Comprehensive Guide to Proper Insulin Pen Usage for Effective Diabetes Management
This comprehensive article explores the proper use of insulin pens in diabetes management, covering types, benefits, techniques, safety tips, and troubleshooting. It aims to help patients optimize their insulin therapy through better understanding and correct usage, leading to improved blood sugar control and quality of life. Whether you use reusable or disposable pens, follow these expert guidelines for safe and effective insulin administration, ensuring long-term health benefits and minimal discomfort.

Comprehensive Guide to Proper Insulin Pen Usage for Effective Diabetes Management
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic and complex disease affecting hundreds of millions of people around the globe. It is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production or the body's inability to effectively use insulin. Managing blood sugar levels is vital to prevent acute complications like hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, as well as long-term health issues such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision impairment. Among various treatment options, insulin therapy remains a cornerstone, especially for Type 1 diabetes and advanced Type 2 diabetes cases. Using insulin properly is essential for optimal glycemic control, and insulin pens have revolutionized the way patients administer their insulin, making the process more efficient, discreet, and user-friendly.
Insulin pens are modern devices designed to simplify the process of insulin administration compared to traditional syringes. They resemble familiar writing pens, providing ease of handling and portability. These devices are equipped with a cartridge or prefilled insulin reservoir, a dial for dose setting, and a pen needle, which is a small, fine needle intended for injection. Understanding how to use these pens correctly can significantly improve adherence to prescribed insulin regimens, reduce discomfort, and enable precise dosing. This comprehensive guide covers the types of insulin pens, their features, proper usage techniques, troubleshooting tips, and safety considerations to help diabetes patients manage their condition more effectively.
Types of Insulin Pens and Their Features
Insulin pens are broadly categorized into two main types: reusable and disposable. Each type offers distinct advantages and considerations that influence user choice based on lifestyle, cost, and personal preferences.
Reusable Insulin Pens: These are designed with a replaceable insulin cartridge, allowing users to refill them with insulin from a larger vial or cartridge. Reusable pens are constructed from durable materials, making them a long-term investment for many diabetes patients. They often come with features such as digital dose memory, dose adjustment options, and compatible needle sizes. The main benefits include cost efficiency over time, reduced waste, and environmental friendliness. However, they require proper cleaning and maintenance, and users need to ensure the compatibility of cartridges with their pens.
Disposable Insulin Pens: Preloaded with a fixed amount of insulin, these pens are discarded after reaching the dose limit or when insulin runs out. They are convenient for their ease of use, portability, and minimal maintenance. Disposable pens are particularly suitable for those who prefer a hassle-free approach or travel frequently. Limitations include higher recurring costs and less flexibility for mixing different insulin types or adjusting doses beyond preset options.
Advantages of Using Insulin Pens
Enhanced convenience and portability, making it easier to carry and administer insulin on the go.
Reduced injection discomfort due to ultra-fine needles, which minimize pain and tissue damage.
Intuitive operation with clear dose settings, reducing the risk of dosing errors.
Increased discretion and privacy compared to traditional syringes, facilitating better social acceptance.
Feature-rich options such as dose memory, electronic alerts, and dose reminders to boost adherence.
Potential Drawbacks and Safety Considerations
Limited capacity for mixing different types of insulin within a single pen, which may necessitate multiple injections.
Higher initial investment for reusable pens and potential ongoing costs for refill cartridges or replacement needles.
Risk of insulin wastage if devices are not properly stored or if doses are missed.
Need for caution regarding insulin expiry, clarity, and correct dose calculation before each injection.
Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice on selecting and using insulin pens to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Proper Technique for Using Insulin Pens
To maximize the benefits of insulin pens and minimize risks, proper technique is essential. Here are key steps and tips for correct usage:
Preparation: Wash hands thoroughly. Verify insulin expiry date and ensure the insulin is clear (for rapid-acting and long-acting insulins) without clumps or particles.
Assembly: Attach a new needle to the pen securely. Prime the pen by dialing 2 units and pressing the injection button to expel air and ensure insulin flow.
Dosing: Dial the prescribed dose accurately. Always double-check the dose setting before injection.
