Comprehensive Guide to Effective Treatments and Medications for Fibromyalgia Symptom Relief
Fibromyalgia is a common chronic disorder characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. This comprehensive guide explores effective medications, including antidepressants, pain relievers, anticonvulsants, and complementary therapies like massage. Proper management involves personalized treatment strategies to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Consulting healthcare providers is crucial for developing a safe and effective treatment plan tailored to individual needs. With the right combination of therapies, patients can achieve meaningful symptom relief and regain their daily functioning.
Understanding Key Medications and Therapeutic Approaches for Managing Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is one of the most common chronic musculoskeletal disorders, second only to osteoarthritis, affecting millions worldwide. Despite its prevalence, diagnosis remains challenging due to its complex and often misunderstood symptoms. Characterized by widespread muscle pain, joint discomfort, persistent fatigue, and sleep disturbances, fibromyalgia significantly impacts quality of life. Fortunately, a variety of treatments—including medications, physical therapies, and lifestyle modifications—are available to help manage symptoms effectively. This comprehensive guide delves into the most effective medications and therapeutic options to alleviate fibromyalgia symptoms, providing hope and relief for patients seeking sustained management strategies.
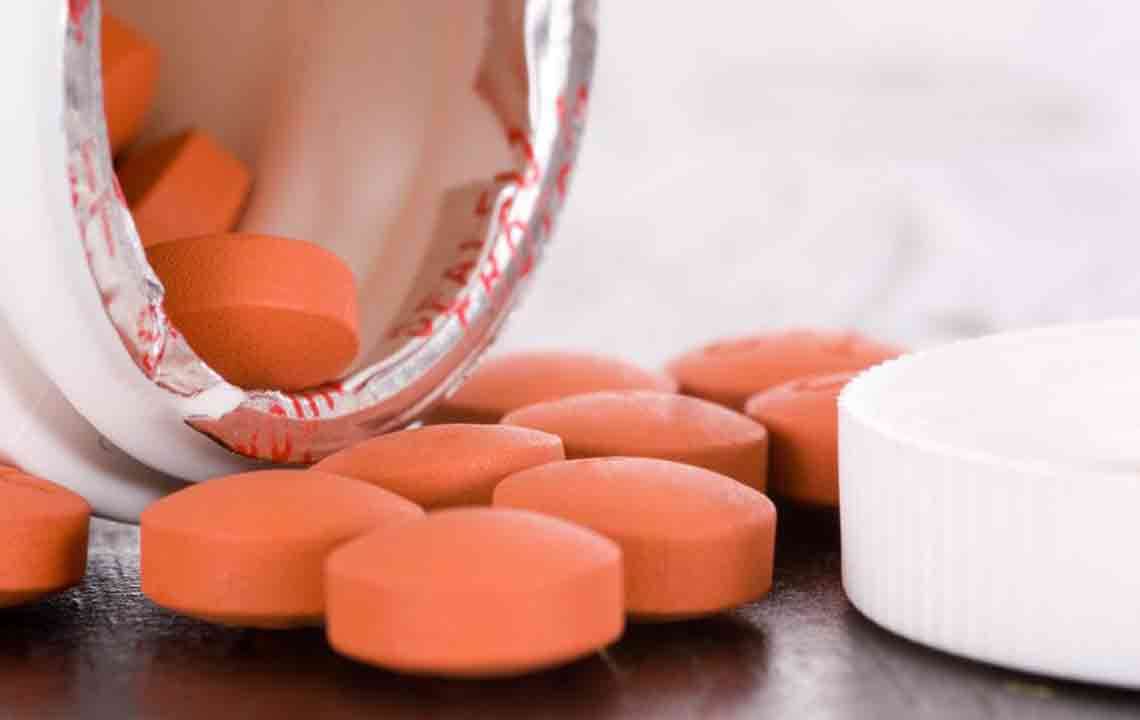
Initial Medical Approach – Antidepressants The cornerstone of fibromyalgia treatment often involves antidepressant medications. These drugs are primarily prescribed to reduce pain perception, improve sleep quality, and counteract associated mood disorders such as depression and anxiety, which frequently accompany the condition. Their dual action on mood and pain pathways makes them particularly suitable for fibromyalgia management. Antidepressants help modulate brain chemicals involved in pain regulation, leading to significant symptom relief. Various classes of antidepressants are used, and typically, healthcare providers tailor the choice based on patient response and side effect profiles.
