Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Addressing Ankle Swelling Causes
Ankle swelling is a common issue with various causes, ranging from temporary conditions like injury and pregnancy to serious health problems such as heart, kidney, or liver issues. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying causes are crucial for timely treatment. This comprehensive guide explores the key factors leading to ankle edema, preventive measures, and when to consult a healthcare professional. Stay informed about how to protect your health by addressing ankle swelling effectively and promptly.
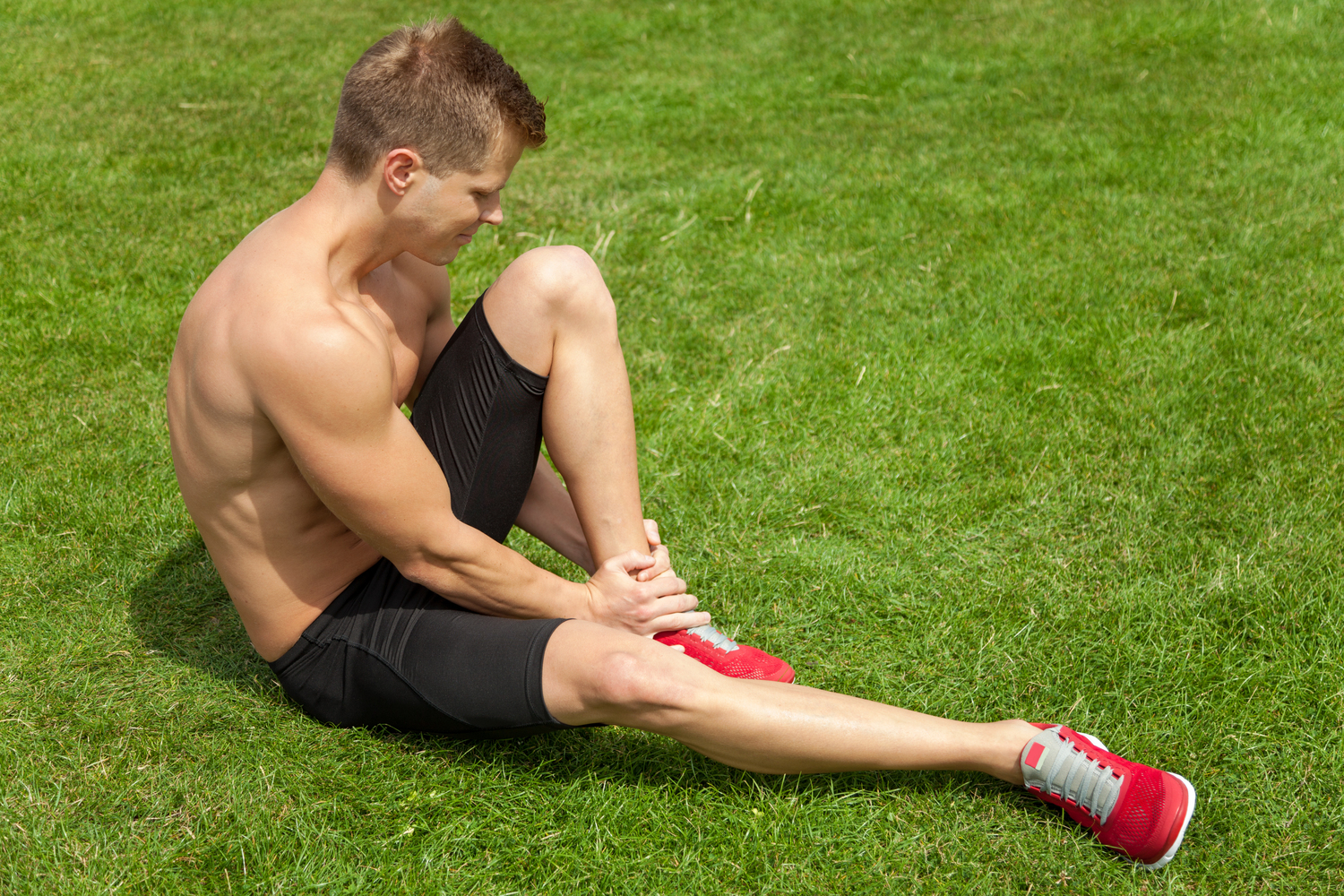

In-Depth Insights into Why Ankle Swelling Occurs
Swelling of the ankles and feet is a common issue experienced by many people, especially after engaging in physical activity or standing for extended periods. Typically, such swelling, medically known as edema, is temporary and subsides after rest or elevation. Nonetheless, when ankle swelling persists or appears suddenly without an obvious reason, it warrants closer medical attention as it could be indicative of underlying health conditions. This comprehensive guide delves into the various causes of ankle swelling, how to recognize symptoms, and when to seek medical advice.
