The Ultimate Guide to Tinnitus: Types, Causes, and Symptoms Explained
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of tinnitus, delving into their causes, symptoms, and management strategies. It provides valuable insights into understanding this common auditory disorder, highlighting natural remedies, and emphasizing the importance of professional diagnosis for effective treatment. Whether you experience occasional ringing or persistent noise, this article offers essential information for better ear health and quality of life.

Comprehensive Understanding of Tinnitus: Variations, Root Causes, and Key Indicators
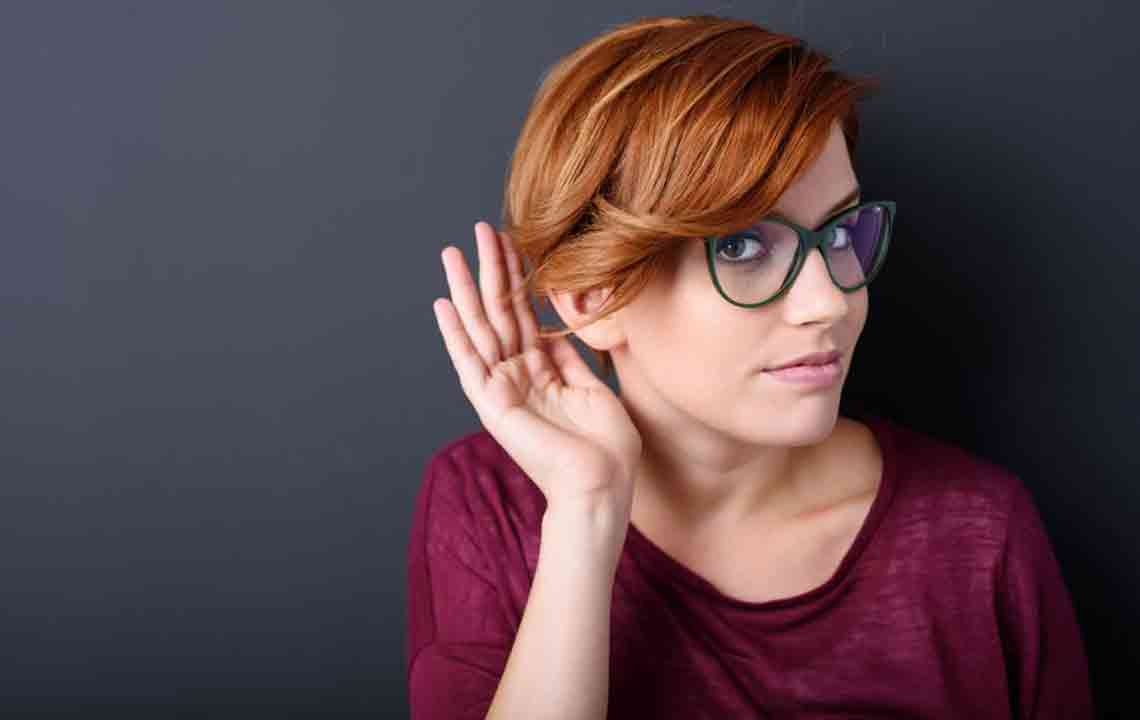
Tinnitus is a common auditory phenomenon characterized by perceiving ringing, buzzing, hissing, or similar sounds within the ears. These sounds can be persistent or occur intermittently, fluctuating in volume and intensity. Many individuals notice that tinnitus becomes more prominent in quiet settings, such as during nighttime or in silent environments. In some cases, the sound aligns with the heartbeat, a condition referred to as pulsatile tinnitus, which may indicate different underlying issues. Globally, it is estimated that over 50 million adults experience tinnitus to some degree. Although often perceived as merely an annoyance, severe and persistent tinnitus can significantly impair a person’s ability to focus, disrupt sleep patterns, and reduce overall quality of life.
While tinnitus is frequently associated with hearing loss, it is essential to understand that the two conditions are distinct. Hearing loss does not necessarily cause tinnitus, nor does experiencing tinnitus automatically imply hearing impairment. This article explores the different types of tinnitus, common causes, and prominent symptoms, providing a comprehensive overview for those seeking clarity about this auditory condition.
Different Types of Tinnitus: An in-Depth Look
Every individual’s experience with tinnitus can vary considerably, and understanding its classification can help in managing and seeking appropriate treatment. Broadly, tinnitus can be categorized into four main types:
Subjective Tinnitus – The most common form, subjective tinnitus occurs when only the affected individual perceives the sound. It often results from damage or alterations in the auditory pathways. Exposure to loud noises—such as concerts, industrial environments, or loud machinery—is a primary cause. This type of tinnitus is typically characterized by a ringing or buzzing sensation that fluctuates throughout the day. Management often involves the use of sound therapy devices, like hearing aids with masking features, which emit calming sounds to help drown out the perceived noise.
Sensory Tinnitus – This form arises due to issues within the auditory system, involving abnormal processing of sound by the brain. It is associated with neural pathways responsible for sound perception and may be linked to neurological conditions or brain processing anomalies. Currently, no definitive cure exists for sensory tinnitus; however, various coping mechanisms and management strategies such as sound therapy, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and medication can help reduce the severity and improve quality of life.
