Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Symptoms of Leukemia and When to Seek Medical Attention
This comprehensive article educates readers about the diverse signs and symptoms of leukemia, emphasizing the importance of early detection. It explains the different types of leukemia, their progression speed, and key indicators such as fatigue, fever, unexplained weight loss, and organ enlargement. Recognizing these warning signs promptly can lead to earlier diagnosis and improved treatment outcomes, saving lives. The article also highlights when to seek medical help and the significance of diagnostic tests. It serves as a vital resource for anyone concerned about blood cancer symptoms or personal health awareness.

Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Symptoms of Leukemia and When to Seek Medical Attention
Detecting early warning signs of leukemia can significantly enhance the chances of successful treatment. Being aware of subtle changes and persistent symptoms in your body is crucial for timely diagnosis and intervention. This detailed guide aims to educate readers about the various signs associated with leukemia, the different types of leukemia, and when to seek medical advice.
Understanding Leukemia: An Overview
Leukemia is a serious form of blood cancer that originates in the bone marrow, the spongy tissue inside your bones where blood cells are produced. This health condition disrupts the normal production of blood cells by causing the marrow to produce abnormal white blood cells, which often multiply uncontrollably. These leukemia cells are abnormal, immature, and dysfunctional, which impairs your body's immune response and other vital functions.
White blood cells play a critical role in defending the body against infections. When leukemia affects these cells, it can lead to symptoms like increased bleeding, anemia, frequent infections, and overall weakening of health. Moreover, leukemia can spread from the bone marrow to lymph nodes, spleen, liver, and other organs, causing swelling, discomfort, and other systemic symptoms. Recognizing these signs early can lead to a quicker diagnosis and more effective treatment options.
White blood cells are essential for fighting infections, but in leukemia, abnormal cells take over, compromising the immune system. This can lead to bleeding problems, anemia, and an increased risk of infections. Leukemia can also infiltrate lymph nodes and vital organs, causing pain and swelling.
Types of Leukemia: A Closer Look
Leukemia is classified into various types based on its progression speed and the affected blood cell type. It primarily divides into acute and chronic forms, with further subtypes depending on the blood cell lineage involved. Here is an in-depth overview of these types:
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): A rapidly progressing leukemia mainly affecting lymphoid cells, common among children but also affecting adults.
Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML): A fast-growing leukemia originating in myeloid cells, prevalent in adults.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): A slow-developing leukemia involving lymphoid cells, typically diagnosed in older adults.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML): Progresses gradually, affecting myeloid cells, and often has identifiable genetic markers such as the Philadelphia chromosome.
Less common variants include hairy cell leukemia and promyelocytic leukemia, which have unique clinical features and treatment approaches. Each type requires specific diagnostic evaluations and tailored treatment plans.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs of Leukemia
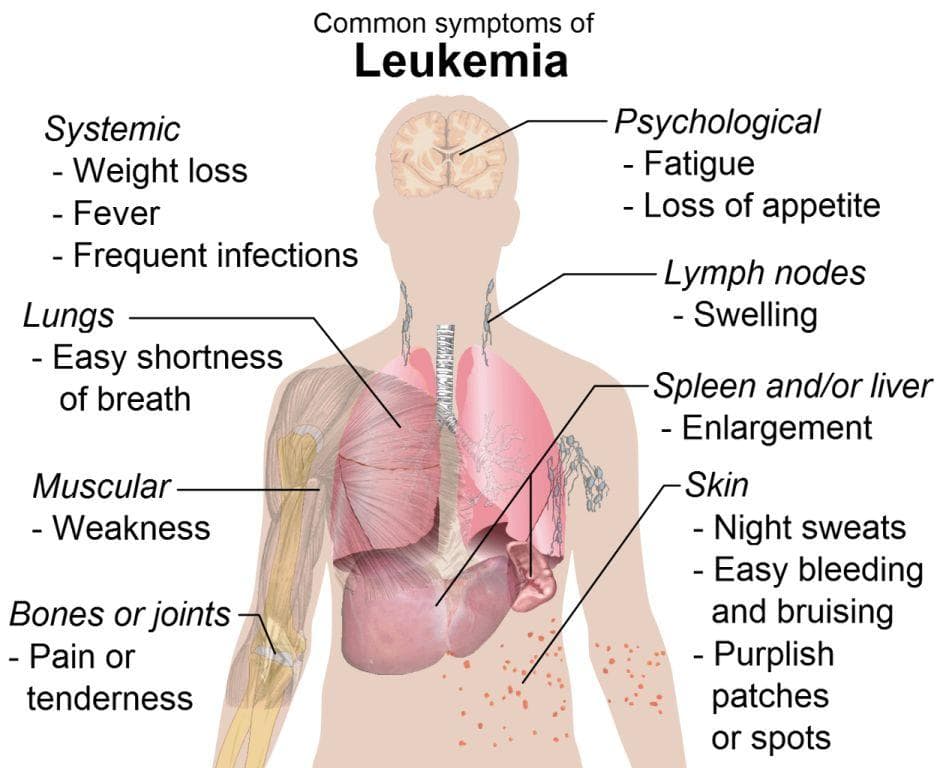
Recognizing the early signs of leukemia can be challenging, as initial symptoms often mimic common illnesses or are subtle. However, persistent and unexplained health changes should prompt medical investigation. Here are the key symptoms to monitor:
Unexplained fatigue or persistent weakness that doesn't improve with rest or sleep.
Recurring fevers, chills, or night sweats that occur without obvious infection.
Unexplained weight loss or loss of appetite over a short period.
Bone or joint pain that persists or worsens over time.
Frequent infections or flu-like illnesses that do not respond to treatment.
Small red or purple skin spots (petechiae) indicative of bleeding issues.
Unusual or heavy bleeding from gums, nose, or rectum.
Heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding.
Persistent headaches that are not relieved by usual medications.
Night sweats that cause significant discomfort.
Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath without exertion.
Sudden or unexplained weight loss or decline in overall strength.
Abdominal discomfort, fullness, or swelling, particularly in the upper abdomen.
Unusual bruising or easy bleeding.
Additional Signs That May Indicate Leukemia
Aside from the common symptoms, there are other specific signs worth noting that suggest leukemia might be present:
Swollen lymph nodes: Noticeable lumps in the neck, armpits, or groin can indicate lymphatic involvement or metastasis.
Anemia: Marked by low red blood cell counts, leading to pallor, fatigue, and breathlessness.
Leukopenia: A deficiency of white blood cells that impairs immune defense, raising the risk of infections.
Thrombocytopenia: Low platelet levels cause increased bleeding tendencies, easy bruising, and petechiae.
Organ Enlargement: An enlarged liver or spleen can cause a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the upper abdomen due to excessive blood cell buildup.
Persistent symptoms such as fever, night sweats, unexplained fatigue, or swelling should never be ignored. If these symptoms persist beyond the typical cold or flu duration, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve treatment success rates and survival chances. If you experience any of these signs, especially in combination, seek medical attention immediately to undergo appropriate diagnostic tests such as blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, or imaging studies to confirm or rule out leukemia.