Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Strategies
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a dangerous condition involving blood clots in deep veins, most often in the legs. This comprehensive article explores symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and preventive strategies essential for early detection and effective treatment. Understanding DVT can help save lives by avoiding serious complications like pulmonary embolism, making awareness vital for health-conscious individuals and those in high-risk groups.
Comprehensive Guide to Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Symptoms, Causes, and Prevention Strategies
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot, or thrombus, within the deep veins of the body, most commonly in the legs. This condition can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and managed promptly, as the clot can travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, leading to a pulmonary embolism, which can cause severe complications or even death. Understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and prevention measures associated with DVT is essential for early detection and effective management.
Deep Vein Thrombosis predominantly affects the deep veins of the lower limbs due to factors like blood flow stasis, vessel wall injury, and hypercoagulability. These factors often act together in a process known as Virchow’s triad, which significantly predisposes individuals to clot formation. DVT can occur in other parts of the body as well, including the arms, pelvis, and abdomen, although these instances are less common.
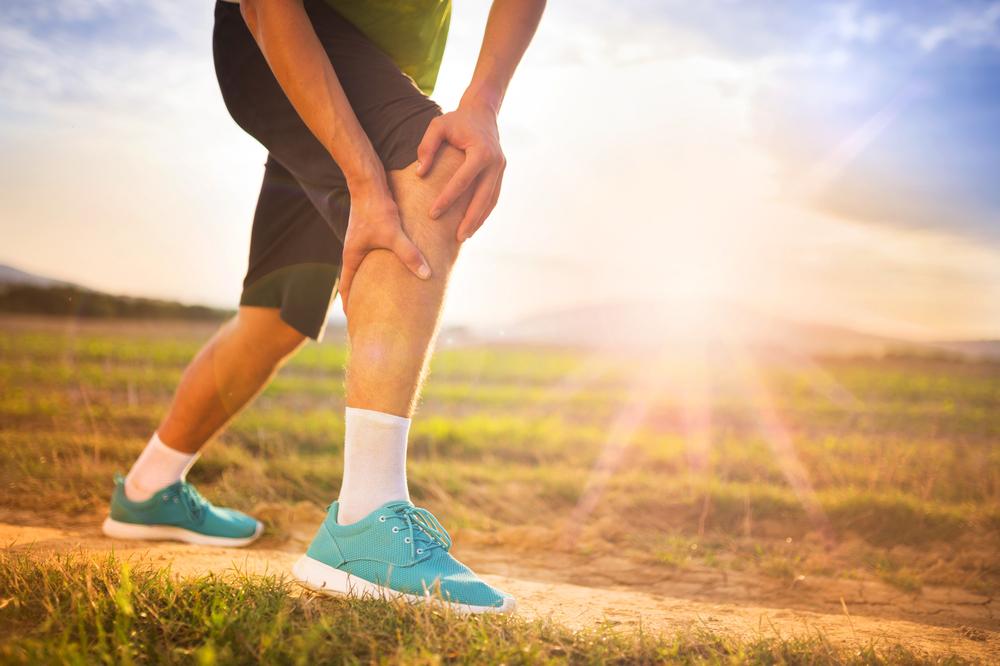
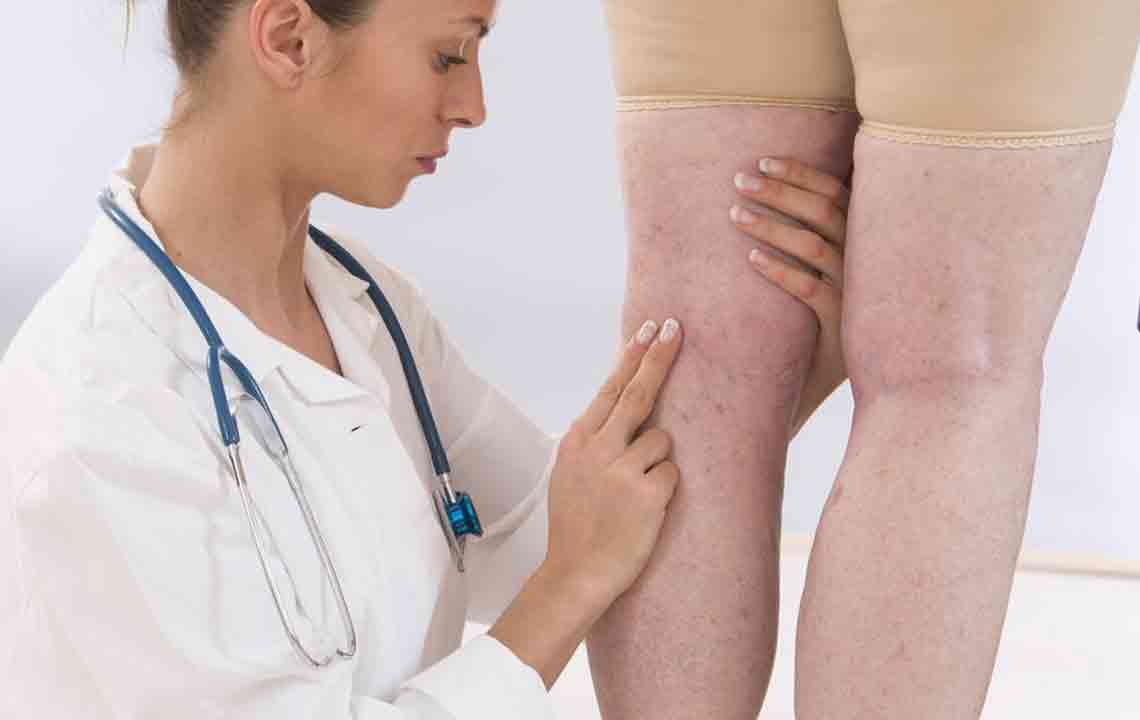
