Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Neuropathy Symptoms Effectively
Discover effective strategies for managing neuropathy symptoms through medications, therapies, and alternative treatments. This comprehensive guide covers pain relief options, physical therapy approaches, and alternative methods like acupuncture and massage, helping patients improve nerve health and quality of life. Tailored management plans can reduce discomfort, improve mobility, and address underlying causes of nerve damage for sustained relief and better health outcomes.

Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Neuropathy Symptoms Effectively
Neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage, can significantly impact quality of life due to symptoms such as numbness, tingling sensations, weakness, and sharp or burning pain primarily affecting the hands and feet. While diabetes remains the leading cause, various other factors can contribute to or exacerbate this condition, including physical injuries, infections, and exposure to toxic substances. Managing neuropathy requires a holistic approach that combines medication, therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and alternative treatments to alleviate symptoms and improve nerve function.
Understanding the Causes of Neuropathy
Neuropathy can stem from multiple origins. Diabetes is one of the most common causes, especially when blood sugar levels are poorly controlled over a long period. High blood glucose can damage nerve fibers and impair nerve signaling. Apart from diabetes, physical trauma resulting from accidents or injuries, infections such as Lyme disease or shingles, and harmful exposures to toxins like certain chemicals or medications can also lead to nerve damage. Recognizing the root cause is crucial for tailoring an effective management plan.
Medications for Neuropathy: An In-Depth Overview
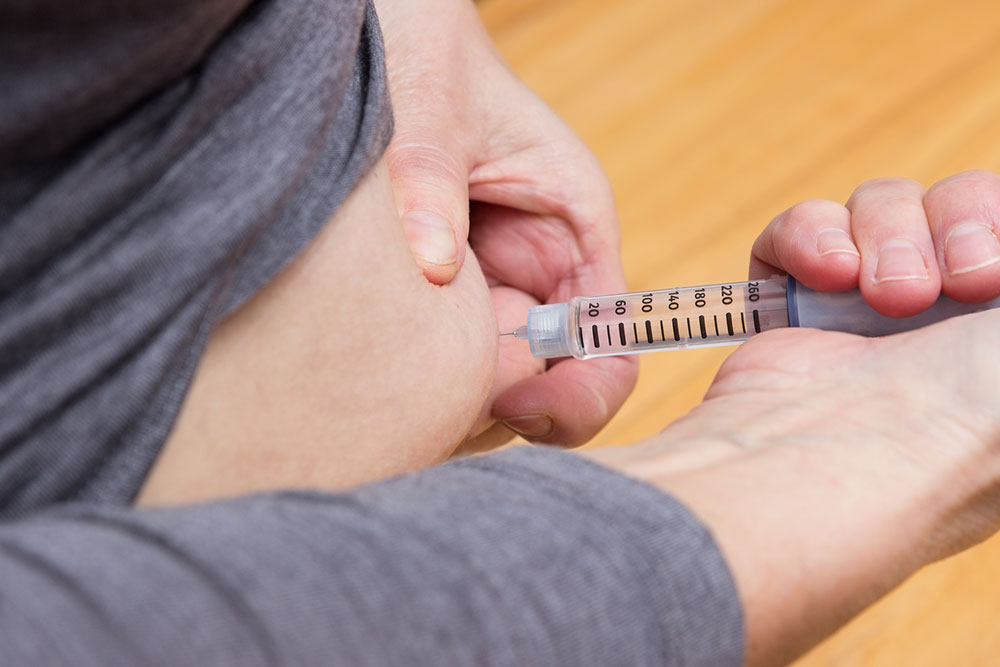
Pain Relievers: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Naproxen and Ibuprofen are frequently used to decrease inflammation and reduce discomfort associated with nerve damage. Acetaminophen can also be administered to manage mild to moderate pain; however, it should be used cautiously, especially in individuals with existing liver issues, as it can cause hepatotoxicity if overused.
Antiseizure Drugs: Medications like Gabapentin and Pregabalin are prescribed to calm overexcited nerve activity, which helps decrease neuropathic pain. These drugs modify nerve signal transmission and are often effective in managing chronic nerve pain.
Topical Remedies: Applying capsaicin cream or utilizing Lidocaine patches directly on affected areas can provide localized pain relief. These topical treatments are beneficial for targeting specific pain points but may have side effects such as skin irritation, drowsiness, or numbness.
Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as low-dose Doxepin or Amitryptyline, can influence pain perception by altering brain chemicals involved in mood and pain pathways. This class of drugs has demonstrated efficacy in managing neuropathic pain, especially in cases refractory to other medications.
Narcotics: For severe and unrelenting pain, opioids like Tramadol or Oxycodone might be prescribed under strict medical supervision. Although effective, these drugs carry significant risks including dependence, tolerance, and side effects like sedation and constipation, necessitating careful monitoring.
Digestive and Bladder Treatments: When neuropathy affects autonomic functions such as digestion or bladder control, dietary modifications and medications—like antispasmodics—can help manage symptoms like gastroparesis, constipation, or bladder overactivity.
Therapies to Relieve Neuropathy Symptoms
Physical Therapy: Engaging in targeted exercises enhances muscle strength, flexibility, and circulation, which may support nerve regeneration and mitigate symptoms. Physical therapy also helps in maintaining mobility and reducing the risk of falls or injuries caused by numbness and weakness.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS): This non-invasive technique uses low-voltage electrical currents to interfere with pain signals transmitted to the brain, offering substantial relief for many patients.
Plasma Exchange and Immune Globulin Therapy: These advanced treatments reduce inflammation and modulate immune responses, particularly effective in autoimmune-related neuropathies. They are usually administered on an outpatient basis and have shown promising results in reducing nerve inflammation and promoting healing.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments
Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese medicine technique involves inserting fine needles at specific points on the body to stimulate nerve function and alleviate neuropathic symptoms. Many patients report significant symptom relief following regular acupuncture sessions.
Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments performed by skilled chiropractors can help restore movement, reduce nerve pressure, and improve overall nerve health, often reducing pain and discomfort.
Massage Therapy: Therapeutic massage targeting affected areas can reduce muscle tension, improve blood flow, and decrease pain points associated with nerve damage.
Alpha-lipoic Acid: An antioxidant supplement widely used in Europe supports blood sugar regulation and nerve health. However, it should be taken under medical supervision due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
In summary, managing neuropathy symptoms involves a comprehensive strategy that includes medication, physical and alternative therapies, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes invasive procedures. Consulting healthcare professionals is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual needs and underlying causes.