Comprehensive Guide to Blood Clots: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, and preventive methods for blood clots, helping readers understand how to identify and reduce risks associated with thrombi. It emphasizes early recognition and medical intervention to prevent serious health emergencies related to abnormal clot formation. Learn vital tips for maintaining vascular health and avoiding life-threatening complications.
Comprehensive Guide to Blood Clots: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
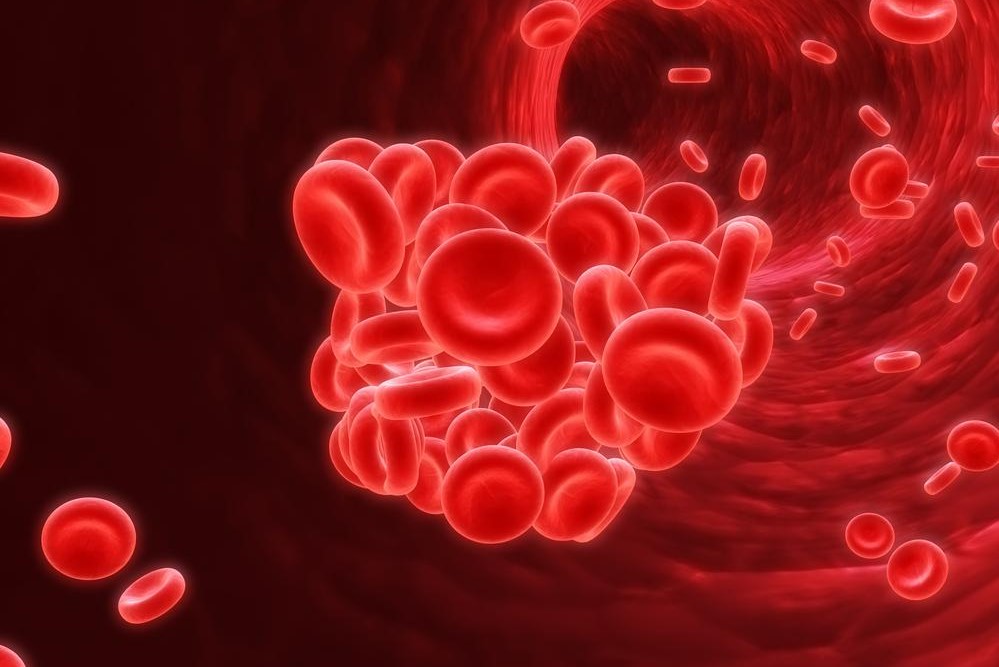
Blood clots, medically known as thrombi, are semi-solid aggregates of blood that form as a natural defense mechanism to prevent excessive bleeding after injury. Under normal conditions, the clotting process is vital for healing wounds. However, when blood clot formation occurs abnormally or in inappropriate locations, it can lead to severe health complications, including life-threatening conditions. Understanding the nuances of blood clots, their causes, symptoms, and preventative measures is essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and preventing emergencies.
Understanding Blood ClotsBlood clotting, or coagulation, involves a complex interplay between blood cells, plasma proteins, and vessel walls. While this process is essential for stopping bleeding, abnormalities can lead to the formation of unwanted clots within blood vessels. These clots can impede normal blood flow, causing tissue damage or organ dysfunction.
One of the critical concerns with blood clots is their potential to migrate through the bloodstream. Mobile clots, especially those that travel to vital organs, pose significant health risks such as strokes, pulmonary embolisms, or heart attacks. These conditions necessitate immediate medical intervention.