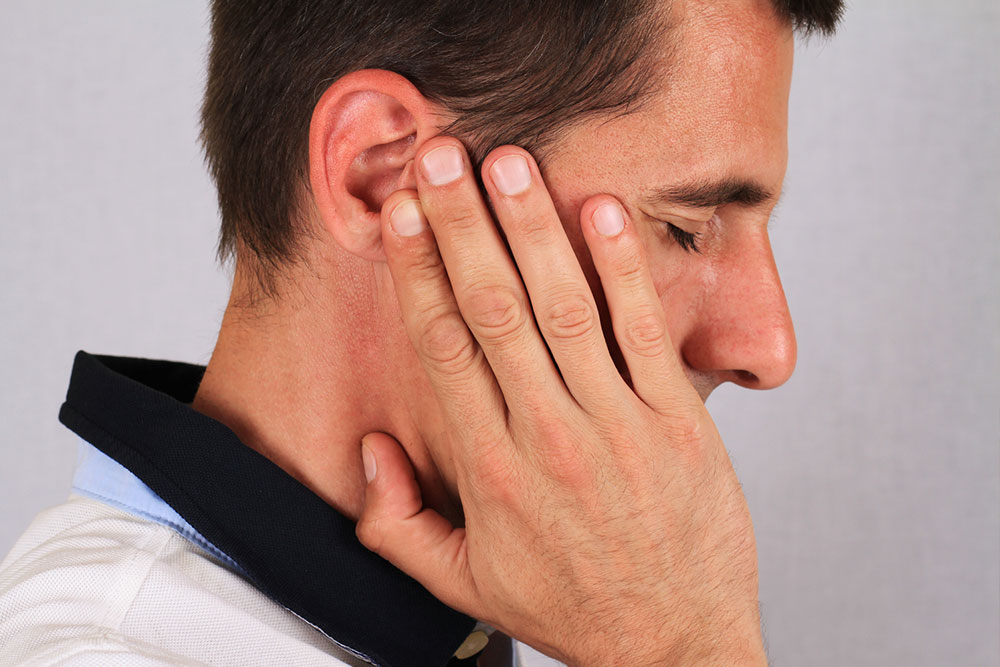
Somatic Tinnitus – Somatic tinnitus seems to be influenced by physical factors affecting the body, such as muscle spasms in the neck, jaw, or ear region. Mechanical disturbances involving the auditory apparatus can provoke this type. People with somatic tinnitus often notice that certain movements, touching specific areas, or posture changes can intensify or diminish their symptoms. Treatment approaches include physical therapy, massage, and sometimes mechanical or dental interventions to address underlying muscular or structural issues. Additionally, some cases have mechanical causes detectable through medical examinations, classified as conductive tinnitus.
Objective Tinnitus – This is a rare subtype where the sound can be heard by a healthcare professional during examination using a stethoscope. Often synchronized with the heartbeat, objective tinnitus may originate from vascular abnormalities, muscle contractions, or other mechanical sources within the ear or head. Treating the underlying cause can often eliminate this form of tinnitus.
Common Causes and Triggers of Tinnitus
Understanding what causes tinnitus is crucial for effective management and prevention. Several factors have been identified as potential triggers or contributors:
Age-Related Hearing Loss – Aging is a significant factor; the natural decline of hearing acuity after age 60 often correlates with the onset of tinnitus symptoms. This is because the degeneration of hair cells in the cochlea impacts sound processing, leading to perceptions of ringing or buzzing.
Exposure to Loud Noises – Continuous or repeated exposure to loud environments, such as construction sites, concerts, and industrial workspaces, can damage inner ear structures and auditory pathways, resulting in tinnitus.
Smoking and Tobacco Use – Nicotine and other chemicals found in cigarettes impair blood flow to the ears and can exacerbate auditory issues, increasing the likelihood of tinnitus.
Gender and Genetic Factors – Research indicates males tend to be at a higher risk, possibly due to occupational exposure or lifestyle factors. Additionally, genetic predispositions may play a role in the susceptibility to tinnitus.
Earwax Blockage and Ear Infections – Excessive earwax buildup can block auditory channels, causing pressure and abnormal sound perception. Infections or inflammations of the middle or outer ear can also trigger or worsen tinnitus.
Medications and Ototoxic Drugs – Certain medications, including high doses of NSAIDs, antibiotics, chemotherapy agents, and diuretics, have been associated with inducing tinnitus. Consultation with healthcare providers is essential before starting or stopping any medication.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Tinnitus
Being aware of the signs helps in early diagnosis and management. Key symptoms include:
A persistent ringing, buzzing, hissing, or whistling sound perceived in one or both ears.
Heightened sensitivity to loud noises, sometimes leading to discomfort.
Emerging or worsening difficulty in hearing or understanding speech.
Feelings of stress, fatigue, anxiety, or depression related to persistent noise perception.
Natural and Home Remedies for Tinnitus Relief
While medical interventions are often necessary for severe cases, many individuals find relief through natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments. Some foods and supplements that may help mitigate symptoms include:
Pineapple – Rich in antioxidants, pineapple can help reduce inflammation and promote ear health.
Apple Cider Vinegar – Known for its detoxifying properties, it may improve circulation and ear function.
Glycerin with Salt – This mixture is sometimes used as a natural remedy to soothe auditory nerves.
Green Tea – Its anti-inflammatory properties can contribute to overall ear health.
Castor Oil – Applying castor oil externally or using it in ear drops (with medical guidance) can potentially provide relief.