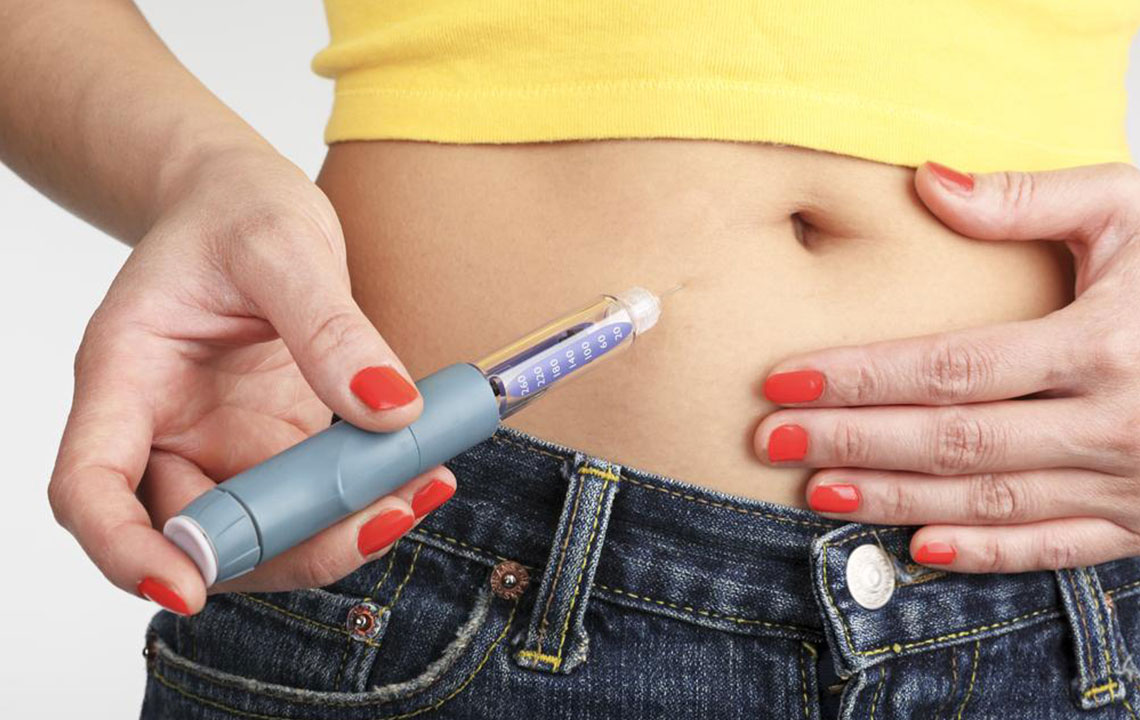
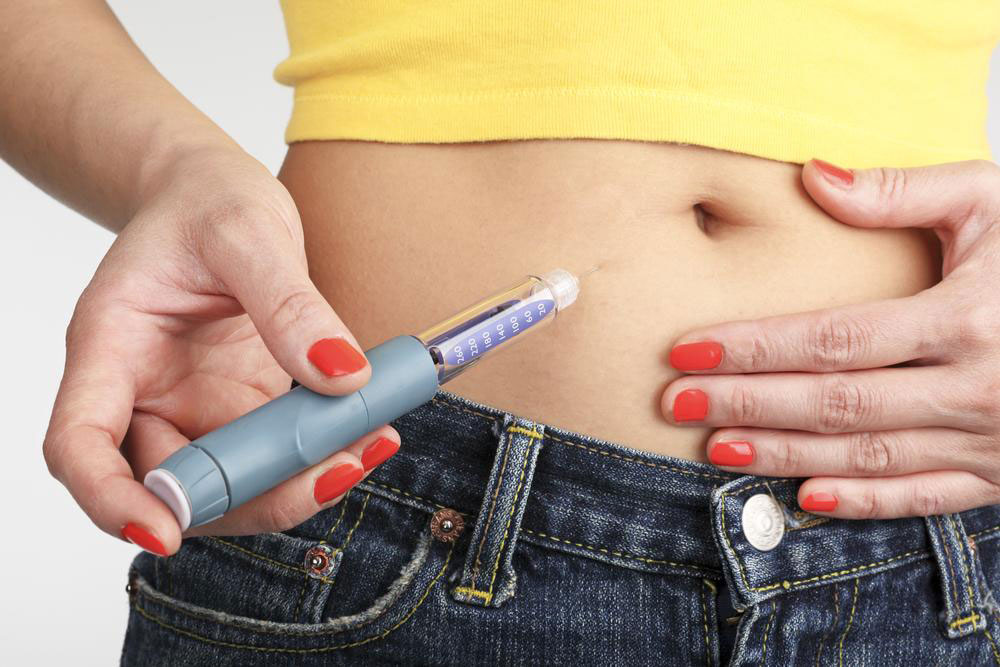
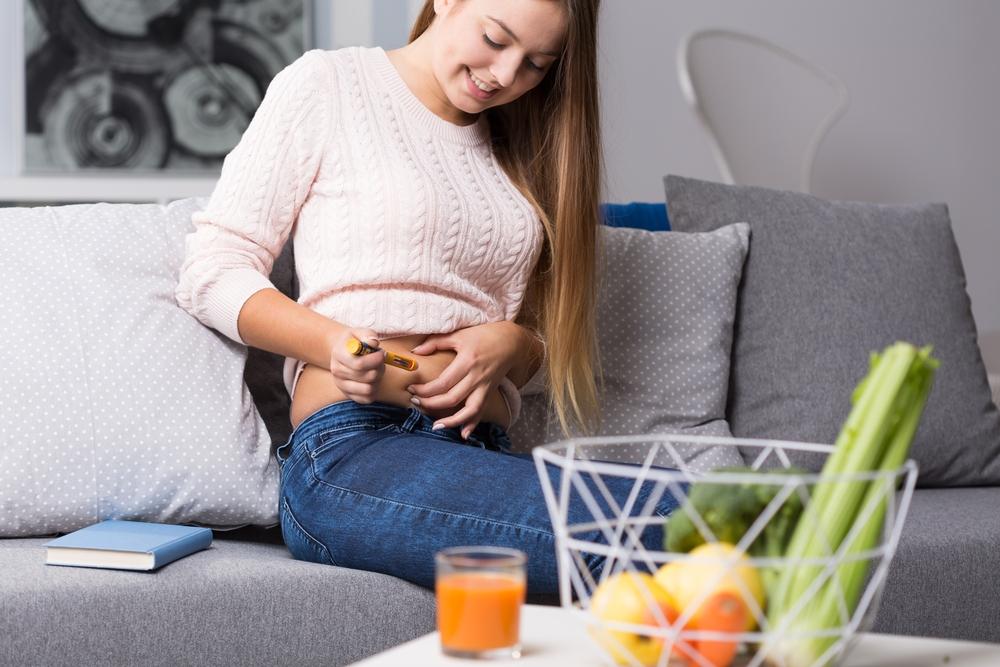
Injection Site: Select an appropriate injection site such as the abdomen, thigh, or buttocks. Rotate sites to prevent lipodystrophy.
Injection Technique: Clean the skin with an alcohol swab. Insert the needle at a 90-degree angle (or 45 degrees if BMI is low). Press the button fully and hold for about 10 seconds to ensure complete delivery of insulin. Remove the needle and dispose of it safely in a sharps container.
Post-Injection Care: Cover injection site if necessary and wash hands. Keep a record of doses to track insulin usage and efficacy.
Storage and Maintenance
Proper storage of insulin pens is crucial for maintaining efficacy. Unopened insulin pens should be stored in the refrigerator and protected from direct sunlight. Once in use, pens can often be kept at room temperature (up to 25°C or as specified by the manufacturer) for a limited period, usually 28 days. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for storage duration and temperature. Regularly inspect pens and needles for any damage, discoloration, or contamination. Use new needles for every injection to prevent infection and ensure patient comfort.
Common Troubleshooting and Tips
If insulin does not flow after priming, check for air bubbles or clogged needle. Replace needle if necessary.
If the dose setting does not match expectations, recalibrate or replace the pen.
Always verify the insulin type and expiry date before use to prevent administration of expired or incorrect insulin.
If leakage or discomfort occurs, assess the injection technique and site. Seek medical advice if persistent issues happen.
Final Thoughts
Using insulin pens correctly is vital for achieving optimal diabetes control, reducing the risk of complications, and improving quality of life. Patients should undergo proper training from healthcare providers, keep track of their insulin use, and adhere strictly to safety and hygiene guidelines. As technology evolves, newer features like digital dose memory, connectivity, and customized dosing options are becoming available to further enhance diabetes management. Always consult your healthcare team for personalized guidance, updates on latest insulin pen models, and support in managing your condition confidently and safely.