Proven Strategies to Prevent Hospital-Acquired Infections and Ensure Patient Safety
This article outlines comprehensive strategies to prevent hospital-acquired infections, emphasizing hand hygiene, PPE, equipment sterilization, environmental cleaning, and staff training. Implementing these measures can significantly reduce infection rates, ensuring a safer environment for patients, staff, and visitors. It highlights the importance of proactive infection control practices in healthcare settings to promote optimal health outcomes and prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
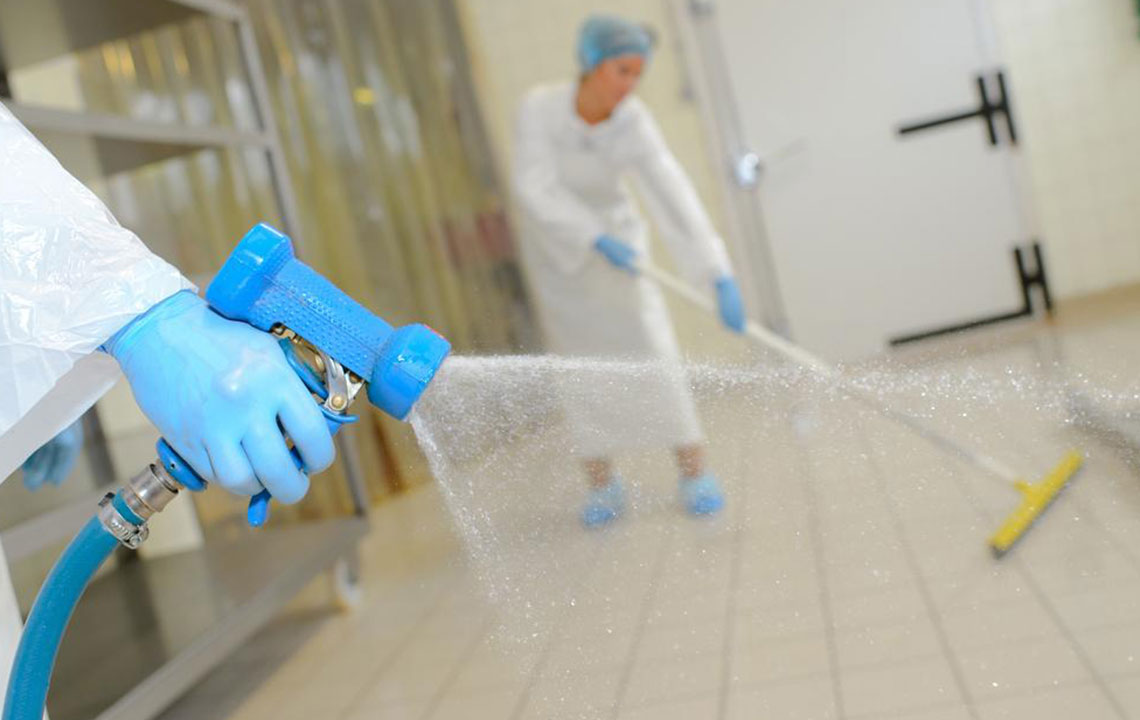

Comprehensive Measures to Minimize Infections in Healthcare Settings
Hospital-acquired infections (HAIs), also known as nosocomial infections, pose significant risks to patient safety and healthcare staff. Studies show that approximately 5-10% of patients admitted to hospitals will acquire an infection during their stay, which can lead to increased morbidity, longer hospitalization periods, and additional healthcare costs. These infections can be caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other pathogens present within healthcare environments. They spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, medical equipment, air droplets, or even via healthcare workers’ hands. Recognizing the various transmission routes is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies to mitigate the risk of HAIs.
Importance of Hand Hygiene: One of the simplest yet most effective methods to prevent the spread of infections is rigorous hand hygiene. Healthcare professionals should regularly wash their hands with soap and water or use alcohol-based hand sanitizers before and after patient interactions. Patients and visitors are also encouraged to practice hand hygiene to reduce contamination. Proper hand hygiene has been shown to significantly decrease the transmission rate of HAIs and is considered a frontline defense in infection control.
Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): PPE such as masks, gloves, gowns, and eye protection serve as barriers preventing the transmission of pathogens. Medical staff should don appropriate PPE during patient care activities, especially when dealing with infectious or immunocompromised patients. Proper donning and doffing procedures are vital to avoid cross-contamination. Advocating for the correct use of PPE within healthcare settings enhances overall safety and reduces infection rates.
Rigorous Medical Equipment Disinfection and Sterilization: Reusable medical equipment, including stethoscopes, blood pressure cuffs, and thermometers, should undergo thorough disinfection after each use. Alcohol wipes and other approved disinfectants can effectively eliminate microbial contamination. For invasive procedures, sterilization of equipment through autoclaving or other sterilization techniques is essential to prevent infection transmission. Proper cleaning protocols must be maintained in all healthcare facilities to uphold the highest safety standards.
Environmental Cleaning and Disinfection: Regular cleaning of surfaces such as bed rails, doorknobs, and medical carts with EPA-approved disinfectants minimizes environmental reservoirs of pathogens. Special attention should be paid to high-touch areas, and routines should be established for deep cleaning protocols to ensure a sterile environment.
Staff Education and Training: Ongoing education on infection prevention protocols informs healthcare workers of the latest best practices. Training sessions can include proper hand hygiene, correct PPE usage, and equipment sterilization techniques. Cultivating an organizational culture that prioritizes patient safety and infection control is essential for sustained improvements.
Visitor and Patient Engagement: Visitors should follow hospital policies on hand hygiene and PPE when necessary. Patients themselves can participate in infection prevention through educating themselves about hygiene practices, covering coughs and sneezes, and adhering to medical advice. Collaborative efforts between staff, patients, and visitors create a comprehensive defense against HAIs.
Leading healthcare institutions emphasize proactive infection control strategies such as surveillance for infections, prompt identification of outbreak sources, and continuous quality improvement initiatives. Implementing these measures effectively not only reduces infection rates but also contributes to a safer, more trusting healthcare environment. Prevention remains the cornerstone of infection control, and adherence to these comprehensive strategies ensures better health outcomes for all parties involved.