Comprehensive Guide to Red Eye: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
This comprehensive guide explores the common causes of red eye, including environmental irritants, infections like conjunctivitis, and serious conditions such as glaucoma and corneal ulcers. It offers practical advice for identification, self-care remedies, and when to seek professional help. Regular eye exams, hygiene practices, and protective measures are emphasized as vital for maintaining optimal ocular health and preventing long-term damage. Whether it's minor irritation or a serious medical issue, understanding and managing red eye effectively can safeguard your vision and eye comfort.
Comprehensive Guide to Red Eye: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management Strategies
The human eye is an incredibly delicate and sensitive organ, constantly exposed to a wide array of environmental and internal factors that can influence its health. Red eye, also known as conjunctival hyperemia, is one of the most common ocular conditions that individuals encounter. While often benign and temporary, red eye can also be a symptom of more serious health issues that require prompt medical attention. Understanding the various causes, recognizing symptoms early, and knowing appropriate treatment options are essential steps to maintaining healthy eyes and preventing long-term damage.
Common Causes of Red Eye
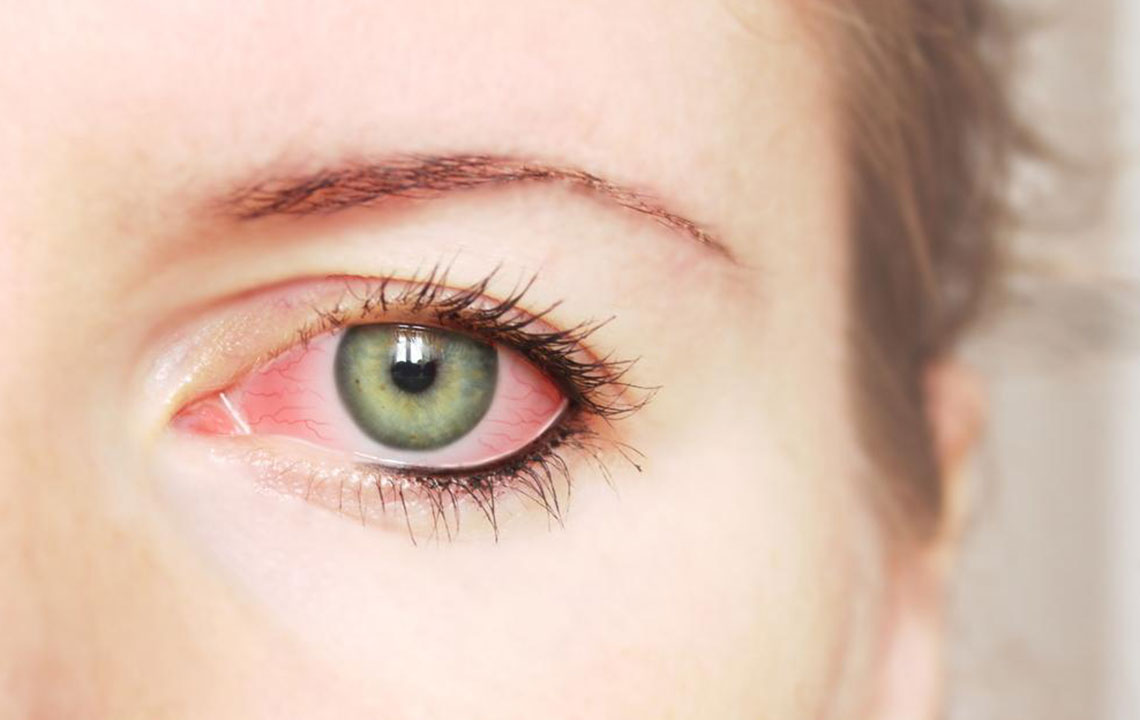
The appearance of redness in the eyes can stem from a variety of causes, ranging from minor irritations to severe medical conditions. Some causes are straightforward and easily manageable, while others demand immediate professional intervention. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth overview of the typical causes of red eye, how to identify them, and suitable solutions for each.
