Comprehensive Guide to Managing Foot Discomfort in Fibromyalgia Patients
Explore comprehensive strategies to manage foot discomfort in fibromyalgia. Learn about causes, diagnosis, and effective treatments including medications, lifestyle changes, supportive footwear, exercises, and natural remedies. Improve quality of life with personalized care designed for persistent foot pain associated with this chronic condition.
Comprehensive Guide to Managing Foot Discomfort in Fibromyalgia Patients
Fibromyalgia is a complex and often misunderstood chronic disorder that manifests through widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and a variety of ancillary symptoms. Originating from Latin roots—"fibro" representing connective tissue, "myo" for muscles, and "algos" meaning pain—this condition profoundly impacts millions worldwide. Understanding the intricacies of fibromyalgia, especially as it pertains to foot discomfort, is essential for effective management and improving patients’ quality of life.
Fibromyalgia’s symptoms are multifaceted, including persistent exhaustion, sleep disturbances, difficulties in concentration (sometimes called "fibro fog"), heightened sensitivity to environmental stimuli such as noise and temperature changes, depression, persistent headaches, abdominal discomfort, and anxiety. These symptoms often intertwine, creating a challenging cycle that hampers daily functioning. Recognizing the root causes and understanding treatment options are pivotal steps in managing this condition effectively.
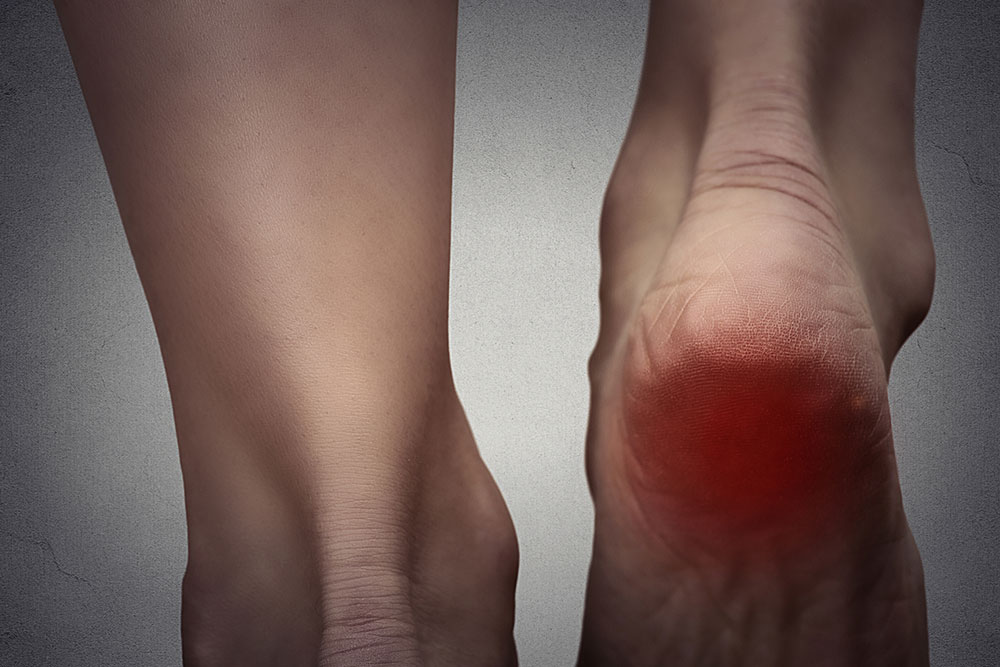
Among the various symptoms, foot pain stands out as a prevalent and often debilitating issue for fibromyalgia sufferers. The pain frequently radiates from the feet to the hips, knees, or lower back, compounding discomfort and affecting mobility. Since feet bear the body's weight, they are particularly vulnerable, and the severity of foot pain can vary widely—from mild aches to severe, persistent discomfort that hampers daily activities. Addressing foot pain is thus a crucial aspect of comprehensive fibromyalgia management.
Understanding the causes of fibromyalgia-related foot pain necessitates an exploration of multifactorial influences:
Infections and Allergic Reactions: Episodes of infections, allergic reactions, or illnesses can trigger or exacerbate fibromyalgia symptoms. Additionally, footwear played a role—unsuitable, tight, or poor-quality shoes can worsen foot discomfort, especially in individuals with heightened sensitivity.
Genetic Predisposition: A family history of fibromyalgia, particularly with instances involving foot pain, increases the likelihood of experiencing similar symptoms. Genetic factors may influence nerve sensitivity or connective tissue vulnerability.
Psychological and Physical Stress: Psychological stressors, including emotional trauma, chronic anxiety, or depression, can manifest physically within the body. Stress-induced muscle tension and nervous system hyperactivity contribute to the sensation of foot pain and overall discomfort.
Diagnosing foot pain related to fibromyalgia involves careful clinical evaluation. Persistent foot pain lasting longer than three months—without an alternative medical explanation—raises suspicion of fibromyalgia. While there are no definitive laboratory tests for fibromyalgia itself, blood tests can be employed to rule out other conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or hypothyroidism, ensuring accurate diagnosis.