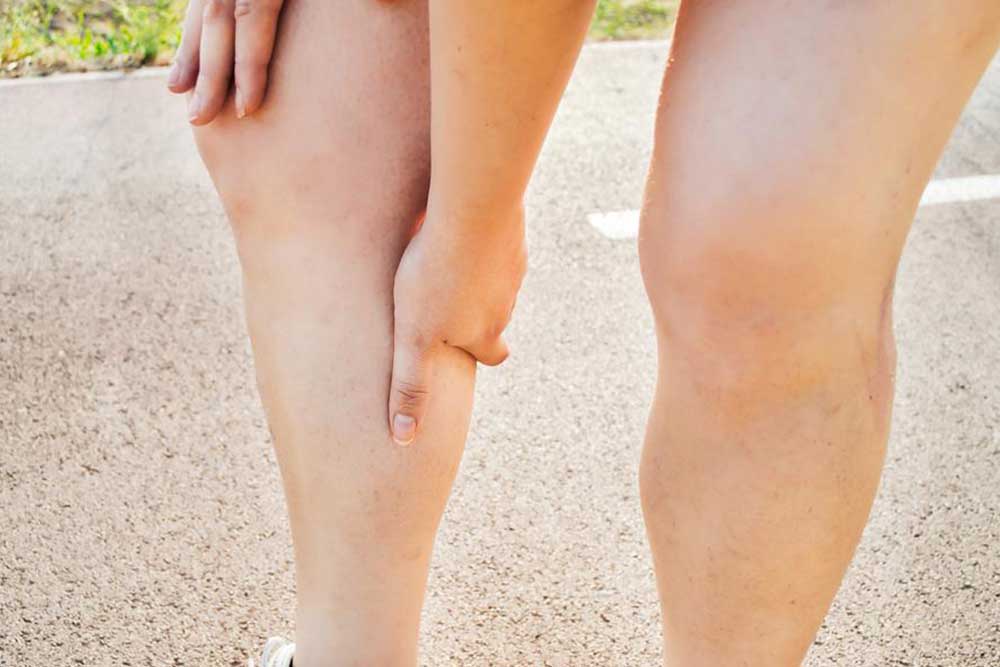
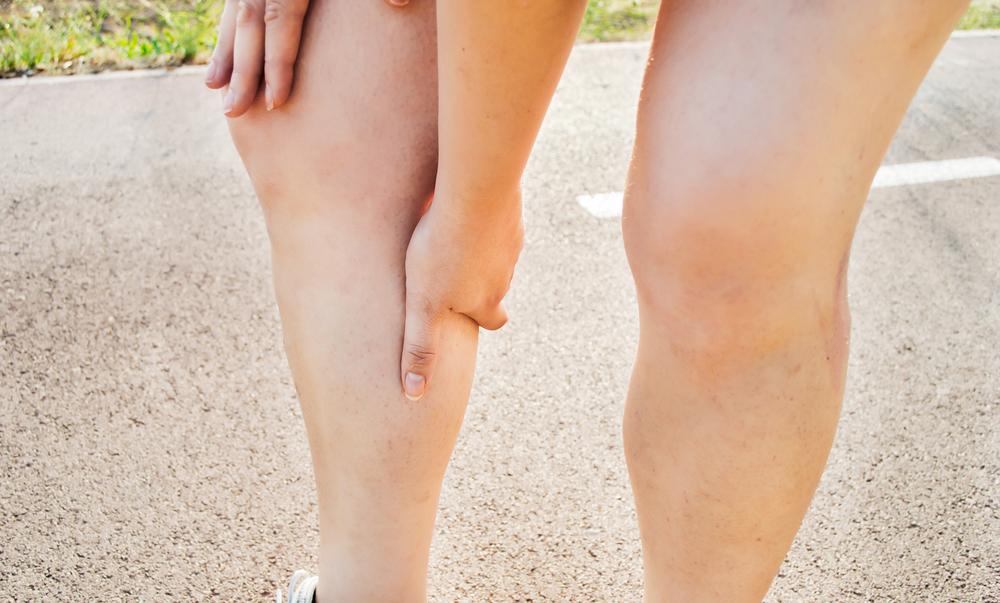
The signs and symptoms of DVT can vary based on the size and location of the clot, but certain symptoms are more common and should prompt immediate medical evaluation. These include sudden swelling in one leg or arm, persistent pain or tenderness that often starts in the calf or thigh, warmth and redness over the affected area, and sometimes cramping or a feeling of heaviness in the limb. It's crucial to acknowledge that DVT may sometimes be asymptomatic, especially in its early stages, making regular check-ups important for those at higher risk.
Risk factors for developing DVT are diverse and include lifestyle, medical history, and genetic predispositions. Common contributors encompass recent injuries or surgeries, which can cause blood vessel damage and promote clotting; prolonged immobilization, such as bed rest or long-haul flights, which lead to blood stagnation; obesity, which increases pressure in the veins; pregnancy, which elevates blood coagulability; age, as the risk increases significantly after 60; certain medical conditions like cancer, heart failure, or clotting disorders; and family history of clotting problems. Additionally, hormonal therapies such as birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy can elevate the clotting tendency.
The danger of untreated DVT lies in its potential to dislodge and travel through the bloodstream to the lungs, resulting in a pulmonary embolism. This condition presents acute symptoms such as sudden shortness of breath, chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and coughing blood. Pulmonary embolism requires immediate emergency treatment to prevent fatal outcomes.
For confirming a diagnosis of DVT, healthcare providers rely on various imaging techniques. Ultrasound Doppler studies are the first-line diagnostic tools because they are non-invasive and highly effective at visualizing blood flow and detecting clots. In some cases, venography—an invasive imaging test involving contrast dye—or MRI scans are used for detailed visualization, especially in complex cases or when ultrasound results are inconclusive.
Prevention is key in reducing the risk of DVT, especially for individuals with known risk factors. Regular physical activity and movement, particularly during long periods of immobility like travel or recovery from surgery, help maintain healthy blood flow. Wearing compression stockings can improve venous circulation and prevent clot formation. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, avoiding smoking, and managing medical conditions effectively are vital preventive measures. For high-risk individuals, healthcare providers may prescribe blood-thinning medications or recommend other prophylactic strategies to minimize risk.
In conclusion, deep vein thrombosis is a condition with potentially serious consequences but is highly manageable with timely diagnosis and appropriate preventive measures. Awareness of symptoms, understanding risk factors, and adopting healthy lifestyle practices can significantly reduce the incidence of DVT and prevent dangerous complications like pulmonary embolism. If you experience symptoms or have risk factors, consult a healthcare professional promptly for assessment and personalized advice. Early detection and proper management can save lives and improve outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.