Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing Blood Clot Symptoms in Different Body Regions
This comprehensive guide explains how blood clots can develop in various parts of the body, highlighting key signs and symptoms to watch for. Early recognition of symptoms related to limbs, brain, heart, abdomen, and lungs can be life-saving. The article emphasizes the importance of understanding risk factors and seeking prompt medical care to prevent serious complications like strokes, heart attacks, and pulmonary embolisms. Whether you suspect a blood clot due to swelling, chest pain, or neurological changes, timely intervention is crucial for effective treatment and improved outcomes.

Understanding the Symptoms of Blood Clots in Various Parts of the Body
Blood clots, medically known as thrombi, are masses formed when blood coagulates within vessels or tissues, disrupting normal circulation. These clots can develop both externally on the surface of the skin and internally within deeper tissues or organ systems. While external blood clots are often visible and sometimes less dangerous, internal blood clots pose significant health threats if not detected early. Recognizing the specific symptoms associated with blood clots based on their location is essential for timely medical intervention and preventing severe complications.
Blood clots can form in various parts of the body, each presenting distinct symptoms. Understanding these tell-tale signs can aid in early diagnosis and treatment. Here, we explore the common locations where blood clots tend to form and their associated symptoms:
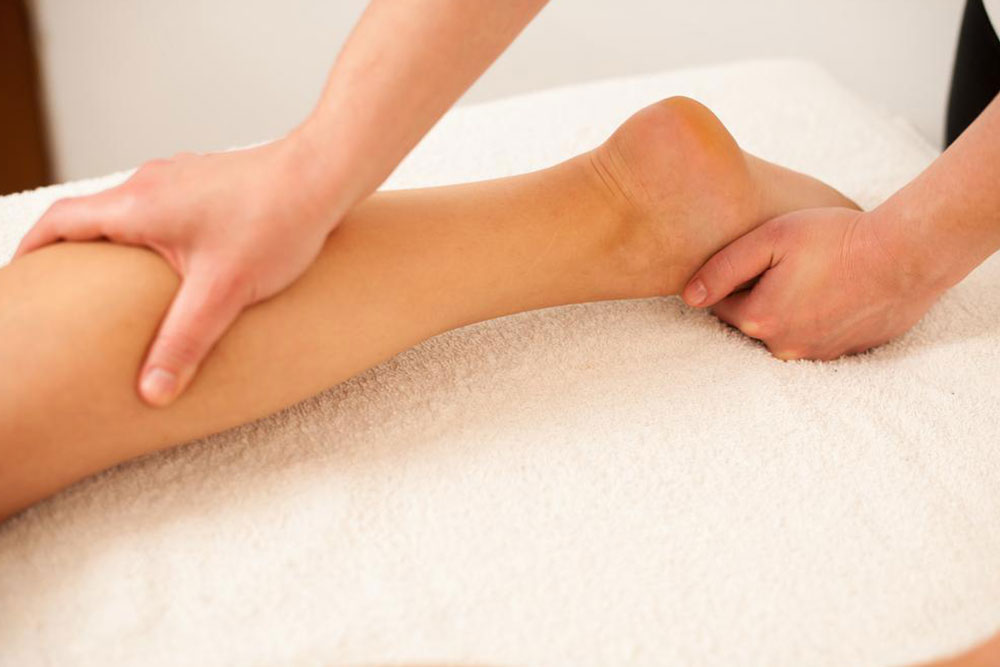
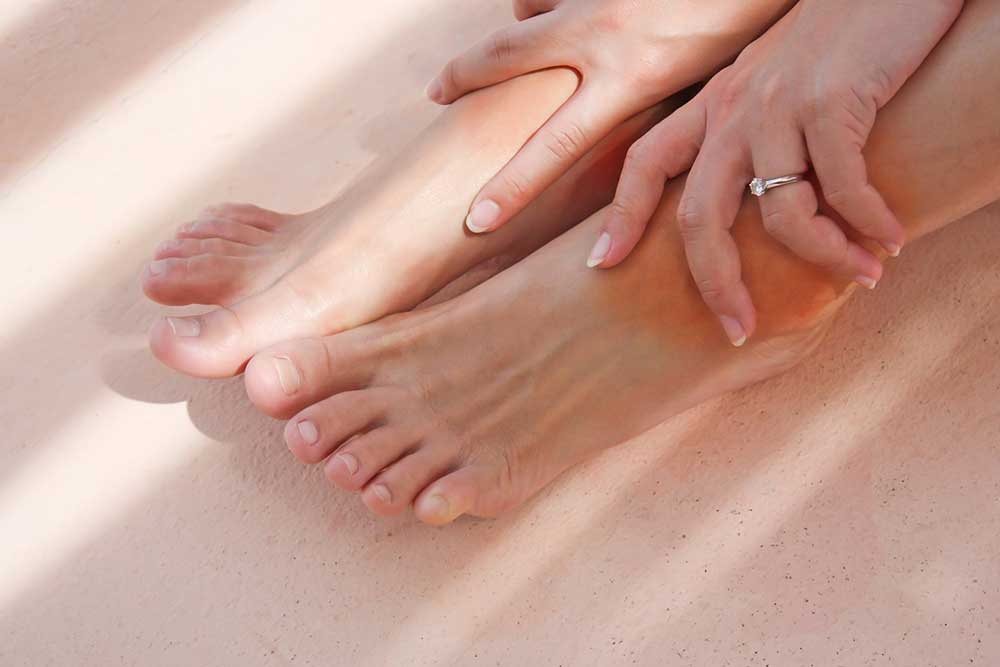
Clots in Limbs (Arms and Legs): Swelling, pain, redness, warmth, and tenderness in the affected limbs are typical signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Such symptoms often occur after periods of immobility or injury and require immediate medical attention as they can lead to more serious complications like pulmonary embolism if dislodged.
Blood Clots in the Brain: When clots form in cerebral vessels, they can block blood flow, leading to stroke. Symptoms may include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, slurred speech, sudden vision changes, seizures, confusion, dizziness, and loss of coordination. Recognizing these symptoms quickly is crucial for prompt stroke treatment.
Other critical areas where blood clots can develop include the heart and abdomen. Each location manifests distinct symptoms that should not be ignored:
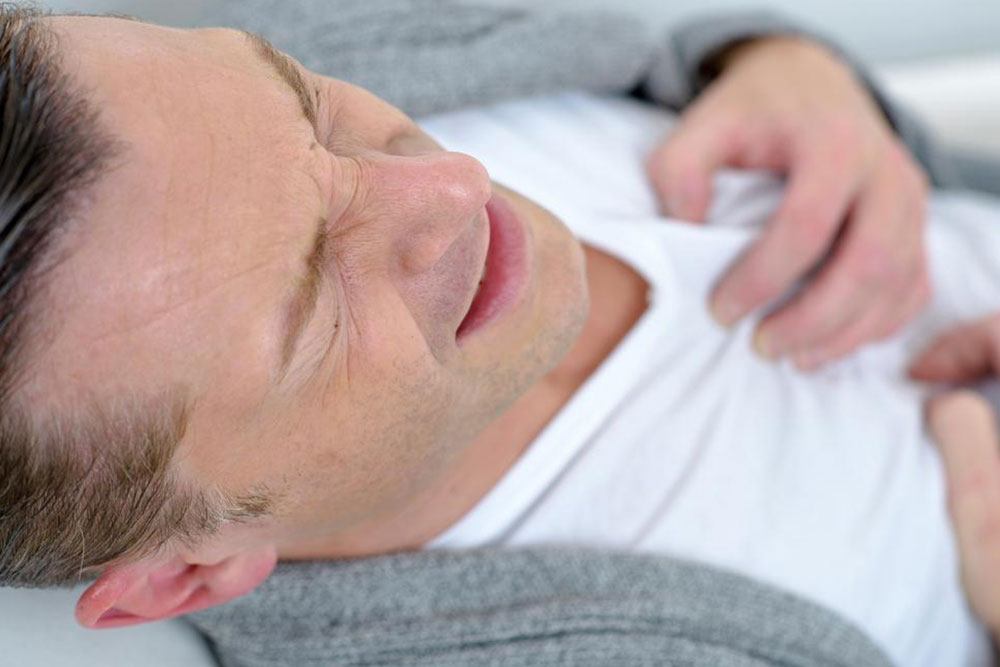
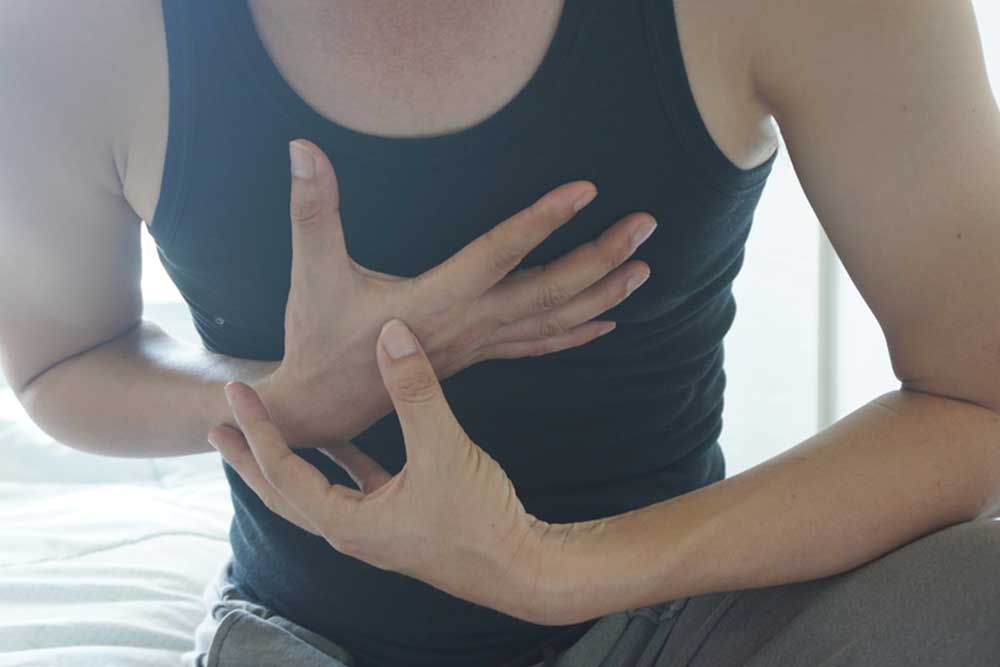
Heart: Coronary blood clots can cause myocardial infarctions (heart attacks). Symptoms often include crushing chest pain that may radiate to the arm, neck, or back, associated with shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, dizziness, and fainting. Immediate medical attention can save lives in these emergency situations.
Abdominal Region: Clots within abdominal vessels might lead to severe abdominal pain, which can be sudden and persistent. Patients may experience nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or gastrointestinal bleeding visible as blood in vomit or stool. Imaging techniques such as CT scans are critical for diagnosis.
Lungs (Pulmonary Embolism): Clots originating from leg veins can dislodge and travel to the lungs, resulting in a pulmonary embolism. Symptoms include sudden sharp chest pain, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, coughing up blood, dizziness, and a feeling of impending doom. This life-threatening condition demands immediate medical intervention.
Understanding these symptoms and being aware of risk factors such as prolonged immobility, recent surgeries, obesity, pregnancy, smoking, and certain genetic conditions can significantly reduce the risk of severe outcomes associated with blood clots. Lifestyle modifications, early diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are fundamental in managing blood clot risks and preventing complications such as strokes, heart attacks, and pulmonary embolisms.