Comprehensive Dietary Approaches for Managing Macular Degeneration
This comprehensive guide explores dietary strategies to manage macular degeneration, emphasizing foods that support eye health and those to avoid. Incorporating colorful vegetables, fruits rich in vitamin C, omega-3 fatty acids from seafood and nuts, alongside medical treatments, can significantly slow disease progression. Maintaining proper nutrition and regular eye care are essential for preserving vision. Learn crucial dietary tips and medical options to help manage this common eye condition effectively and improve your quality of life.

Effective Nutrition Strategies to Support Eye Health in Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration is a progressive eye condition that primarily affects the central part of the retina, leading to vision deterioration. Existing in two main forms—dry and wet—each causes significant visual impairment, but they differ in their underlying mechanisms. Dry macular degeneration involves the thinning of macular tissues, while wet macular degeneration is characterized by abnormal blood vessel growth beneath the retina, often leading to rapid vision loss. While medical treatments are vital, adopting specific dietary habits can substantially support your eye health and potentially slow disease progression.
Key Nutritional Choices for Eye Support:
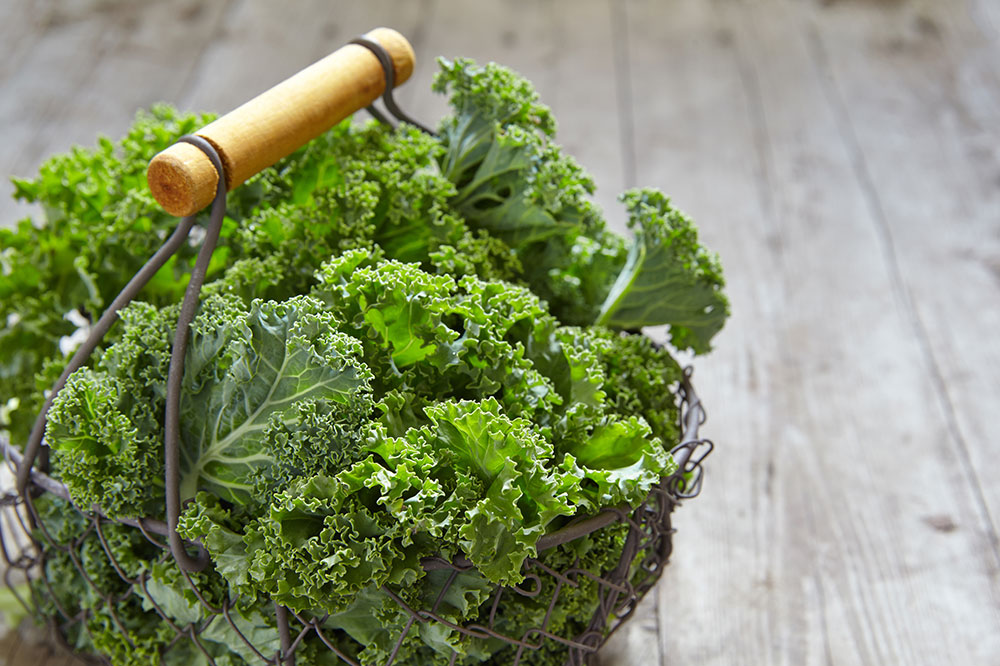
Colorful Vegetables: Incorporate an abundance of vegetables like corn, carrots, collard greens, spinach, red peppers, and sweet potatoes into your daily diet. These foods are high in carotenoids such as lutein and zeaxanthin, crucial antioxidants that help shield retinal cells from oxidative damage and improve visual function. Regular consumption of these vegetables can support overall eye health and may help delay the progression of macular degeneration.
Adding foods rich in carotenoids like spinach, carrots, and sweet potatoes is vital for maintaining healthy eyesight, especially for individuals facing macular degeneration.
Fruits Rich in Vitamin C: Fruits such as berries, oranges, grapefruit, kiwi, and pineapple are excellent sources of vitamin C, which plays a crucial role in strengthening blood vessel walls and preventing retinal leaks. These antioxidants can help mitigate damage associated with wet macular degeneration, providing a protective effect for compromised eyes.