Normal Causes of Ankle Swelling
Many individuals encounter ankle swelling after strenuous activity, which is usually a normal response to increased blood flow and inflammation in the tissues. For example, walking or running can cause temporary fluid accumulation in the lower extremities. Similarly, standing for long hours, especially in hot weather, can lead to mild swelling due to pooling of blood and fluid in the legs. Rest, elevation, and compression often alleviate this type of swelling without any need for medical intervention.
Pregnancy-Related Swelling
Pregnant women frequently experience swelling in the ankles, feet, and legs as a result of increased blood volume and hormonal changes that cause fluid retention. Mild swelling during pregnancy is common and generally harmless. However, healthcare providers advise caution because significant swelling accompanied by other symptoms like high blood pressure, severe headaches, visual disturbances, or nausea may indicate preeclampsia, a serious pregnancy complication requiring urgent medical care.
Injury and Sprains
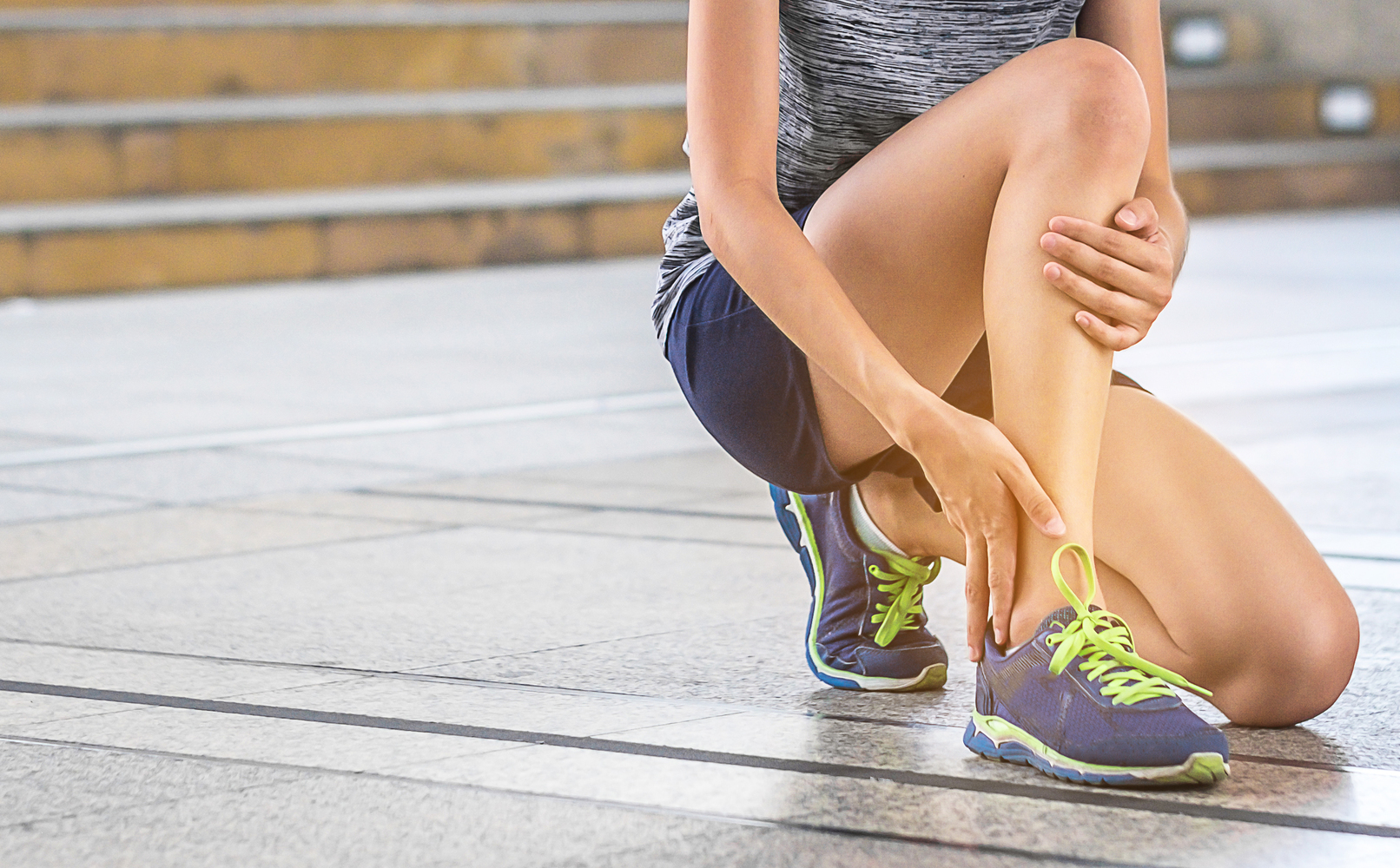
Musculoskeletal injuries, particularly ankle sprains, are a common cause of swelling. These injuries involve overstretching or tearing ligaments, which leads to inflammation, pain, and swelling. Immediate treatment with rest, ice application, compression, and elevation (RICE) helps reduce swelling and prevent further damage. Persistent swelling after injury may suggest complications such as ligament tears or joint damage, necessitating consultation with a healthcare professional.
Medical Conditions Contributing to Ankle Swelling
Several medical conditions can result in chronic or severe ankle swelling, often requiring diagnosis and management. Key among these are:
Lymphedema: A condition where lymphatic fluid accumulates in the tissues due to blocked or damaged lymphatic vessels, often leading to persistent swelling, usually in one limb.
Cardiac Issues: Heart failure can cause fluid retention, leading to swelling in the ankles and legs, especially after prolonged periods of activity or standing.
