Comprehensive Nutritional Approaches to Managing and Slowing Macular Degeneration Progression
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies for managing macular degeneration effectively. This detailed guide emphasizes the importance of nutrient-rich foods like leafy greens, citrus fruits, and omega-3s, along with tips on foods to avoid. Integrating nutrition with medical treatments can slow disease progression, support retinal health, and preserve vision. Empower yourself with knowledge and practical tips to maintain eye health through a balanced diet and proactive healthcare approaches.

Comprehensive Nutritional Approaches to Managing and Slowing Macular Degeneration Progression
Macular degeneration is a prevalent eye condition that affects millions worldwide, with estimates surpassing 10 million individuals impacted. This condition represents a major cause of vision loss and is characterized by the deterioration of the central portion of the retina, known as the macula. As a leading cause of irreversible vision impairment among adults, effective management strategies are essential. While medical treatments such as intraocular injections and laser therapy are available to slow disease progression, recent research highlights the significant role that diet and nutrition play in supporting eye health and potentially delaying the worsening of the condition.
Understanding how nutrition influences eye health can empower patients and caregivers to make informed dietary choices. Incorporating specific nutrients and foods proven to support retinal health can be a natural, accessible, and cost-effective way to complement medical interventions. This article explores detailed nutritional strategies, recommended foods, and dietary considerations specifically tailored for managing macular degeneration effectively.
Key Nutrients Essential for Eye Health
To effectively support ongoing eye health and slow the progression of macular degeneration, it is crucial to focus on specific nutrients that have been scientifically linked to retinal function and visual preservation. These key nutrients include carotenoids, antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals. Emphasizing the intake of foods rich in these nutrients can help maintain retinal integrity, reduce oxidative stress, and promote vascular health.
Top Foods to Incorporate for Macular Degeneration Support
Leafy Green Vegetables
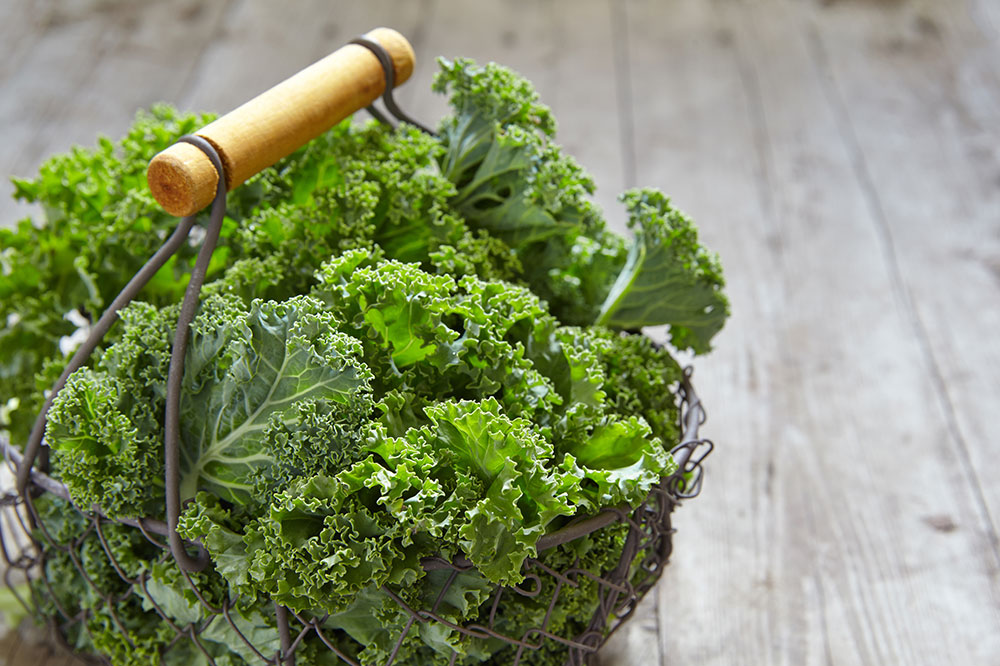
Leafy greens such as kale, spinach, collard greens, and watercress are packed with carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin. These compounds are concentrated in the macula and serve as natural light filters, protecting retinal photoreceptor cells from damage caused by high-energy light exposure. Regular consumption of these vegetables has been associated with a lower risk of developing advanced age-related macular degeneration (AMD). To maximize benefits, incorporate a variety of colorful greens into salads, smoothies, or stir-fries.
