. Each plays a unique role and complements the others to optimize health outcomes.
Vitamins and Minerals
Micronutrients like vitamins and minerals are essential for numerous bodily functions. They support immune health, aid in metabolic processes, strengthen bones, and help maintain skin and hair health. Incorporate a colorful variety of vegetables such as spinach, broccoli, carrots, and bell peppers, which are packed with vital micronutrients. Fruits like berries, oranges, and bananas add an extra layer of nutritional benefit, providing antioxidants and essential vitamins.
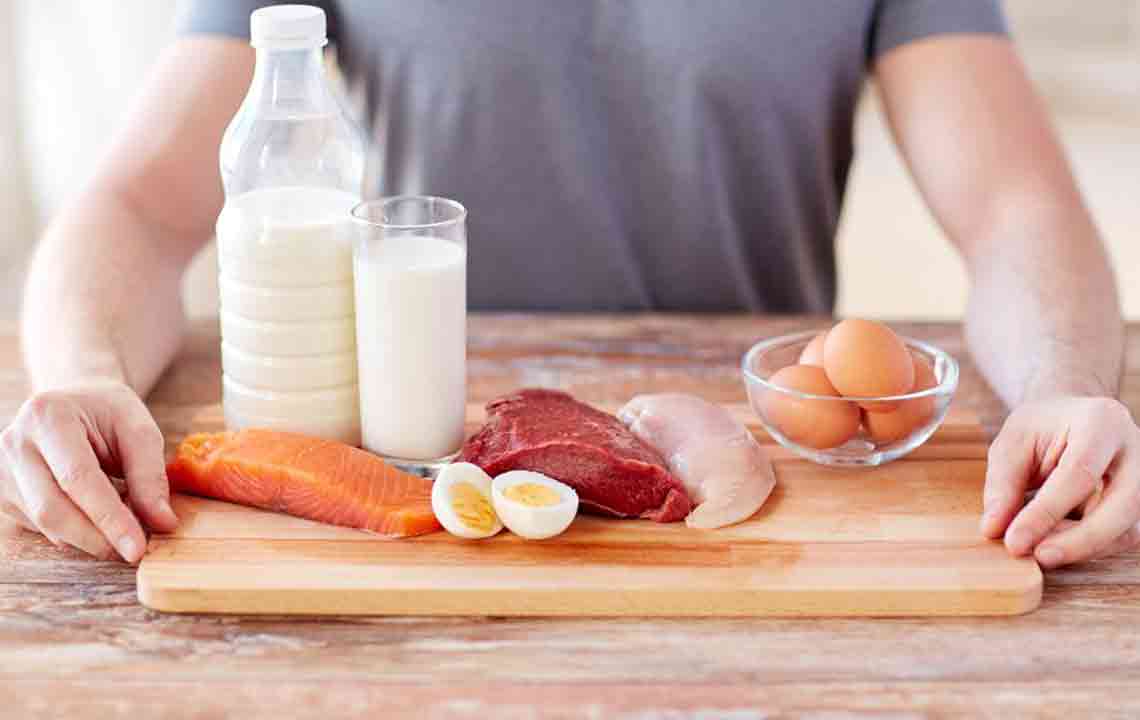
Proteins
Proteins are the building blocks of the body, responsible for repairing tissues, building muscles, and supporting growth and development. Protein intake is especially critical during growth phases such as childhood, adolescence, pregnancy, and recovery from illness. Good sources include lean meats, fish, dairy products, eggs, legumes, beans, and plant-based options such as tofu and quinoa. Aim to include a variety of sources to ensure you meet about 30-35% of your daily caloric needs from proteins, depending on age and activity level.
Carbohydrates
As the primary energy source, carbohydrates are vital for maintaining daily activity levels and brain function. However, the quality of carbs matters—whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are preferable over refined sugar and processed grains. Fiber-rich carbs promote digestive health, help regulate blood sugar levels, and keep you feeling full longer, reducing overeating and snacking on unhealthy foods.
Fats
Fats are essential for energy storage, hormone production, and nutrient absorption. Healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, as well as monounsaturated fats present in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, are beneficial for cardiovascular health. It’s advisable to limit intake of trans fats and excessive saturated fats, often found in fried foods and processed snacks, which can elevate cholesterol levels and increase heart disease risk.
Practical Guidelines for Maintaining a Balanced Diet
Consistency and planning are key to sustaining healthy eating habits. Keeping a food journal helps in tracking meal portions and identifying nutritional gaps. Structuring your day with five small, nutrient-dense meals every three hours promotes better digestion, stabilizes blood sugar levels, and prevents overeating.
Making Informed Food Choices
Educate yourself about the nutritional content of foods and avoid impulsive consumption of highly processed options. Prioritize whole, minimally processed foods that provide high nutrient density. Incorporate a variety of colorful vegetables and fruits, lean proteins, fiber-rich grains, and healthy fats into your daily intake.
Limit Intake of Less Healthy Foods
Processed foods are often laden with added sugars, excessive salt, and unhealthy fats, which can contribute to chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Replace snacks like chips, candies, and baked goods with fresh fruits, nuts, seeds, or homemade healthy treats to improve your health outcomes.
The Role of Dairy and Calcium
Dairy products are an excellent source of calcium, vital for strong bones and teeth, as well as muscle function and nerve transmission. If lactose intolerance or preferences lead you to avoid dairy, consider fortified plant-based alternatives or supplements to prevent conditions like osteoporosis and ensure adequate calcium intake.
Managing Oil and Sugar Intake
Overconsumption of oils and sugars is linked to various health issues, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Use oils rich in healthy fats for cooking, such as extra virgin olive oil, and limit the use of refined sugars in your diet. Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or fresh fruit when possible.
The Synergy of Diet and Physical Activity
A balanced diet coupled with regular physical activity amplifies health benefits. Whether it’s walking, jogging, cycling, or strength training, staying active supports weight management and improves cardiovascular health. Adjust your dietary intake based on your activity level, ensuring adequate energy supplies for workouts. Incorporate energy-boosting snacks rich in carbs and protein before exercise to enhance performance and recovery.
Embarking on a journey towards a healthier lifestyle requires commitment to both nutritious eating and regular movement. Small, sustainable changes in your diet and activity routines can lead to profound health improvements over time. Embrace the principles of balance, variety, and moderation today — your body will thank you for it, and lifespan health will be your reward.