Comprehensive Guide to Tinnitus: Understanding Types, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide delves into tinnitus, exploring its types, causes, and various management strategies aimed at alleviating symptoms. It covers medical options like hearing aids, cochlear implants, and therapy techniques such as counseling and sound masking. Understanding the underlying reasons—from ear damage to health conditions—helps in developing effective treatment plans. Although no permanent cure exists, personalized approaches significantly improve quality of life for those affected by tinnitus, making heightened awareness and timely intervention crucial.

Comprehensive Guide to Tinnitus: Understanding Types, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
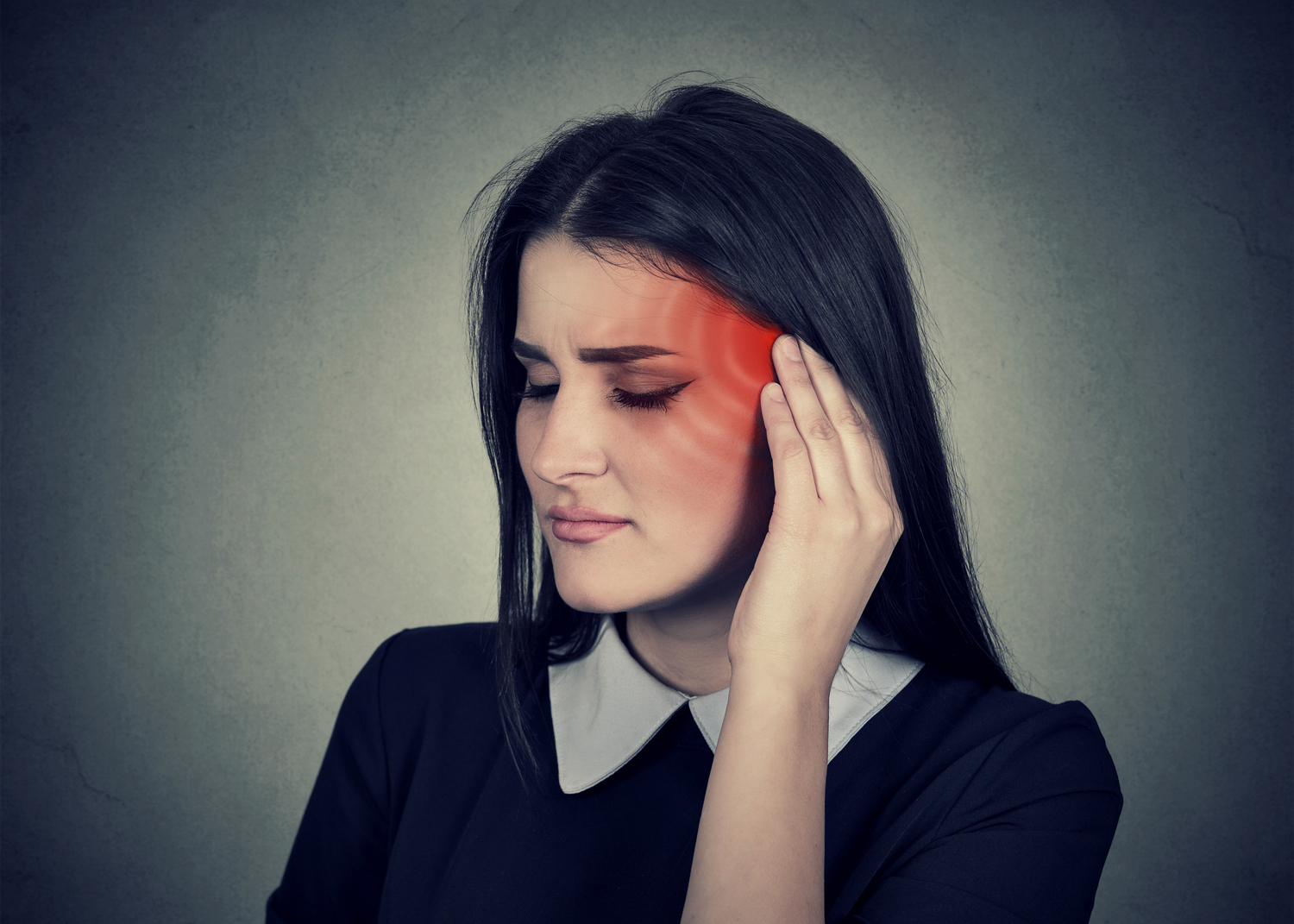
Tinnitus is a common auditory condition characterized by the perception of ringing, buzzing, hissing, clicking, or roaring sounds in the ears, which are not caused by external noises. Many individuals experience these sounds temporarily after exposure to loud music or noisy environments, but for some, tinnitus persists long-term, impacting daily life and emotional well-being. Understanding the different aspects of tinnitus, including its types, causes, and ways to manage it, is essential for those affected and their healthcare providers to seek appropriate interventions for relief and improved quality of life.