Citrus Fruits and Berries
Citrus fruits such as oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and limes, along with berries like strawberries, blueberries, and kiwi, are rich sources of vitamin C. This antioxidant supports blood vessel health, reduces oxidative stress, and may help slow disease progression. A diet abundant in vitamin C-rich foods strengthens the capillaries in the eye, which is especially important since vascular health plays a critical role in retinal integrity. Incorporate fresh fruits into snacks, cereals, or salads for a healthful boost.
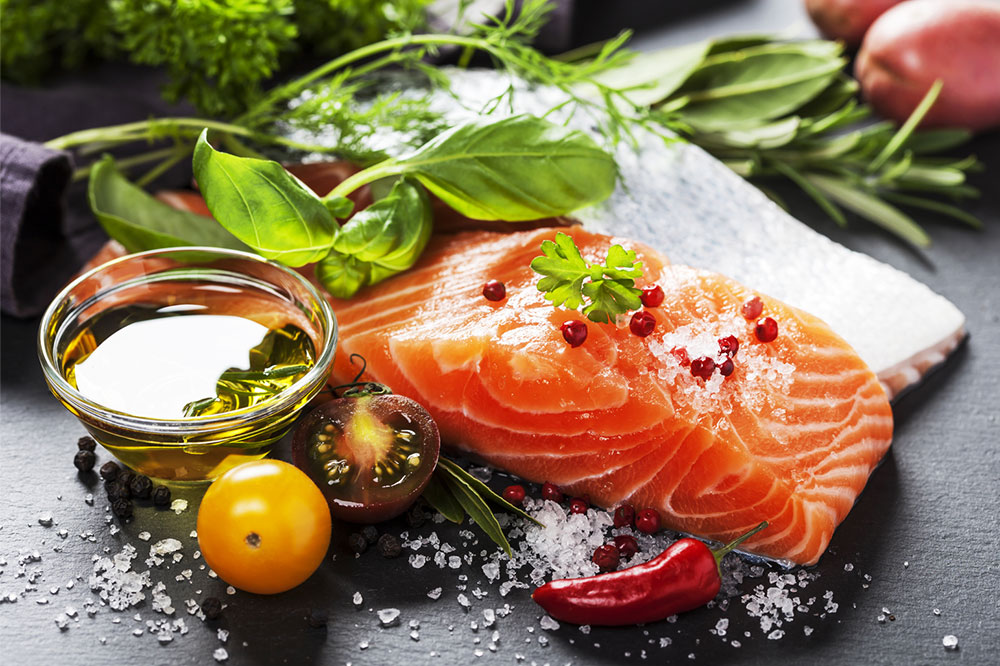
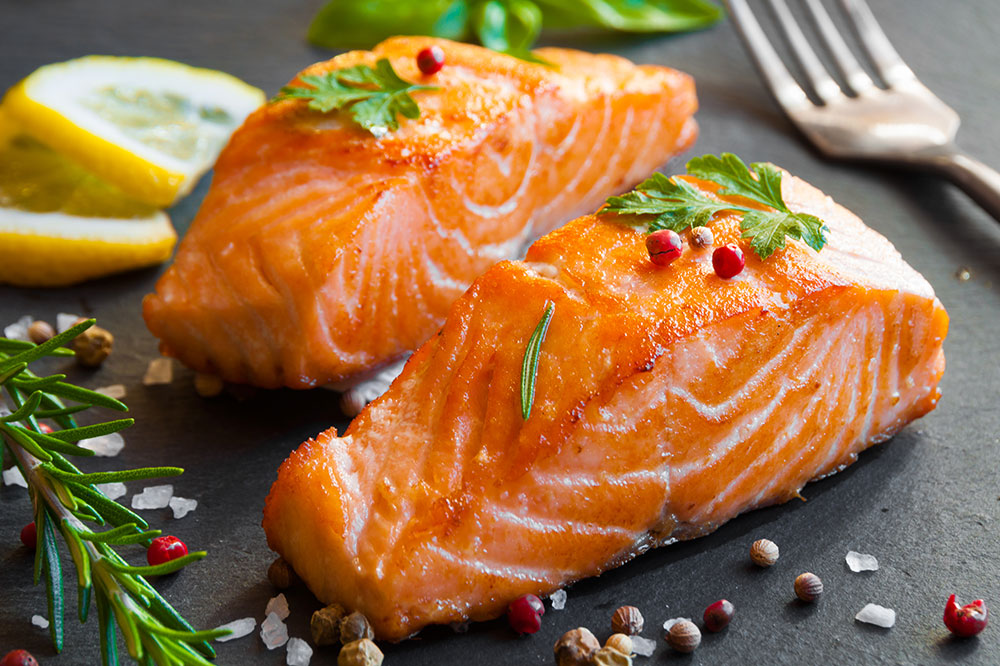
Omega-3 Fatty Acids from Marine and Plant Sources
Fatty fish including salmon, sardines, mackerel, herring, and trout are primary sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA. These healthy fats are vital for maintaining retinal cell structure and reducing inflammation. For individuals who prefer plant-based options, walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and algae oils provide an ample supply of ALA, a precursor to EPA and DHA. Regular inclusion of omega-3-rich foods can significantly contribute to retinal health and potentially mitigate disease progression.
Foods to Limit or Avoid for Eye Health Preservation
In addition to emphasizing beneficial foods, it's equally important to minimize consumption of foods that may exacerbate macular degeneration or impair overall eye health. Certain dietary habits can accelerate retinal damage and contribute to further vision loss.
Processed and Packaged Foods
These often contain preservatives, artificial colors, flavors, and additives that lead to increased oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially worsening retina health. Avoid high-sodium processed snacks, fast foods, and sugary items.
Unhealthy Fats and Trans Fats
Foods rich in trans fats and excessive saturated fats—such as fast foods, fried items, and processed meats—impair blood flow, promote inflammation, and may accelerate degeneration of retinal tissues. Limit intake of margarine, shortening, and hydrogenated oils.
Refined Carbohydrates and Sugary Beverages
Excess sugar intake can lead to blood sugar spikes and increase oxidative stress, which contributes to aging and degeneration of ocular tissues. Reduce consumption of sugary drinks, pastries, and white bread.
