Comprehensive Guide to Eyelid Swelling: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies for eyelid swelling and inflammation. It details common issues like allergies, infections, and serious conditions such as orbital cellulitis and thyroid eye disease. By understanding these factors, individuals can better identify early signs and seek timely medical care to maintain healthy, functioning eyes. Proper eye hygiene practices and protective measures are emphasized to prevent eyelid problems and ensure overall eye health.
Comprehensive Guide to Eyelid Swelling: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention Strategies
The human eye, often called the window to the soul, is an incredibly delicate and complex organ that demands meticulous care and protection. The eyelids play a vital role in safeguarding the eyes from environmental hazards such as dust, smoke, harsh chemicals, airborne particles, and intense light sources. Despite their protective function, the eyelids are susceptible to inflammation, swelling, and redness, which can be persistent and disruptive to daily life. Understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting effective prevention measures are essential for maintaining eye health and preventing potential vision-threatening conditions.
Inflammation of the eyelids, also known as blepharitis or eyelid inflammation, can manifest as swelling, redness, itchiness, or a combination of these symptoms. In severe cases, eyelids may adhere or stick together, particularly after sleep, leading to discomfort and impaired vision. Persistent or recurrent eyelid inflammation may serve as a sign of underlying health issues such as orbital cellulitis, thyroid eye disease (also known as Graves' orbitopathy), or eye herpes. Therefore, early detection and treatment are crucial to address both the symptoms and their causes effectively.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Eyelid Inflammation
Typical signs of eyelid inflammation include the following:
Swelling or puffiness around the eyelids
Persistent redness or erythema
Itchy sensations around the eye area
Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Discharge or pus, often indicating infection
Excess tearing or watery eyes
Eyelids sticking together, especially after waking
Being aware of these symptoms can help in identifying potential problems early and seeking appropriate medical care.
Major Causes of Eyelid Swelling and Inflammation
Various factors can lead to eyelid swelling, ranging from common allergies to serious health conditions that threaten vision. Here’s an in-depth overview of the most common causes:
Allergic Reactions: Exposure to environmental allergens such as pollen during springtime, dust mites settled in indoor environments, pet dander, certain cosmetics, or contact lens solutions can trigger allergic responses. These responses often involve inflammation, swelling, and itching of the eyelids.
Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): This infectious or allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane covering the sclera and inside of the eyelids, can cause significant swelling, redness, and discomfort.
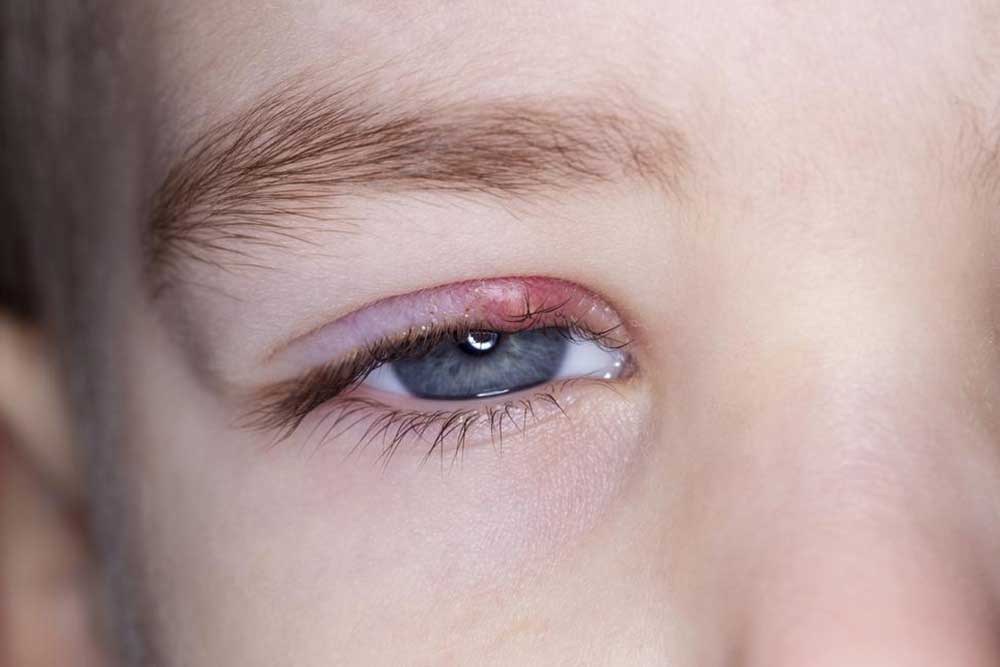
Styes (Hordeolum): These are small, localized bumps that develop along the eyelid margins due to infection or blockage of the meibomian glands, leading to swelling, tenderness, and sometimes pain.
Eye Injuries: Trauma resulting from accidental scratches, blows, or foreign objects entering the eye can cause acute swelling, redness, and pain.
More causes include:
Contact Lens Infections: Improper hygiene, sharing lenses, or extended wear can lead to bacterial or viral infections that cause eyelid swelling.
Blepharitis: This chronic condition involves inflammation of the eyelid margins owing to dysfunction of oil glands, resulting in redness, crusting, and swelling.
Chalazion: A benign, painless swelling caused by blockage of the meibomian gland, often developing away from the edge of the eyelid.
Crying: Excessive tearing can cause temporary puffiness and swelling of the eyelids.
There are other more serious causes of eyelid inflammation, such as:
Orbital Cellulitis: A severe bacterial infection impacting the tissues around the eye, characterized by painful swelling, redness, and sometimes fever.
Herpes Simplex Virus: Viral infection causing ocular herpes, which can lead to eyelid inflammation, ulcers, and vision disturbances.
Thyroid Eye Disease (Graves’ Orbitopathy): An autoimmune condition associated with hyperthyroidism, resulting in swollen, bulging, and puffy eyelids, often accompanied by discomfort and vision issues.
To mitigate the risk of eyelid inflammation, maintaining proper eye hygiene is essential. Regular eyelid cleaning, avoiding exposure to bright lights, smoke, and pollutants, and ensuring adequate sleep are some of the effective measures to prevent infections and inflammation. Additionally, wearing protective eyewear and practicing good contact lens hygiene significantly reduce the chances of eyelid-related issues.
In conclusion, eyelid swelling and inflammation are symptoms with a wide array of causes—ranging from benign allergies to severe infections and autoimmune diseases. Recognizing early signs and symptoms, understanding the potential causes, and consulting healthcare professionals promptly can help in effective management and prevention of more serious complications related to eye health.