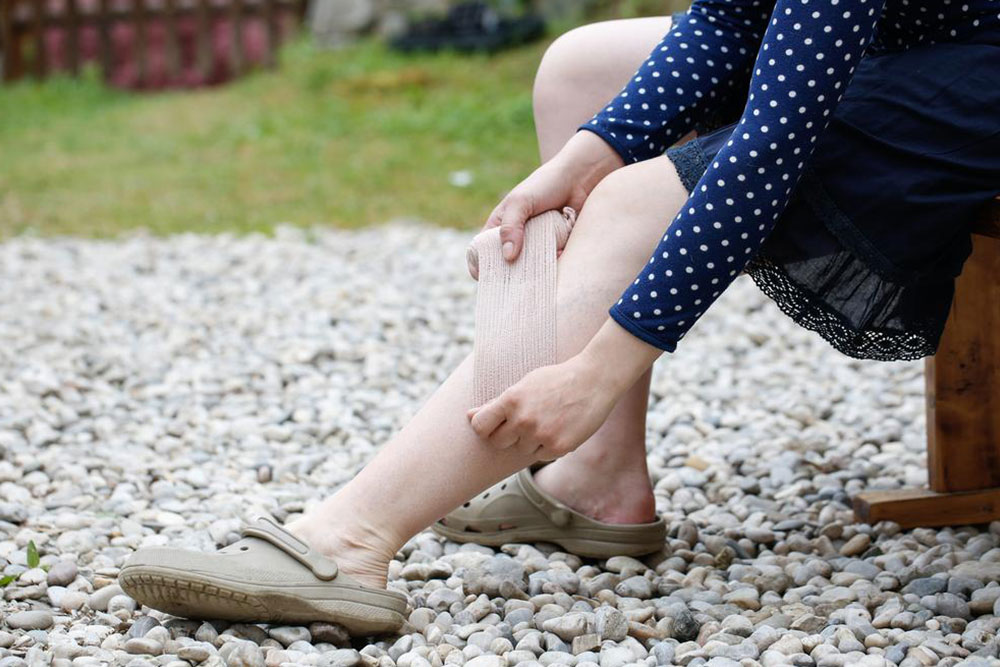
Clots that form in veins, particularly in the deep veins of the legs, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), tend to be resistant to natural breakdown and require prompt treatment to prevent complications like pulmonary embolism. Recognizing early symptoms of blood clots is crucial, as prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent severe outcomes.
Factors Contributing to Blood Clot FormationBlood clots result from complex interactions among various risk factors that alter normal blood flow or promote clotting. These factors include injuries to blood vessels, surgeries, certain medical conditions, lifestyle choices, and other health-related issues. Understanding these risk factors is essential for prevention and early intervention.
Vascular injury from trauma or invasive procedures can expose blood to subendothelial tissue, initiating clot formation
Prolonged immobility, such as bed rest or long flights, can slow blood flow and increase clot risk
Chronic health conditions like cancer, heart disease, or autoimmune disorders can disrupt normal hemostasis
Use of hormonal therapies, such as birth control or hormone replacement therapy, can elevate the risk
Genetic predispositions, including clotting disorders like factor V Leiden, increase susceptibility
Lifestyle factors, including smoking, obesity, and sedentary habits, contribute significantly to clot development
In addition to these factors, infections, dehydration, and certain medications can further predispose individuals to clot formation. Prevention involves managing these risk factors through lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, and awareness.
Recognizing Symptoms of Blood ClotsEarly detection of blood clots is vital for effective treatment. Symptoms vary depending on the location and size of the clot, and awareness can be life-saving.
Chest pain, especially sharp or persistent, may indicate a pulmonary embolism or heart-related issues
Neurological symptoms such as sudden weakness, numbness, speech difficulties, or paralysis suggest a stroke caused by clot obstruction
Swelling, tenderness, redness, and warmth in the leg or arm are typical signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
Breathlessness, chest discomfort, and coughing up blood can indicate a pulmonary embolism resulting from a traveling clot
Immediate medical assessment is essential if any of these symptoms are present. Diagnostic tools like Doppler ultrasound, CT scans, and blood tests help confirm the presence of a clot.
Treatment and PreventionEffective management of blood clots involves a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical intervention. Anticoagulants, blood thinners, and thrombolytic agents are common pharmacological treatments aimed at dissolving clots or preventing their growth.
In addition to medication, preventive measures play a significant role in reducing clot risk. These include staying physically active, avoiding prolonged immobility, maintaining a healthy weight, and routinely monitoring blood health in predisposed individuals. For high-risk patients, preventive strategies such as compression stockings or anticoagulant therapy may be recommended.
Understanding the importance of lifestyle modifications and adherence to medical advice can significantly lower the chances of blood clot formation, reducing the risk of severe complications like strokes, heart attacks, or pulmonary embolisms.