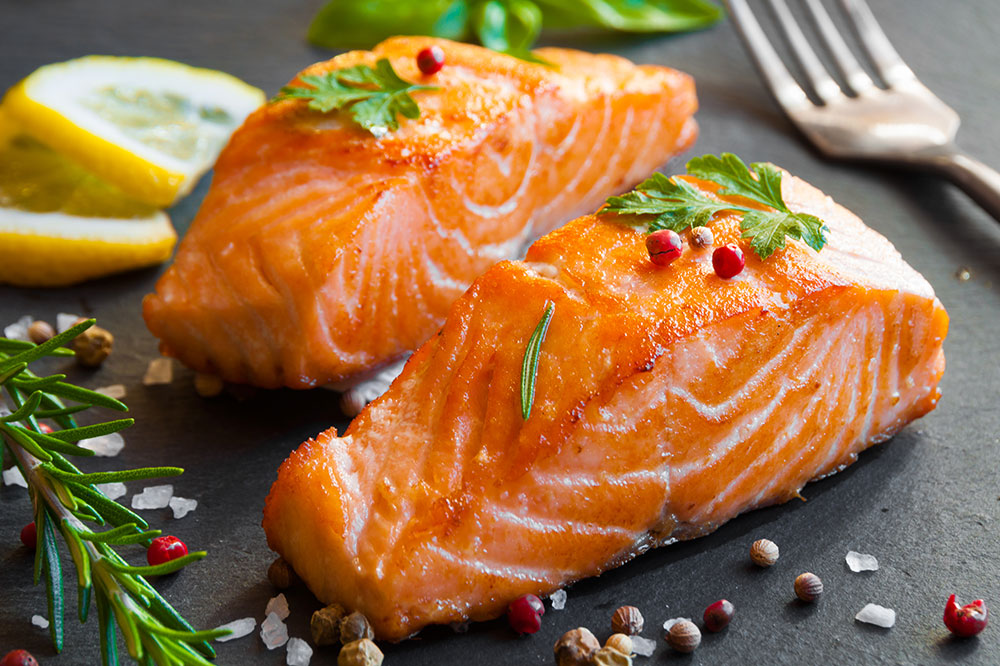
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Sources: Incorporate seafood like salmon, mackerel, and sardines along with nuts and seeds such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These foods are abundant in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for maintaining retinal integrity, reducing inflammation, and supporting the development of healthy blood vessels. Regular intake of omega-3s can potentially slow the progression of macular degeneration and improve overall eye comfort and function.
In addition to carotenoids, omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E contribute to the development of healthy blood vessels and the maintenance of cellular health within the eye. These nutrients can help reduce inflammation, support cellular repair, and improve the appearance and function of the skin and eye tissues.
Foods to Limit or Avoid: Maintaining a diet that promotes good circulation and prevents the clogging of retinal blood vessels is vital. Certain foods can hinder these processes and exacerbate macular degeneration symptoms.
Processed Snacks and Fast Foods: These foods are often high in trans fats, poor-quality saturated fats, excessive sodium, and preservatives. Consuming them regularly can lead to arterial plaque buildup, restricting blood flow to the eyes and worsening retinal health.
Full-fat Dairy Products: High in saturated fats, dairy products like cheese, full-fat milk, and butter can contribute to arterial narrowing, reduce circulation, and potentially accelerate the progression of eye degenerative conditions.
Certain Oils: Oils such as palm oil and coconut oil are rich in saturated fatty acids. Regular consumption may promote arterial stiffening and impair blood flow, negatively impacting eye health.
Medical Management and Monitoring: For individuals diagnosed with macular degeneration, a comprehensive eye examination is essential to determine the stage and severity of the disease. Treatment options may include intravitreal injections of medications like bevacizumab (Avastin), ranibizumab (Lucentis), aflibercept (Eylea), and brolucizumab (Beovu). These injections work by inhibiting abnormal blood vessel growth and reducing leakage to improve vision and mitigate symptoms. Combining these treatments with healthy dietary habits provides an integrated approach to managing the condition effectively. Regular medical follow-ups and lifestyle modifications are key to maintaining visual health and preventing further deterioration.