Comprehensive Guide to Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms of Leukemia
Learn about the vital signs and symptoms of leukemia, a serious blood cancer. Early detection through awareness of symptoms like fatigue, unexplained bleeding, swollen lymph nodes, and frequent infections can dramatically improve treatment outcomes. This comprehensive guide covers different types of leukemia, diagnostic methods, and treatment options to help patients and caregivers recognize the disease early and seek prompt medical attention for better prognosis.

Leukemia is a complex form of blood cancer that significantly impacts the body's ability to produce healthy blood cells. It primarily targets the bone marrow—the core tissue inside bones responsible for generating blood cells—and the lymphatic system, which is integral to immune function. This disease causes abnormal proliferation of immature or dysfunctional white blood cells, which can interfere with the body's ability to fight infections, carry oxygen, and clot blood effectively. Understanding the subtle and overt signs of leukemia is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management, thereby improving treatment outcomes and patient survival rates.
Leukemia is more common among men, with an estimated 30,000 new cases reported annually in various populations worldwide. The disease can manifest in several forms, including acute and chronic types, each with distinct progression rates and symptom profiles. In the early stages, many individuals remain asymptomatic, which underscores the importance of regular medical check-ups for early detection. As the disease advances, several symptoms become evident, signaling the need for immediate medical evaluation.
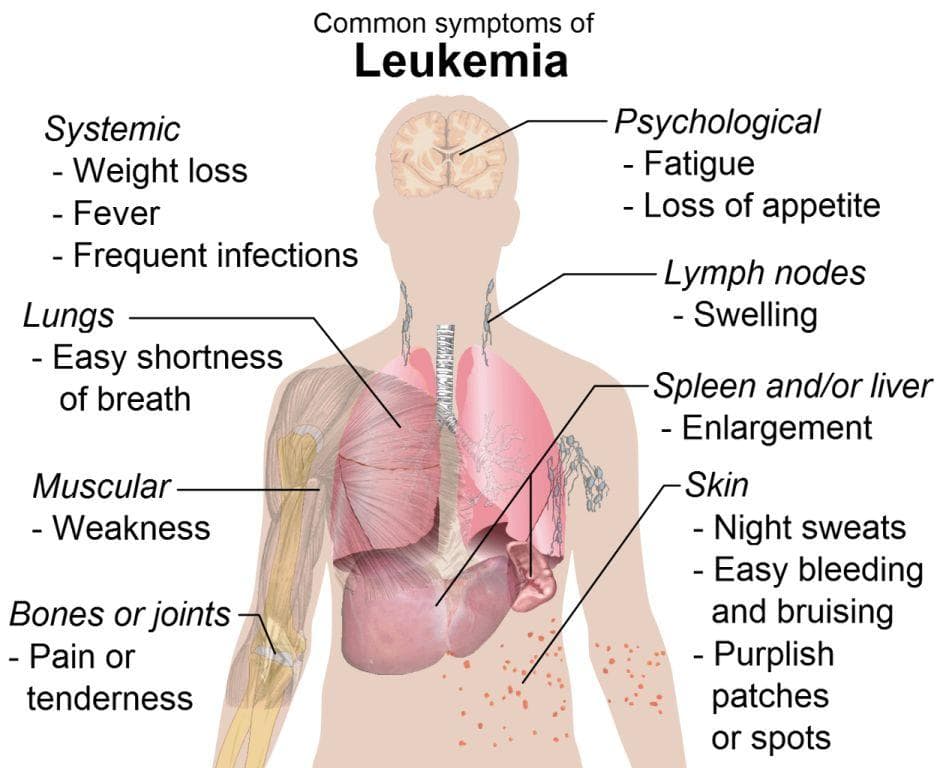
Among the most prevalent early symptoms are unexplained bleeding or easy bruising, which may occur even from minor injuries. Persistent fatigue and weakness are common due to anemia—a condition characterized by low red blood cell counts—leading to pallor, shortness of breath, and decreased stamina. Swollen lymph nodes, often palpable under the arms, in the neck, or groin, represent the body's response to malignant cell infiltration and immune system activation.
Patients with leukemia are also highly susceptible to infections because the abnormal white blood cells cannot function correctly, resulting in increased episodes of sore throats, rashes, fever, and other illness symptoms. Bleeding manifestations might include bleeding gums, nasal hemorrhages, or tiny skin spots called petechiae—small red or purple spots resulting from broken blood vessels. Additional signs include unintentional weight loss, night sweats, and discomfort or swelling in the abdomen's left side due to an enlarged spleen or liver. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to prompt diagnosis and treatment, which is vital for improving prognosis.
Understanding the importance of early detection in leukemia cannot be overstated. Healthcare professionals recommend regular blood tests and hematological assessments, especially for individuals with risk factors such as a family history of blood cancers, exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, or genetic predispositions. Advances in diagnostic tools like blood smears, bone marrow biopsies, and molecular testing help identify leukemia at its earliest stages. Once diagnosed, treatment options may include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation, or stem cell transplants, depending on the leukemia type and stage. Supportive care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life is also an integral part of comprehensive leukemia treatment.
In conclusion, being aware of the signs and symptoms of leukemia empowers individuals to seek medical attention promptly, which can dramatically affect treatment success. Regular health screenings, especially for those at higher risk, combined with a keen eye for subtle health changes, are essential strategies in combating this serious disease. Early intervention not only increases survival rates but also enhances overall health and well-being for patients diagnosed with leukemia.