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) Among the earliest and most studied treatments for fibromyalgia are tricyclic antidepressants such as nortriptyline and amitriptyline. These medications have been used for decades to manage chronic pain conditions. They work by increasing levels of neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, which help suppress pain signals and promote relaxation of tense muscles. Improved sleep quality is also a notable benefit. However, TCAs come with potential side effects including dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness, and constipation, which patients need to discuss thoroughly with their healthcare providers. Proper dosage adjustments and monitoring can help mitigate these adverse effects.
In addition to TCAs, several other antidepressants have gained approval for fibromyalgia treatment. Medications like duloxetine (Cymbalta), milnacipran, and venlafaxine are frequently recommended due to their proven efficacy. The FDA has approved Savella (milnacipran) and Cymbalta (duloxetine) specifically for treating fibromyalgia symptoms. Personal variation in response to these medications suggests that healthcare providers often recommend trying different options to identify the most effective and tolerable treatment for each patient. Regular follow-up allows for dosage adjustments and monitoring of side effects, ensuring optimal symptom management.
Pain Management Strategies Since pain is a primary and persistent symptom, targeted pain relief options are critical components of treatment plans. The choice of pain medications depends largely on individual responses and symptom severity.
Over-the-Counter Analgesics Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is commonly recommended for mild to moderate pain relief. It helps elevate pain thresholds, thereby reducing the perception of discomfort. Regular use can improve daily functioning and mood by alleviating persistent soreness.
NSAIDs Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including ibuprofen and aspirin, may be used as adjuncts to other treatments. While they do not directly target fibromyalgia pain, they can help reduce any accompanying inflammatory symptoms. Because long-term use poses risks such as gastrointestinal irritation, kidney issues, and cardiovascular concerns, patients should consult healthcare professionals for safe administration. Those with pre-existing liver conditions should exercise caution, especially when using acetaminophen, due to potential hepatotoxicity.
Muscle Relaxants Medications like cyclobenzaprine are often prescribed to ease muscle tension and improve sleep quality. These drugs relax tense muscles, reducing discomfort and promoting restorative rest. Side effects may include dry mouth, dizziness, or in rare instances, hallucinations, which necessitate medical supervision.
Anticonvulsant Drugs Originally developed for seizure control, drugs such as pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) have been repurposed for fibromyalgia. They work by modulating nerve pain transmission, leading to reduced discomfort, fatigue, and improved sleep patterns. These medications tend to be effective for many patients, offering a significant improvement in daily functioning.
Additional Pharmacological Options Benzodiazepines might be prescribed short-term to relax muscles and improve sleep, particularly when symptoms include restless legs syndrome or severe muscle spasms. Opioids like tramadol, hydrocodone, and oxycodone are considered only in cases where other therapies have failed, due to their potential for dependence and side effects. Their prescription requires careful monitoring.
Beyond medications, incorporating complementary therapies can substantially enhance symptom relief. Massage therapy, in particular, offers notable benefits.
Massage Therapy Techniques including myofascial release, shiatsu, and Swedish massage help reduce muscles tension and pain, improve circulation, and promote relaxation. Regular massage sessions can contribute to better sleep, decreased muscle stiffness, and stress reduction. These therapies also support physical and mental well-being, helping patients manage daily challenges more effectively.
Fibromyalgia affects approximately 3-6% of the global population and predominantly impacts women. Although it is a chronic condition, proper management using a combination of medications, physical therapies, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support can lead to significant improvements in quality of life. Consulting healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans is essential for achieving the best outcomes while minimizing side effects and enhancing overall well-being. Managing fibromyalgia requires patience, consistency, and a comprehensive approach tailored to individual needs.