Daily Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
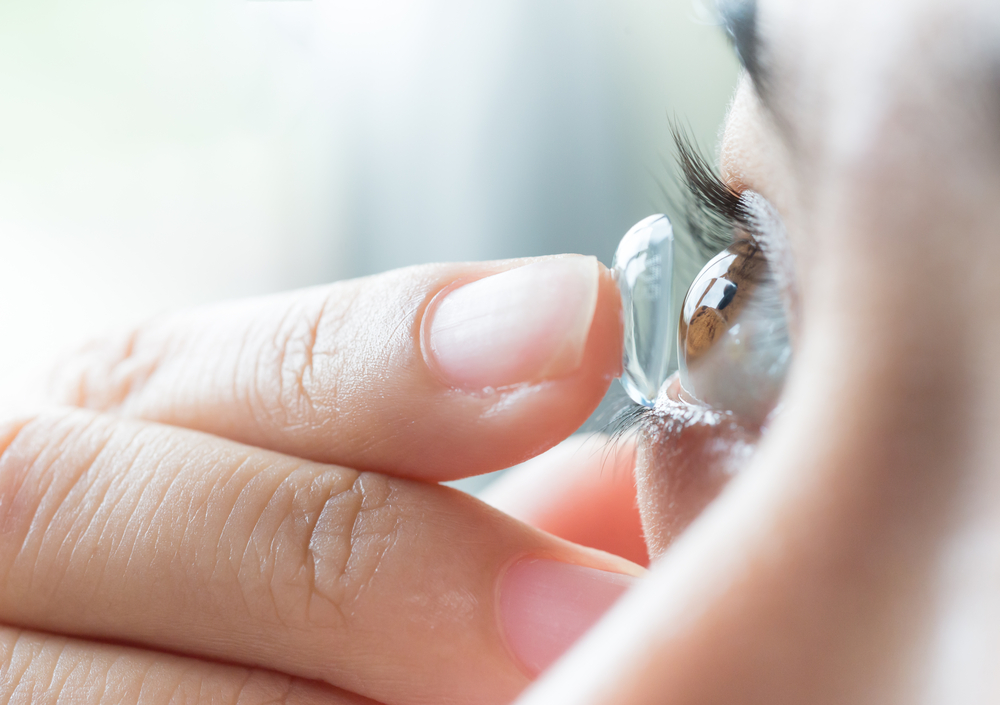
One of the most frequent reasons for red eyes is daily exposure to environmental irritants. Dust particles, air pollution, pollen, and other allergens can cause inflammation of the ocular surface, leading to redness. Inadequate sleep or irregular sleep patterns contribute to tired, bloodshot eyes due to fatigue affecting blood flow and tear production. Extended hours of screen time—such as working on computers, tablets, or smartphones—often cause eye strain, dryness, and redness. Similarly, contact lens wearers may experience redness if lenses are not cleaned properly or worn for extended periods, which can lead to oxygen deprivation and irritation.
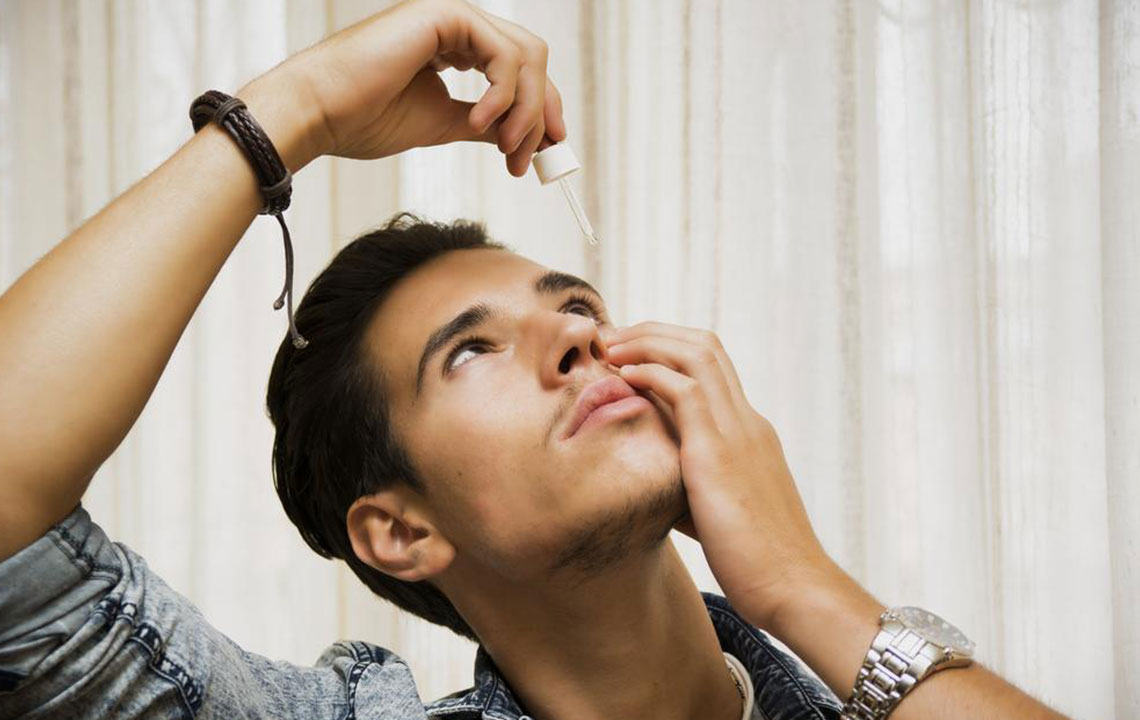
To mitigate these issues, simple home remedies and lifestyle adjustments are effective. Ensuring adequate rest and sleep helps restore ocular health. Using warm compresses can enhance blood circulation and aid in lubricating the eyes. Cold compresses are beneficial in reducing swelling, inflammation, and irritation, especially after prolonged exposure to bright screens or allergens. Artificial tears or lubricating eye drops help wash away dust particles, soothe dryness, and maintain moisture balance in the eyes. Wearing protective glasses outdoors and maintaining proper hygiene when handling contact lenses are crucial preventive steps.
