Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Symptoms of Thyroid Eye Disorder
This comprehensive article explores the signs and symptoms of thyroid eye disorder, also known as Graves' orbitopathy. Early detection through symptoms like protruding eyes, swelling, dryness, and double vision is crucial for effective treatment. The article emphasizes the importance of timely medical intervention, diagnostics, and management strategies to prevent complications. It offers insights into how individuals can recognize these indicators early and seek prompt care to preserve eye health and vision. Understanding these symptoms empowers patients and healthcare providers to address thyroid eye disease proactively, enhancing therapeutic outcomes and quality of life.

Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Symptoms of Thyroid Eye Disorder
Thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy, more commonly known as Graves' orbitopathy, is an autoimmune condition that predominantly affects the tissues surrounding the eyes. This complex disorder results from an immune response that targets the tissues around the orbit, leading to a wide range of ocular symptoms. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for effective management and to prevent serious complications that could impair vision or cause aesthetic concerns.
Thyroid eye disease (TED) typically presents through noticeable clinical signs that prompt further medical evaluation. Identifying these indicators early can help doctors tailor personalized treatment strategies, reducing discomfort, preventing progression, and safeguarding ocular health. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the key symptoms and signs of thyroid eye disorder, covering everything from protruding eyes to subtle changes in vision, so patients and healthcare providers can act swiftly and effectively.
Understanding the Primary Symptoms of Thyroid Eye Disorder
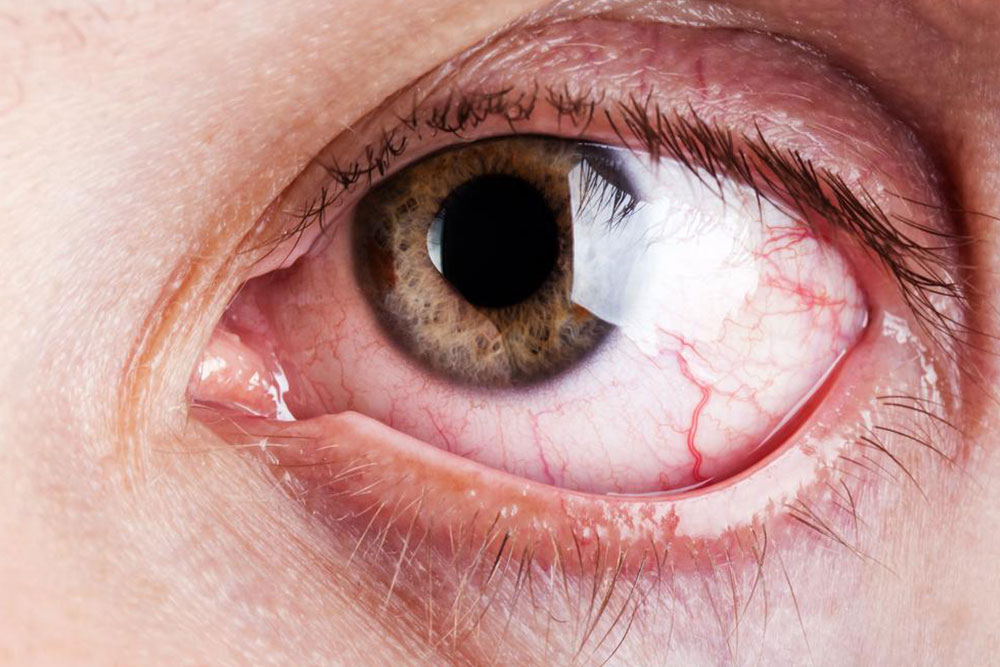
The hallmark feature of thyroid eye disorder is exophthalmos, or bulging eyes, which results from swelling and inflammation of the fatty tissues and muscles behind the eye. This protrusion is often the first visible sign that prompts individuals to seek medical advice.
Protruding eyes not only alter facial appearance but also cause significant discomfort. The exposure of the eyeballs increases the risk of dryness, irritation, and even corneal damage if left untreated. Patients often experience watering, redness, and a gritty sensation, which can interfere with daily routines and quality of life.
Swelling of the tissues around the eyes, especially in the eyelids and eyelid margins, is another prominent symptom. This periorbital edema results from fluid accumulation due to immune-mediated inflammation. The swelling can cause a puffiness appearance, restrict eye movement, and make blinking or closing the eyes difficult, leading to discomfort and secondary infections.
