Comprehensive Guide to Peripheral Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Peripheral neuropathy is a complex nerve condition that causes numbness, pain, and weakness. This comprehensive guide explores its causes, symptoms, and diverse treatment options, emphasizing early diagnosis and holistic care. Learn about effective therapies including medication, lifestyle changes, and innovative treatments like electrical nerve stimulation and dietary supplements. Understanding these methods can help manage symptoms, prevent progression, and improve quality of life for those affected by nerve damage, especially in chronic cases related to diabetes, injuries, or autoimmune diseases.

Comprehensive Guide to Peripheral Neuropathy: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Peripheral neuropathy, often referred to simply as neuropathy, is a complex condition characterized by damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves that extend from the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. These peripheral nerves play a crucial role in transmitting sensory information, motor commands, and autonomic functions throughout the body. When these nerves are compromised due to injury, disease, or other factors, it can lead to a wide array of symptoms, significantly impacting an individual’s quality of life.
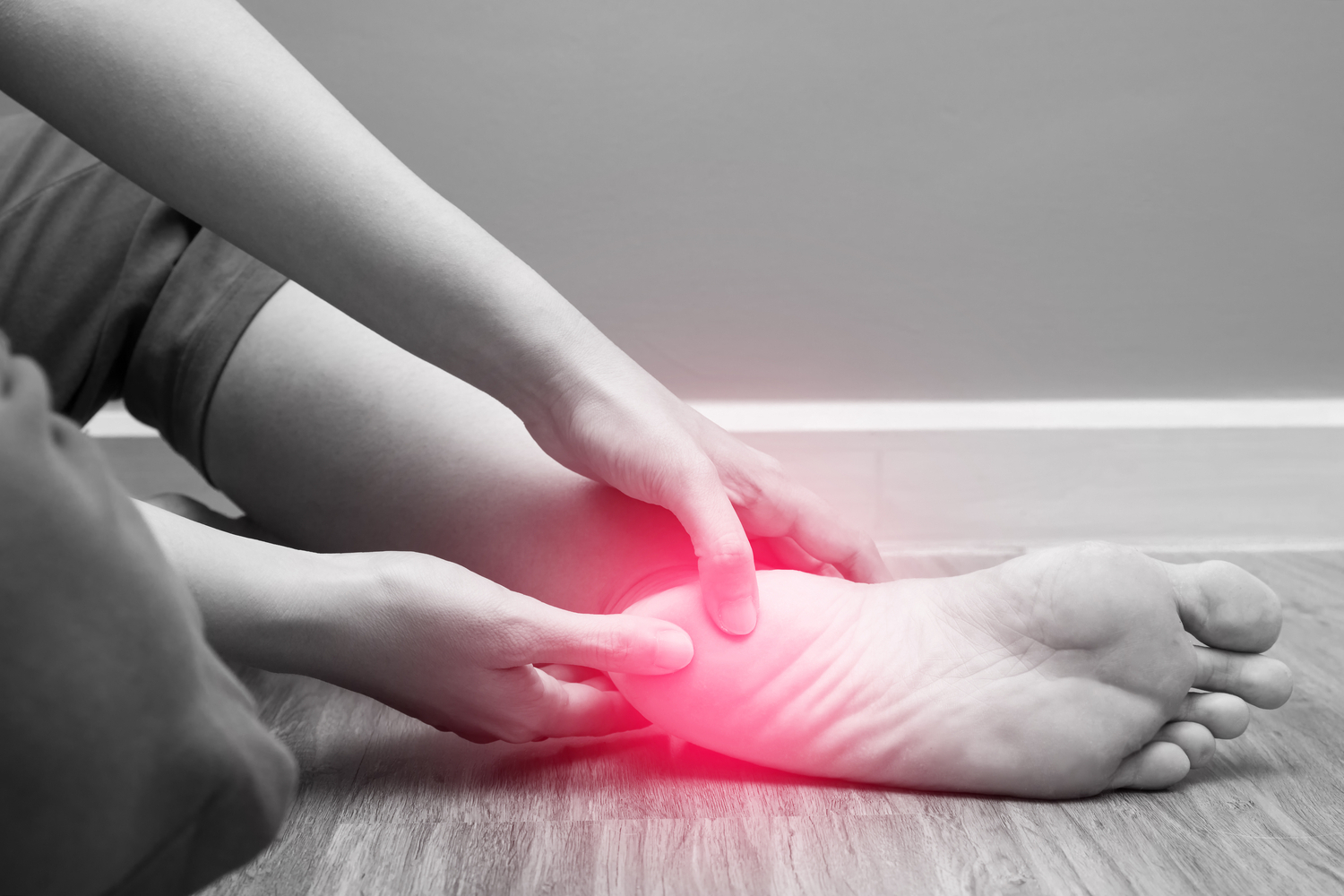
The nervous system relies on a flawless communication network to coordinate bodily functions seamlessly. The peripheral nervous system is primarily composed of motor nerves that control muscle movements, sensory nerves that transmit sensations like pain and temperature, and autonomic nerves that regulate involuntary functions such as blood pressure and digestion. These nerves are made up of neurons capable of transmitting electrical signals rapidly. Damage to any part of this intricate system can cause disruptions that manifest as numbness, weakness, tingling, burning sensations, and even paralysis in severe cases.
