Complete Guide to Insulin Pens: Usage Tips, Types, and Best Practices
This comprehensive guide provides detailed insights into insulin pens, their various types, proper usage, storage tips, and safety precautions. It aims to help diabetics choose the right device, use it correctly, and maintain optimal blood glucose control with confidence, making insulin therapy more effective and manageable for daily life.
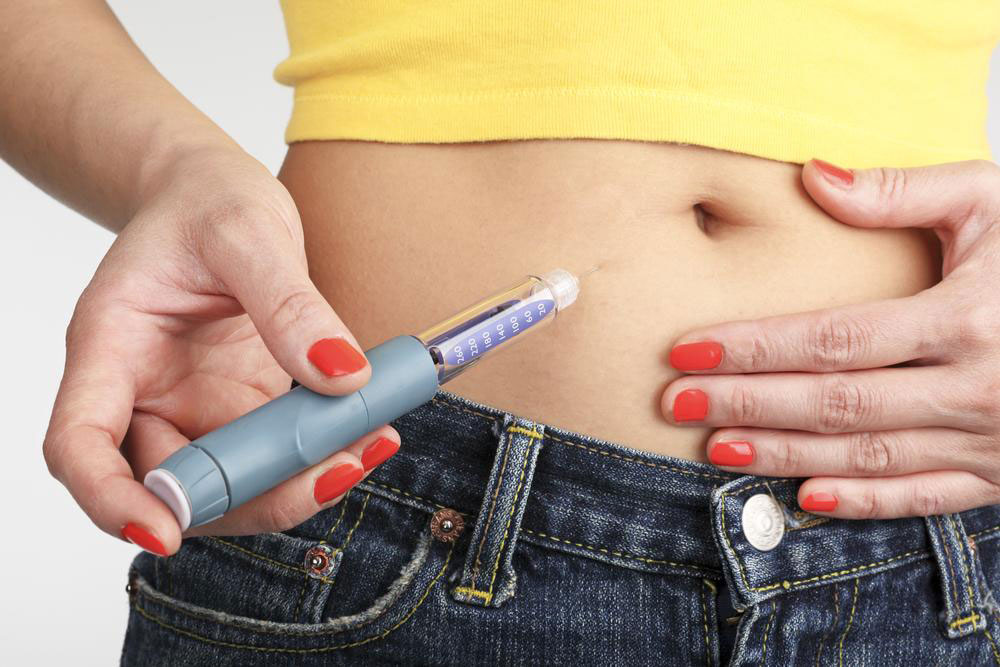

Understanding Insulin Pens: A Comprehensive Guide for diabetics
Managing diabetes effectively often involves regular insulin injections to maintain stable blood glucose levels. Over the years, insulin pens have revolutionized the way patients administer insulin, offering a more convenient, portable, and precise alternative to traditional syringe methods. These devices are designed with user comfort and accuracy in mind, combining an insulin cartridge, a disposable needle, and an adjustable dial to ensure correct dosing.
Insulin pens are capable of delivering a wide range of doses—typically from as low as 0.5 units up to 80 units per injection—catering to both mild and severe insulin needs. They come with adjustable increment options, often allowing for half-unit or one-unit adjustments, making it easier for users to fine-tune their doses according to their healthcare provider’s recommendations. This flexibility helps diabetics manage their condition more precisely and with greater convenience.
Types of Insulin Pens: Disposable vs Reusable
Disposable Insulin Pens: These are pre-filled with insulin and designed for single use. Once the insulin in the pen is depleted or after a set period (usually between 7 to 28 days, depending on insulin type), the entire pen is discarded. They are highly convenient for travel or occasional use, as they require no maintenance or cartridge replacements.
Reusable Insulin Pens: These pens feature a durable body with a replaceable insulin cartridge. With proper care, reusable pens can last over a year, providing a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution. When the insulin runs out, simply replace the cartridge, reducing waste and ongoing expenses.
Choosing between disposable and reusable pens depends on individual preferences, frequency of use, budget, and lifestyle. Always use a fresh, sterile needle with each injection to prevent infections and ensure hygiene. Needles come in various sizes and gauges, compatible with all types of insulin pens, and should match your comfort and injection site.