Understanding the Different Types of Tinnitus
Tinnitus is primarily a symptom rather than a standalone medical condition, often signaling underlying health issues. It manifests mainly in two categories: objective and subjective tinnitus. Although objective tinnitus is quite rare, it can be heard by both the individual and a clinician during examination. Subjective tinnitus, which accounts for the vast majority of cases, involves the perception of internal sounds solely by the affected individual and is influenced by inner ear health, neural pathways, and other factors.
Causes of Tinnitus: Unraveling the Underlying Factors
The origins of tinnitus are diverse, making diagnosis and treatment a complex process. Damage to the delicate hair cells within the inner ear is one of the most common reasons, often resulting from prolonged exposure to loud noises, aging, or ear trauma. When these tiny hair cells are damaged or destroyed, they can send irregular signals to the brain, leading to the perception of ringing or buzzing sounds.
In addition to hair cell damage, blockages caused by excessive earwax buildup, infections in the ear canal or middle ear, or benign growths like acoustic neuromas can contribute to tinnitus symptoms. Age-related hearing deterioration, known as presbycusis, also increases vulnerability as the auditory system gradually degenerates.
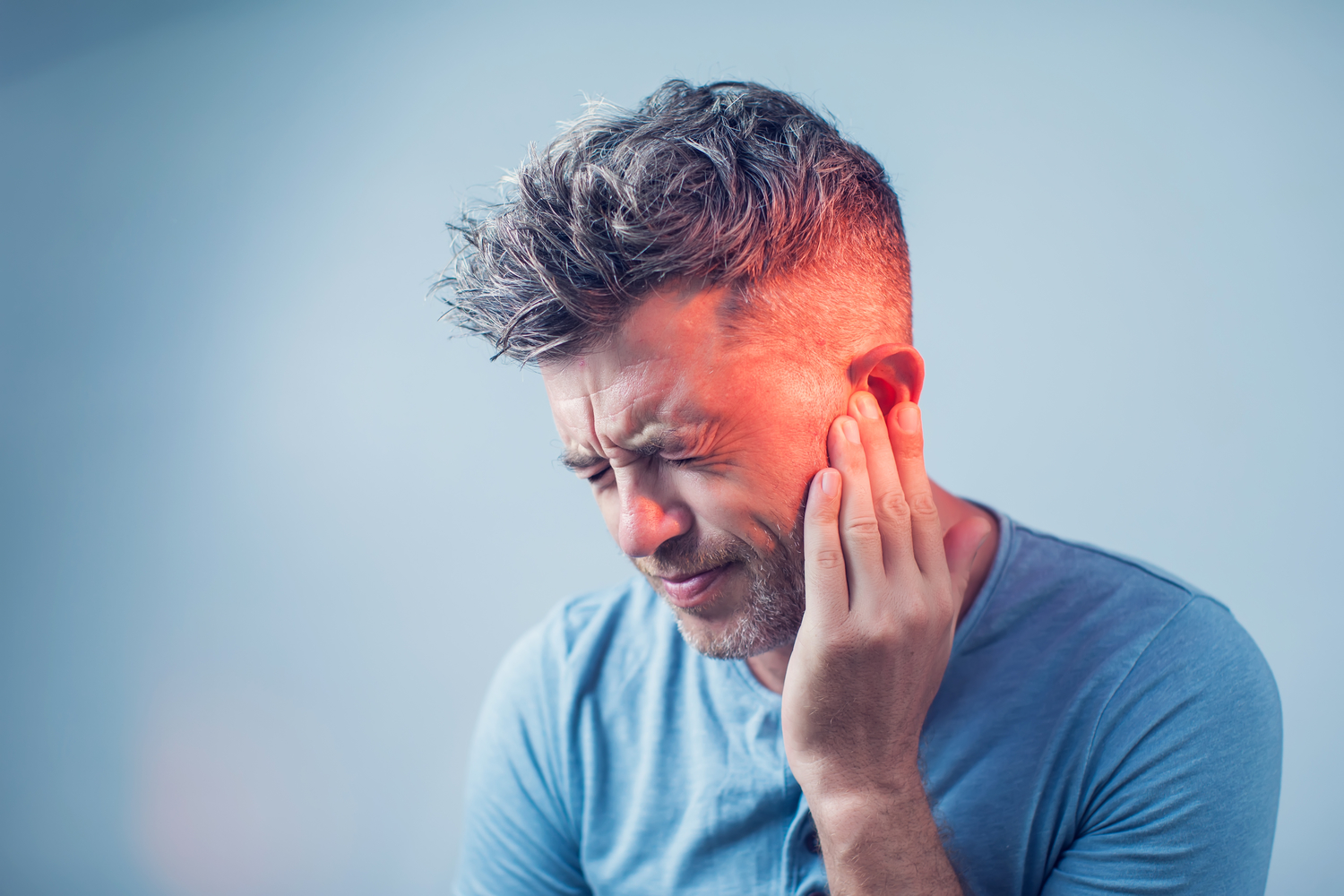
Head injuries or concussions can create abnormal perceptions of sound due to neurological disruptions. Furthermore, certain medications, especially ototoxic drugs such as high doses of NSAIDs, antibiotics, or chemotherapy agents, are known to induce tinnitus as a side effect. Medical conditions like migraines, vascular disorders, and autoimmune diseases may also disrupt inner ear and neural functions, resulting in persistent tinnitus.
Other underlying health issues, including ear diseases (such as otosclerosis), neurological disorders (such as multiple sclerosis), blood vessel abnormalities, or hypertension, can also influence tinnitus development. Accurate diagnosis relies on comprehensive hearing tests, neurological assessments, and medical history analysis to identify specific causes, though complete cures remain elusive. Treatment approaches typically focus on managing symptoms and improving hearing capability.