Effectively managing foot pain in fibromyalgia patients encompasses a variety of strategies aimed at alleviating discomfort and improving functionality:
Pharmacological Treatments: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, or strong pain relievers such as tramadol can prove beneficial in reducing foot pain. Moreover, medications initially designed for nerve pain, including anticonvulsants like gabapentin and pregabalin, are frequently prescribed to modulate nerve hypersensitivity associated with fibromyalgia.
Lifestyle Modifications: Integrating holistic approaches such as meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises helps manage stress levels, which can exacerbate symptoms. Improving sleep hygiene, maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, and regular foot massages can also significantly mitigate symptoms.
Appropriate Footwear and Orthotics: Choosing comfortable, supportive shoes tailored to individual foot structure is vital. Orthotic insoles can provide additional arch support and cushioning, distributing weight more evenly and alleviating pressure points. Alternating footwear helps prevent localized stress and promotes foot health.
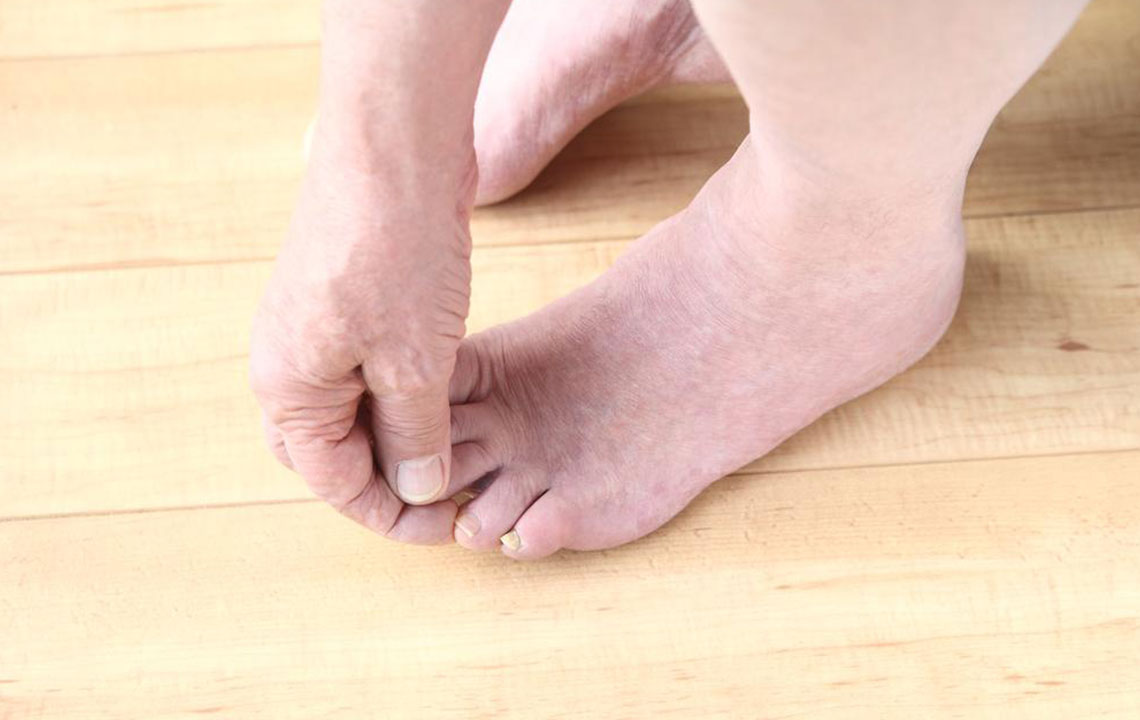
Foot and Nerve Exercises: Techniques such as reflexology, stretching routines, and targeted foot massages help improve circulation, reduce fatigue, and relieve pain. Engaging in mild to moderate exercise tailored to the individual's capacity enhances muscle strength and flexibility.
Warm Foot Baths and Natural Remedies: Soaking feet in warm water combined with soothing ingredients like baking soda, Epsom salt, and ginger can relax tense nerves, promote circulation, and diminish discomfort. Regular warm baths serve as an effective home remedy for symptom relief.
Additional Supportive Measures: Wearing anklets offers warmth retention and gentle support, easing discomfort and promoting foot health. Maintaining proper foot hygiene, regular monitoring of foot health, and avoiding excessive strain are essential preventive strategies.
Given the chronic nature of fibromyalgia, ongoing management and a proactive approach are necessary. Patients should continually educate themselves about the condition, stay vigilant for symptom changes, and work closely with healthcare professionals. Early intervention when symptoms worsen can substantially reduce the risk of complications and improve overall well-being.
In summary, understanding the multifaceted aspects of foot discomfort in fibromyalgia is crucial for effective management. Combining medical treatments with lifestyle adjustments and supportive footwear can significantly enhance comfort and mobility. Patients benefit from a multidisciplinary approach that involves physicians, physiotherapists, and holistic practitioners to develop personalized care plans.