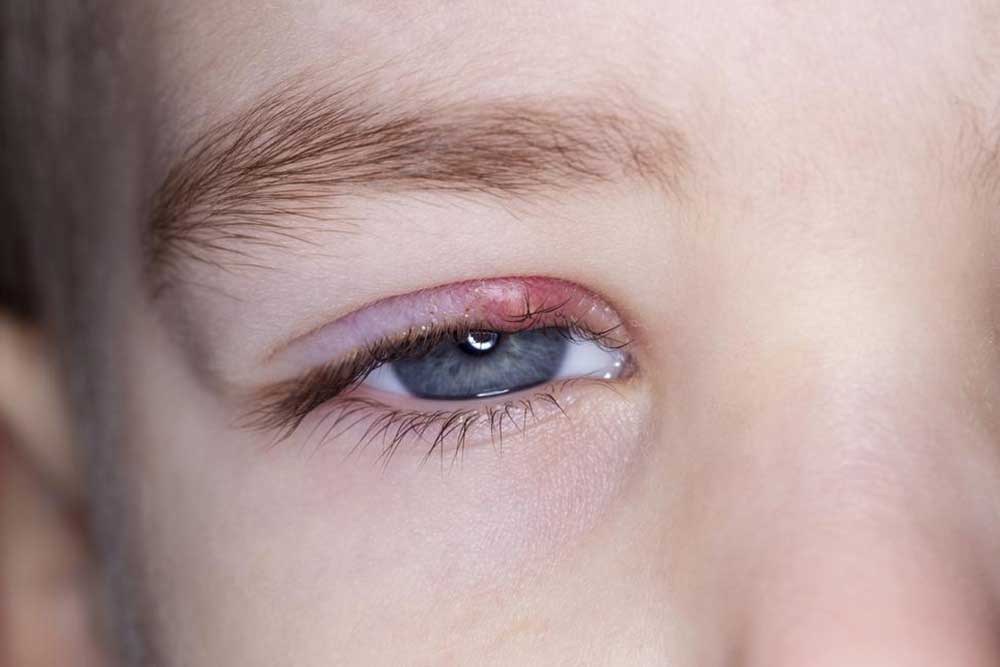
Conjunctivitis: The Pink Eye Syndrome
One of the most common infectious causes of red eye is conjunctivitis, popularly called pink eye. It involves inflammation of the conjunctiva—the thin, transparent tissue that covers the white part of the eye and lines the eyelids. Conjunctivitis can be caused by bacterial or viral infections, or allergic reactions. Symptoms include redness, intense itching, excessive watering, and sticky discharge that often crusts over during sleep. The contagious nature of conjunctivitis demands careful hygiene practices and prompt treatment.
Managing conjunctivitis involves consulting an eye care professional for accurate diagnosis. Bacterial conjunctivitis often requires antibiotic eye drops or ointments, while allergic conjunctivitis may be treated with antihistamine or anti-inflammatory eye drops. Good hygiene practices, such as avoiding sharing towels, pillowcases, or eye makeup, and washing hands frequently, are vital to prevent spread. Discontinuing contact lens use during the infection is usually recommended until symptoms resolve fully.