Strategies for Managing and Treating Tinnitus
Despite the lack of a definitive cure for tinnitus, various therapies and interventions are effective in alleviating its symptoms and improving quality of life. The primary goal of management is to reduce the perception of symptoms and help individuals cope better with their condition.
Hearing aids are often prescribed for individuals with concurrent hearing loss. By amplifying external sounds, hearing aids can mask or diminish the prominence of tinnitus, providing relief and enhancing communication experiences. In cases where earwax buildup or infections are triggering tinnitus, simple procedures such as ear irrigation or medical treatment can resolve blockage-related symptoms.
For severe cases, cochlear implants have proved beneficial, especially for individuals with profound hearing loss accompanied by persistent tinnitus. These devices bypass damaged parts of the inner ear, restoring auditory input and reducing the patient's perception of troubling sounds. Counseling and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) are also valuable, helping individuals develop coping strategies, reduce anxiety, and improve emotional resilience associated with tinnitus.
Other management tools include sound masking devices, which generate gentle background noise to cover the ringing or buzzing sounds. Relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and stress management are essential components, as stress can exacerbate tinnitus symptoms. Moreover, addressing underlying health conditions like hypertension or vascular issues can effectively reduce symptom severity.
Recent advances in tinnitus research focus on neuromodulation, pharmaceuticals, and sound therapy, promising new avenues for treatment in the future. Although a universal cure remains unavailable, personalized and multidisciplinary approaches offer hope for millions affected by this challenging condition.
Ultimately, understanding tinnitus; its causes, types, and management options, empowers patients and healthcare providers to take proactive steps towards alleviating symptoms, improving life quality, and exploring emerging therapies for long-term relief.