Consult a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable type of pen based on your specific medical condition and lifestyle needs. Proper guidance can help prevent errors and optimize insulin therapy.
Selecting the Ideal Insulin Pen
Identify whether you prefer a disposable or reusable pen based on your usage and lifestyle
Check the maximum and minimum dosage capacities to ensure compatibility with your insulin needs
Consider the increment options—half-unit or one-unit—to enable precise dose measurement
Review the durability and construction material if opting for reusable pens to ensure longevity
Features such as dose correction, easy dialing, or adjustable settings can enhance user experience
A display that shows remaining insulin levels helps prevent accidental running out
Opt for a pen with larger dial numbers or clear markings for easy readability, especially important for seniors or visually impaired users
Your choice of insulin pen should align with your daily routine, comfort, and medical requirements. Prioritize ease of use, durability, and features that enable accurate dosing.
Proper Storage and Handling of Insulin Pens
Proper storage of insulin pens is vital for maintaining their effectiveness. Unlike insulin vials, which must usually be stored in a refrigerator until first use, insulin pens do not require refrigeration once in use. In fact, many are best stored at room temperature to avoid insulin degradation from temperature fluctuations. Keep your pens in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and heat sources to preserve insulin stability.
Store pens away from freezing temperatures—insulin stored below 0°C can become damaged and ineffective. Conversely, exposure to temperatures above 30°C can also compromise insulin quality. Never store pens with attached needles; removing the needle before storage maintains sterility and prevents damage or accidental injections. Always check the expiration date before use—most insulin pens are effective for 7 to 28 days once opened, depending on the type of insulin used.
How to Use an Insulin Pen Correctly
If you're new to insulin pen usage, seeking guidance from your healthcare provider or diabetes educator is highly recommended. Here is a comprehensive overview of proper technique:
Remove the pen from the refrigerator approximately 30 minutes prior to injection to allow it to reach room temperature—this minimizes discomfort during injection
Verify the insulin type and check the expiration date before use