Kidney Disorders: Kidney problems impair fluid and electrolyte balance, resulting in edema in the lower extremities.
Liver Diseases: Conditions like cirrhosis lead to decreased protein production and fluid imbalance, often causing swelling.
Infections and Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or infections in the leg can lead to significant swelling, redness, and warmth, requiring immediate medical evaluation.
Medication Side Effects
Some medications may cause ankle swelling as an adverse effect. Notably, certain blood pressure drugs (like calcium channel blockers), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and corticosteroids can lead to fluid retention. Patients experiencing new or worsening swelling while on medication should consult their healthcare provider to adjust treatments or explore alternatives.
Recognizing Symptoms and When to Seek Help
While mild, occasional swelling usually does not require urgent care, persistent or worsening edema, especially when associated with other symptoms such as pain, redness, warmth, difficulty breathing, chest pain, or rapid heartbeat, should prompt immediate medical evaluation. Early diagnosis of underlying health issues can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Preventive Measures and Management Strategies
To reduce the risk or severity of ankle swelling, individuals can take various proactive steps, including maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, elevating legs during rest, avoiding prolonged standing, and wearing compression stockings if recommended. Managing underlying health conditions with appropriate medications and lifestyle changes is crucial for long-term control.
In conclusion, ankle swelling can arise from a variety of causes ranging from benign to life-threatening conditions. Understanding the symptoms and causes can guide timely medical consultation and treatment. If you experience persistent, severe, or unexplained swelling, it is essential to seek professional healthcare advice promptly to determine the root cause and receive appropriate treatment.