Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Prevent and Manage Cancer Effectively
This comprehensive guide explores critical dietary and lifestyle strategies to prevent and manage cancer effectively. Emphasizing foods to limit or avoid, such as red meats, fried foods, and alcohol, it also discusses the importance of early detection, healthy living, and modern targeted treatments like Venetoclax. By adopting these guidelines, individuals can reduce their cancer risk and support ongoing treatment efforts, enhancing overall health and well-being.

Essential Nutritional Guidelines for Cancer Prevention and Management
Cancer is a complex group of diseases characterized by abnormal cellular growth that can invade nearby tissues and spread throughout the body via the bloodstream or lymphatic system. With more than a hundred different types, some forms of cancer are relatively easier to detect early and respond well to treatment, whereas others remain elusive during their initial stages due to subtle or non-specific symptoms. Therefore, adopting proper dietary habits can significantly influence your risk of developing certain cancers and assist in managing existing conditions.
Foods to Limit or Avoid for Better Cancer Prevention
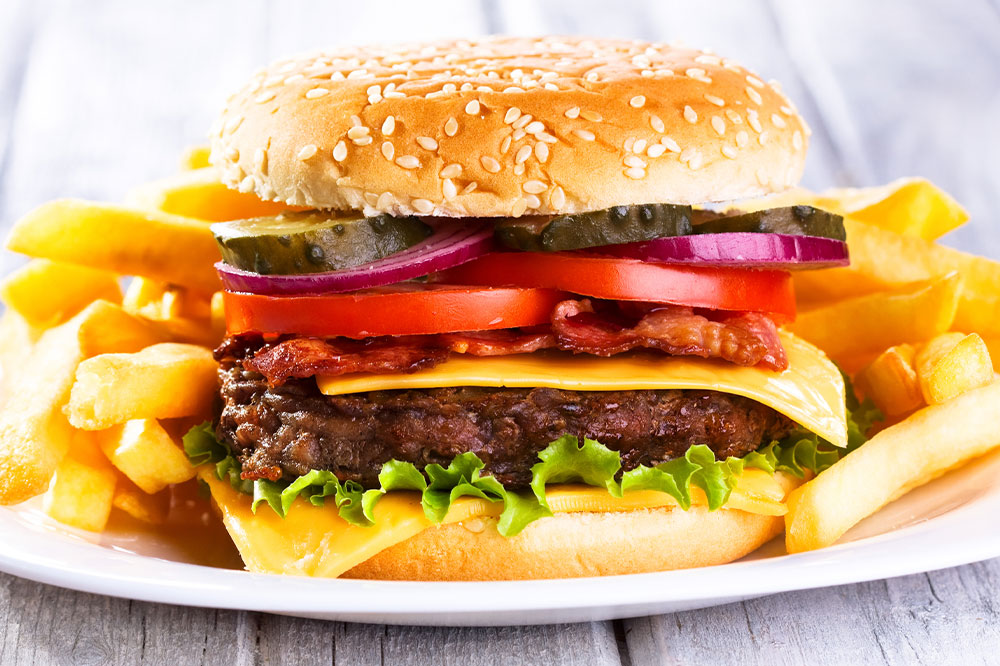
Red Meat and Processed Meats
Consuming red meats, such as beef, pork, and lamb, in excess has been linked to an increased risk of various cancers, particularly colorectal cancer. The preparation and curing processes involved with red meats can introduce carcinogenic substances like N-nitroso compounds and heterocyclic amines. These substances are formed when red meat is cooked at high temperatures, such as grilling or frying, which can create harmful compounds capable of damaging DNA and promoting cancer cell growth. Limiting intake of red meats and opting for leaner, plant-based protein sources can reduce these risks.
Additionally, foods prepared through frying at high temperatures should be consumed sparingly. Fried foods, such as fried chicken, French fries, and snacks, can lead to the formation of acrylamide, a carcinogenic compound that forms when starchy foods are cooked at high heat. Excessive fried food consumption is also associated with elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels, which increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and consequently, certain types of cancer. To support cancer prevention, it’s advisable to favor cooking methods like steaming, boiling, baking, or grilling at moderate temperatures.
Alcohol Consumption and Its Risks
Many studies have established a link between excessive alcohol consumption and an increased risk of developing various cancers, including mouth, throat, esophagus, liver, colon, and breast cancers. Alcohol is metabolized into acetaldehyde, a toxic compound capable of damaging DNA and impairing the body’s natural ability to eliminate carcinogenic substances. Furthermore, alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system’s defenses and interfere with cancer treatments, making management more challenging. Reducing alcohol intake or abstaining altogether can significantly enhance your overall health and lower cancer risk.
Difficult-to-Detect Cancers and the Role of Diet and Lifestyle
Some cancers, such as prostate cancer, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), often evade early detection because symptoms can resemble common infections or benign conditions. These include urinary issues, swollen lymph nodes, or fatigue. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, which is why maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle is vital. Consuming a diet rich in antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients can support the immune system, reduce inflammation, and potentially slow the progression of such cancers.
Medications and Targeted Cancer Therapies
In addition to dietary and lifestyle adjustments, modern medicine offers various treatment options, including targeted therapies. For instance, VENCLEXTA (Venetoclax) is a highly specialized oral medication primarily prescribed for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). It acts as a BCL-2 inhibitor, promoting apoptosis in cancer cells, and is often combined with other agents to enhance treatment efficacy. Integrating such targeted therapies with nutritional strategies can improve patient outcomes and quality of life.