With the rising prevalence of neuropathy worldwide, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options becomes critical. Especially among older adults, nerve damage can lead to increased fall risk due to loss of sensation in the feet, which may result in serious injuries. Therefore, early diagnosis and intervention are essential to manage symptoms effectively and improve patients' overall health outcomes.
Major Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
Traumatic injuries: Physical trauma from accidents, falls, or surgeries can directly damage nerves, leading to neuropathy.
Metabolic disorders: Conditions such as diabetes and hypothyroidism significantly contribute to nerve damage due to metabolic imbalances.
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels: High glucose levels in diabetic individuals can cause chronic nerve damage over time.
Inflammatory conditions: Autoimmune illnesses like rheumatoid arthritis and Guillain-Barré syndrome cause nerve inflammation, impairing function.
Chemotherapy: Cancer treatments, especially certain chemotherapeutic agents, can damage peripheral nerves, resulting in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy.
Toxin exposure: Excessive alcohol consumption, exposure to heavy metals, and environmental toxins can cause nerve deterioration.
Effective Treatment Strategies for Peripheral Neuropathy
Managing peripheral neuropathy requires a multifaceted approach tailored to the underlying cause and specific symptoms. Successful treatment often involves a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and complementary therapies that aim to alleviate pain, prevent further nerve damage, and promote nerve regeneration.
1. Targeted Medical Treatments
Mononeuropathy Management: When a single nerve is affected, treatment may include physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, or surgical decompression to relieve pressure on the nerve. For example, carpal tunnel syndrome—a common mononeuropathy—can often be treated successfully through carpal tunnel release surgery.
Polyneuropathy Management: The more widespread nerve damage typical in polyneuropathy can be addressed through comprehensive care plans that include medications for pain relief, physical therapy, and addressing systemic causes such as diabetes or autoimmune diseases.
2. Diagnostic and Functional Tests
Food Protein Testing: Identifying food sensitivities that trigger immune reactions can help reduce inflammation that hinders nerve repair. Eliminating problematic foods and using immune modulating therapies can enhance recovery.
Stress Hormone Evaluation: Salivary cortisol testing assesses adrenal gland function, offering insights into stress-related impacts on nerve health. Managing stress hormones can improve overall nerve recovery.
3. Innovative and Supportive Therapies
Electrical Nerve Stimulation: This therapy applies low-voltage electrical currents to affected nerves, effectively blocking pain signals and providing relief from neuropathic pain. It is often used in conjunction with other treatments for optimal results.
Reducing Toxin Exposure: Limiting alcohol intake and quitting smoking are crucial to prevent further nerve deterioration caused by toxins. Environmental toxin removal and lifestyle changes are foundational in management.
Diet, Nutrition, and Supplementation: Incorporating a diet rich in nerve-supportive nutrients such as vitamins D and B12 can significantly contribute to nerve regeneration. Supplements like fish oil, which provides omega-3 fatty acids, and amino acids may promote nerve repair and reduce inflammation.
Blood Sugar Management: For diabetic patients, meticulous control of blood glucose levels is vital in preventing and slowing the progression of diabetic neuropathy. This can be achieved through medications, diet, and lifestyle modifications.
Alternative and Complementary Medicine: Acupuncture, herbal remedies, and natural supplements have shown potential in alleviating neuropathic pain and supporting nerve healing. These therapies should complement conventional treatments and be administered under professional guidance.
In summary, the treatment of peripheral neuropathy demands a holistic approach that addresses both the symptoms and root causes. Early diagnosis combined with targeted therapy can significantly improve patient outcomes, minimizing discomfort and enhancing nerve function. As research advances, new therapies and innovative approaches continue to evolve, offering hope to millions affected by this challenging condition.