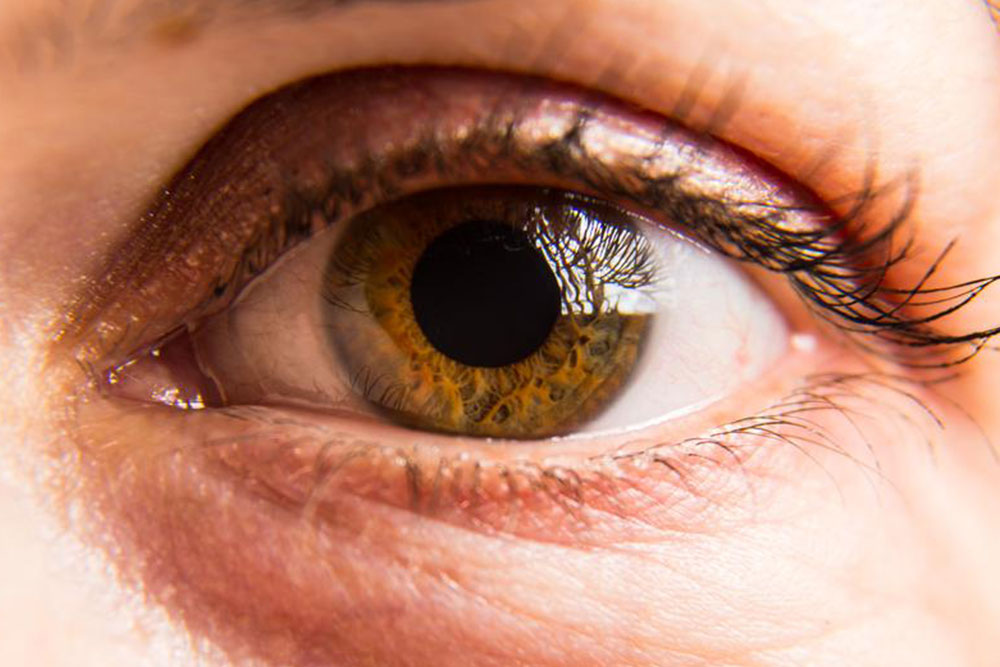
One of the common complaints amongst patients is the sensation of grit or foreign objects in the eyes. This gritty feeling arises from the dryness caused by impaired tear production and eyelid dysfunction. The dryness worsens with blinking, exposure to wind, or bright lighting, causing additional irritation and discomfort.
Other Key Clinical Indicators of Thyroid Eye Disease
Immune-related impairment of tear glands leads to decreased tear production, resulting in dry, irritated eyes. This condition, known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, often presents with redness, blurred vision, and a feeling of grittiness, especially during environmental exposures like wind or sun.
Double vision, or diplopia, significantly hampers daily activities. It occurs because the inflammation and swelling interfere with the proper alignment and coordination of the eye muscles. Patients might notice that objects appear doubled or misaligned, which can impact tasks such as reading, driving, or even simple daily movements. Prompt diagnosis and management are essential to prevent worsening symptoms and preserve vision.
Inflammation and swelling within the orbit can cause dull aches or sharp pains in the eyes, often accompanied by a sensation of pressure. These symptoms tend to intensify following prolonged eye movement or physical exertion, highlighting the importance of early intervention.
Lagophthalmos, the inability to fully close the eyelids, is another characteristic sign. This condition typically results from eyelid retraction or bulging, exposing the cornea to environmental hazards. If not treated, lagophthalmos can lead to serious issues like corneal ulcers or keratitis due to dryness and irritation.
Sensitivity to light, or photophobia, is frequently reported. It results from corneal dryness and increased inflammation, making patients uncomfortable in brightly lit environments. Wearing sunglasses or avoiding direct sunlight can temporarily alleviate symptoms but does not address the underlying cause.
Visual disturbances, including blurred or fluctuating vision, are common in thyroid eye disorder. These changes stem from muscle swelling, nerve involvement, and corneal dryness, complicating routine activities. Regular ophthalmological assessments are necessary for effective treatment and stabilization.
Eyelid retraction produces a distinctive staring or wide-eyed look. This feature is not only aesthetically noticeable but also contributes to dryness and irritation. Managing eyelid retraction often involves medical or surgical interventions to improve comfort and facial appearance.
Comprehensive Management and When to Seek Medical Help
If you notice any of these symptoms, including protruding eyes, swelling, dryness, double vision, or pain, it is vital to consult an ophthalmologist or endocrinologist promptly. Early diagnosis allows for more effective treatments, which may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, radiotherapy, or surgical procedures aimed at relieving pressure, reducing inflammation, and improving eye function.
Additionally, managing underlying thyroid dysfunction through medication and regular blood tests is essential for controlling the progression of eye symptoms. Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding environmental irritants, using artificial tears, and protecting the eyes from wind and bright lights, are also recommended to minimize discomfort.
Preventive Measures and Living with Thyroid Eye Disease
While some aspects of thyroid eye disorder can be managed effectively, prevention focuses on early detection and comprehensive treatment of thyroid dysfunction. Patients with Graves' disease or other thyroid abnormalities should undergo regular eye examinations and work closely with healthcare providers to monitor changes.
Patients are encouraged to adopt habits that preserve eye health, such as maintaining good eyelid hygiene, using humidifiers in dry environments, and avoiding rubbing or irritating the eyes. Proper eye protection combined with medical therapies can significantly improve quality of life and prevent worsening of symptoms.
Summary
Recognizing the symptoms of thyroid eye disorder early can lead to timely interventions that alleviate discomfort, prevent vision loss, and improve facial aesthetics. Key indicators include protruding eyes, eyelid swelling, dryness, double vision, and eyelid retraction. Healthcare professionals recommend prompt consultation upon noticing these signs to ensure appropriate treatment and management strategies. With advances in medical therapies and surgical options, many individuals with thyroid eye disease can achieve significant symptom relief and maintain a good quality of life.