Sudden Hemorrhages and Other Acute Conditions
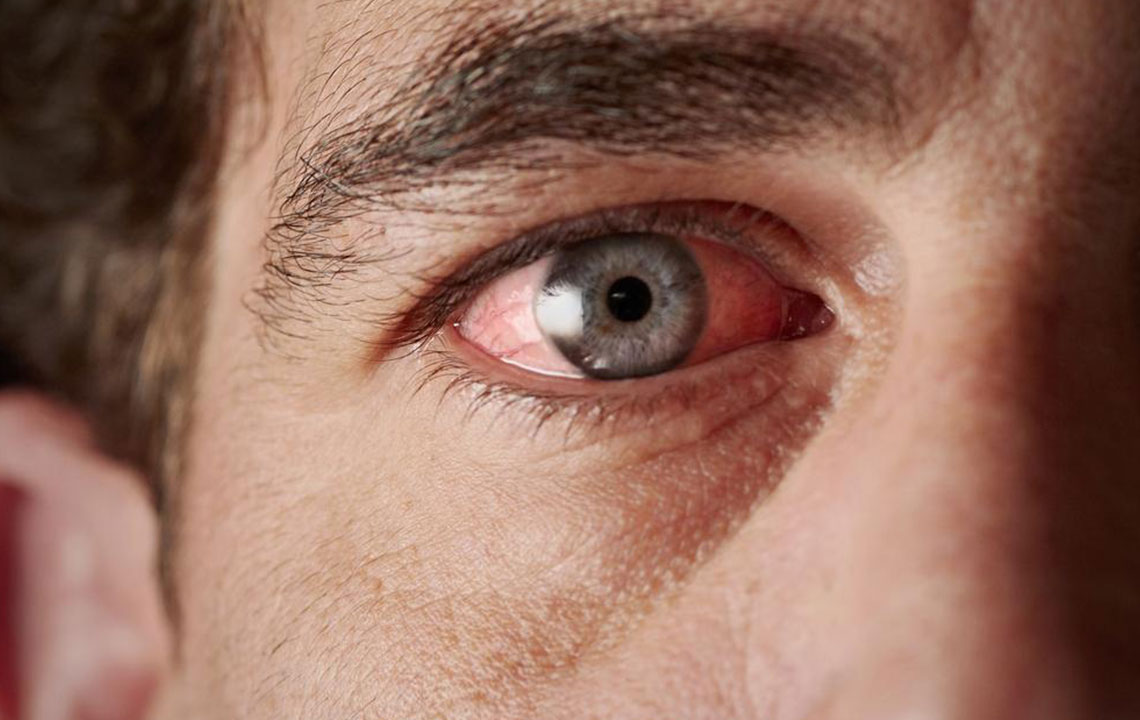
Subconjunctival hemorrhage, often called a burst blood vessel in the eye, presents as a bright red patch on the white part of the eye. It frequently results from sudden increases in pressure caused by coughing, sneezing, heavy lifting, or minor trauma. Although alarming in appearance, this condition is typically harmless and resolves on its own within a week or two. Applying artificial tears can alleviate discomfort, and avoiding rubbing the eyes is advisable. If bleeding persists or is accompanied by pain, vision disturbances, or recurrent episodes, medical evaluation is necessary.
Another serious condition is glaucoma, especially prevalent among people over 40. Elevated intraocular pressure damages the optic nerve and can cause permanent vision loss if left untreated. During an acute glaucoma attack, symptoms such as intense eye redness, pain, nausea, headache, and blurred vision appear suddenly and require immediate emergency medical attention. Regular eye examinations are essential for early detection and management, especially for high-risk individuals with a family history of glaucoma.
Corneal Ulcers and Other Serious Eye Infections
Corneal ulcers are painful, open sores that develop on the cornea—the clear front surface of the eye. They are commonly seen in contact lens users due to bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. Symptoms include redness, severe light sensitivity, a sensation of something foreign in the eye, decreased vision, and increased tearing or discharge. Corneal ulcers require urgent medical attention to prevent scarring and potential vision loss. Treatment typically involves antimicrobial eye medications prescribed by an ophthalmologist, along with recommendations for lens hygiene and usage.
Prompt diagnosis and consistent treatment are vital in managing serious eye infections. Preventive measures include proper contact lens care, avoiding wearing lenses during eye infections, and protecting the eyes from injury and contamination.
Accurate diagnosis and timely treatment are the cornerstones of managing red eye effectively. While many causes are minor and resolve with home care, others necessitate professional medical intervention. Regular eye checkups, good hygiene practices, and protective measures are key to maintaining ocular health and preventing complications. If you experience persistent redness, pain, vision changes, or unusual discharge, consult an eye care professional promptly for comprehensive evaluation and tailored treatment plans. Remember, healthy eyes are essential for quality of life and overall well-being.