Inspect the insulin to ensure it appears clear if using a fast-acting or short-acting insulin; cloudy insulins should be gently rolled or inverted to mix evenly
Clean the top of the pen with an alcohol swab to maintain hygiene
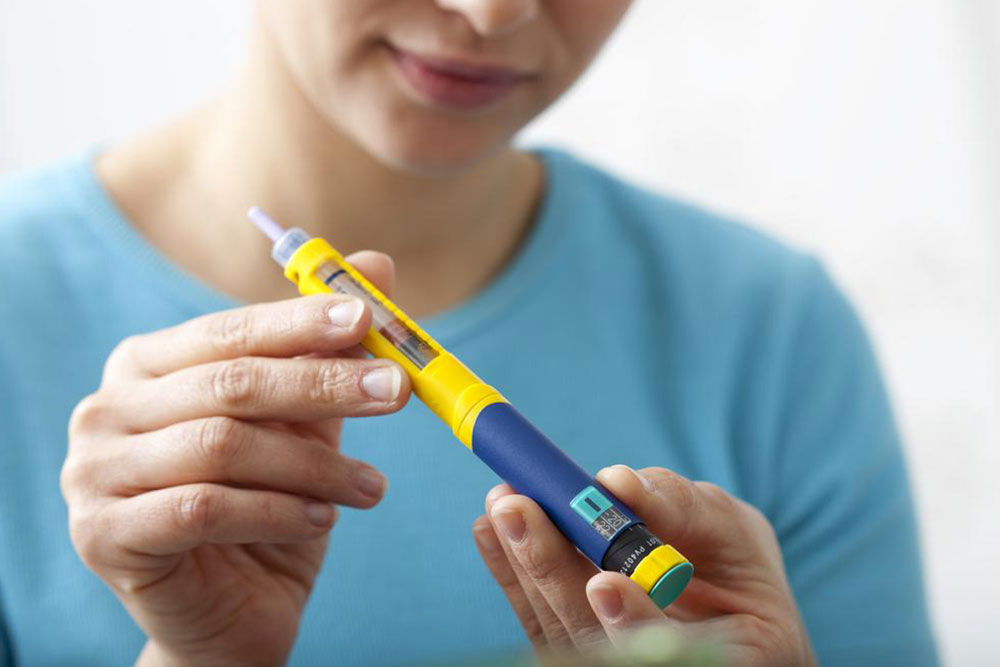
Attach a new sterile needle, ensuring it is securely fastened to prevent leaks
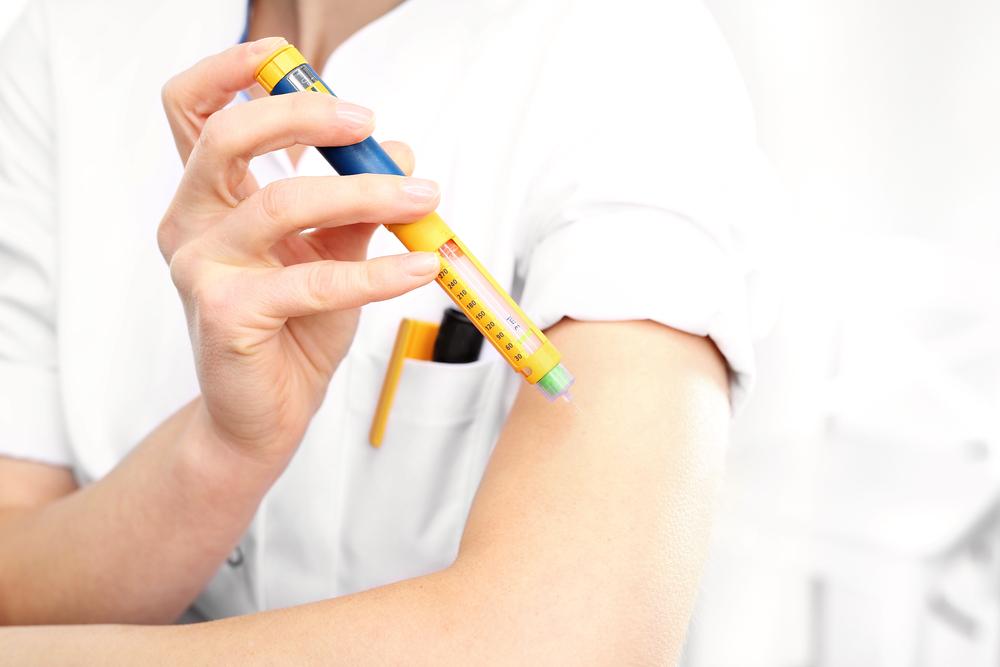
Turn the dose selector to the prescribed units, ensuring accuracy by double-checking the displayed measurement
Select an appropriate injection site—common locations include the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm—and rotate sites regularly to prevent lipohypertrophy (lumps or swelling under the skin)
Hold the pen at a 90-degree angle to the skin and insert the needle fully
Inject the insulin steadily and hold the needle in place for about 10 seconds to ensure the full dose is delivered—this prevents insulin leakage
Carefully remove the needle and dispose of it safely in a designated sharps container
In case of over-dialing, some pens allow for correction by expelling the excess insulin or resetting the dose according to manufacturer instructions. Always avoid injecting into bruised, sore, or inflamed skin areas, as this can affect absorption. Regularly monitor your blood glucose levels after injections to ensure dose accuracy and effectiveness.
Risks, Precautions, and Best Practices
Using insulin pens correctly is critical for effective diabetes management. Incorrect dosing can lead to hypoglycemia (dangerously low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), both of which can have serious health consequences. Closely monitor your blood glucose levels following insulin injections to ensure appropriate responses.
Maintaining proper hygiene and handling is essential to prevent infections. Always use a new needle for every injection, and clean the pen’s top with alcohol before use. Be cautious when storing and handling insulin pens; avoid exposure to extreme temperatures and keep the pens away from children and pets.
If you experience issues such as difficulty in administering the correct dose, or if you notice that insulin is not working as expected, consult your healthcare provider promptly. Regular check-ups and education about insulin therapy improve safety and effectiveness.
In summary, insulin pens are a modern, patient-friendly device that simplifies diabetes management. By choosing the appropriate type, handling it properly, and adhering to medical advice, diabetics can maintain better control over their condition and improve their quality of life.