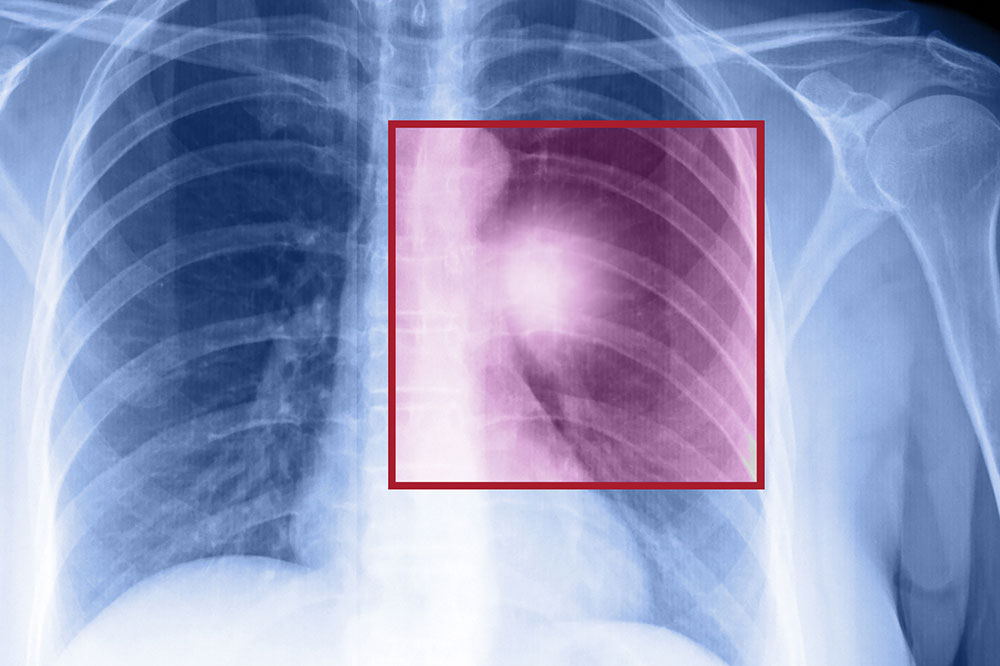
Essential Insights into Lung Cancer: Key Indicators and Early Warning Signs
This comprehensive article on lung cancer highlights essential indicators, symptoms, and early warning signs crucial for timely diagnosis and improved treatment outcomes. Understanding risk factors and preventive measures can significantly reduce the disease's impact. Emphasizing screening protocols and symptom awareness aims to encourage early detection, ultimately saving lives by enabling prompt medical intervention.
Lung cancer is one of the most common and deadly types of cancer worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. It originates in the lung tissue and can develop in various forms, primarily categorized into small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Understanding the key indicators and early warning signs is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment, which significantly improves survival rates. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the primary indicators of lung cancer, risk factors, symptoms, and the importance of early detection to help you stay informed and proactive about your respiratory health.
**Types of Lung Cancer and Their Characteristics**
Lung cancer mainly appears in two major forms: small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). SCLC is characterized by rapid growth and early spread to distant sites, making it more aggressive. NSCLC, which accounts for approximately 85% of lung cancers, grows more slowly and has different subtypes like adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. Recognizing the differences between these types aids in selecting appropriate treatment strategies.
**Causes and Risk Factors**
The primary risk factor for lung cancer is cigarette smoking, responsible for approximately 85% of cases. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke damage lung cells, leading to mutations that can initiate cancer. However, non-smokers are also susceptible, especially those exposed to secondhand smoke, radon gas, asbestos, or other environmental carcinogens. Genetic predisposition, age, and a history of respiratory diseases further influence risk levels. Recognizing these factors emphasizes the importance of preventive measures and early screening.
**Why Early Detection Matters**
Many lung cancers are diagnosed at an advanced stage, partly due to the subtlety of initial symptoms. Early detection significantly improves prognosis, offering more treatment options and increasing survival chances. Screening programs, like low-dose computed tomography (LDCT), have proven to be effective in identifying lung cancer early in high-risk populations. Regular health check-ups and awareness of symptoms are vital components of early detection efforts.
**Recognizable Symptoms and Indicators of Lung Cancer**
Early signs of lung cancer can often be mistaken for common respiratory illnesses, which highlights the importance of awareness. The most typical symptoms include persistent cough, changes in cough patterns, and increased sputum production. A cough that produces blood or rust-colored mucus is a serious warning sign that warrants immediate medical evaluation. Other symptoms may include chest pain, especially during deep breathing or coughing, and unexplained weight loss.
Fatigue and weakness are common as the disease progresses, often accompanied by shortness of breath or wheezing. Some patients notice voice changes or hoarseness, indicating nerve involvement. Weak immunity can lead to frequent respiratory infections such as pneumonia or bronchitis. In more advanced cases, symptoms like yellowing of the skin (jaundice), bone pain, or swelling in the face or neck could occur, signaling metastasis.
**Additional Signs and Serious Indicators**
As lung cancer progresses, symptoms can become more severe. Bone pain may occur due to metastasis, and swelling of the face, neck, or arms suggests superior vena cava syndrome, caused by tumor compression. Skin changes, such as clubbing of fingers or new skin lesions, can also be indicators of disease progression. Recognizing these signs early is essential for prompt intervention and improving treatment outcomes.
**Diagnostic Methods and Screening**
Diagnosing lung cancer involves imaging techniques such as chest X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans to visualize tumors and assess spread. A biopsy remains the definitive method for diagnosis, which involves collecting tissue samples for microscopic examination. Blood tests may aid in evaluating overall health and function of organs. For high-risk individuals, screening with low-dose CT scans is recommended to detect tumors at an early, treatable stage.
**Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes**
Prevention plays a critical role in reducing lung cancer incidence. Smoking cessation is the most effective step; numerous resources and programs are available to assist individuals in quitting smoking. Avoiding exposure to known carcinogens such as radon and asbestos can further lower risk. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, regular exercise, and avoiding pollutants contribute to respiratory health. Monitoring environmental risks and adhering to safety protocols at workplaces also reduce exposure to harmful substances.
**Conclusion**
Lung cancer remains a significant health challenge worldwide, but awareness of key indicators and early warning signs can dramatically improve outcomes. Recognizing symptoms like persistent coughing, blood-stained sputum, chest pain, and unexplained weight loss allows for timely medical consultation and diagnosis. Emphasizing preventive health measures such as quitting smoking, regular screening, and avoiding environmental hazards can significantly lower the risk. Early detection not only enhances treatment options but also significantly increases survival chances. Stay vigilant, prioritize respiratory health, and consult healthcare providers if any concerning symptoms arise.