Complementary Medical Treatments and the Role of Nutrition
Beyond diet, medical interventions such as anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) therapies—including Bevacizumab (Avastin), Ranibizumab (Lucentis®), Aflibercept (Eylea®), and Brolucizumab (Beovu®)—are the standard of care for certain types of macular degeneration. These treatments help inhibit abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage, thereby slowing vision loss. However, integrating nutritional strategies can enhance treatment outcomes and provide additional protection against disease progression.
Consulting with ophthalmologists and nutritionists ensures a comprehensive management plan tailored to your specific stage of AMD, lifestyle, and overall health. Combining medical treatments with dietary modifications offers the best chance to preserve vision and improve quality of life.
Practical Dietary Tips for Maintaining Eye Health
Incorporate a colorful plate—aim for a variety of green, orange, yellow, and red vegetables and fruits to ensure a broad spectrum of antioxidants and carotenoids.
Opt for fatty fish at least twice a week or include plant-based omega-3 sources daily.
Reduce processed snack intake and limit fried foods to support vascular and retinal health.
Maintain hydration and consider supplementation if dietary intake is insufficient, following healthcare provider recommendations.
Conclusion: Empower Your Eye Health Through Nutrition
Managing macular degeneration involves a multifaceted approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle choices, and targeted nutrition. By prioritizing a diet rich in leafy greens, colorful fruits, healthy fats, and essential nutrients, individuals can support retinal health and potentially slow the progression of vision loss. Proactive dietary habits alongside medical guidance can help preserve sight and enhance overall well-being. Remember, early intervention and consistent nutritional support are key in maintaining eye health over the long term.
Adopting these nutritional strategies can lead to improved eye health outcomes, reduce dependency on invasive treatments, and maintain higher quality of life through preserved vision. Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals regularly, and make dietary choices that prioritize your visual health today.