Understanding Medical Causes of Severe Hair Loss and Effective Solutions
This comprehensive article explores common medical causes of severe hair loss, including genetic factors, autoimmune disorders, hormonal imbalances, and stress-related conditions. It discusses symptoms, underlying mechanisms, and a wide range of effective treatment options to help those affected. Early diagnosis and professional intervention are key to managing hair thinning issues effectively, restoring hair health, and improving well-being. Whether dealing with hereditary baldness or autoimmune-related hair loss, understanding these conditions empowers individuals to seek appropriate solutions and regain confidence in their appearance.
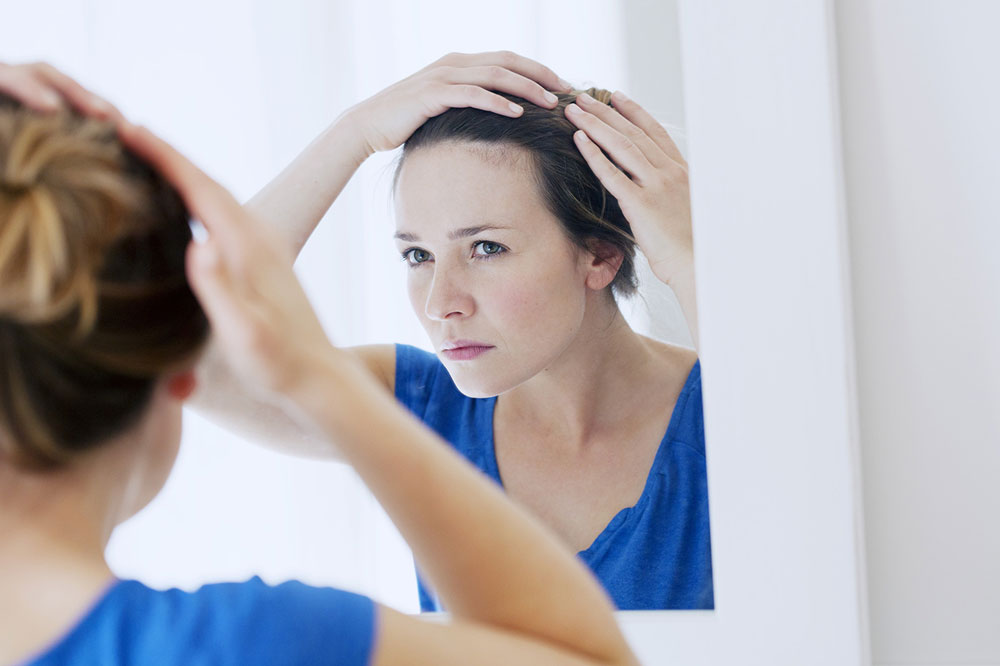

Hair health is an important aspect of overall well-being and self-esteem. Under normal circumstances, hair naturally cycles through shedding and renewal processes, with small amounts falling out daily to make room for new growth. However, when hair loss becomes excessive or sudden, it often signals underlying health problems that demand medical attention. Recognizing these causes is crucial for effective treatment and regaining healthy hair. From hormonal imbalances to autoimmune conditions, several medical issues can lead to significant hair thinning or baldness. This comprehensive guide explores common medical conditions associated with severe hair loss and discusses potential treatments and management strategies for each.
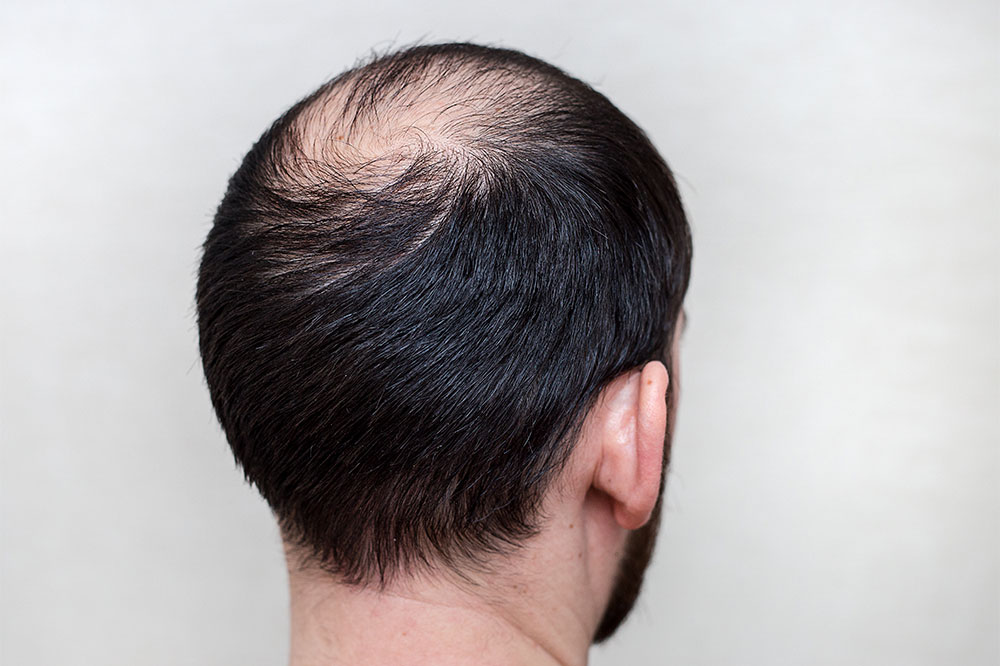
Genetic Hair Loss: Androgenetic Alopecia
One of the most common reasons for hair loss worldwide is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. This condition is hereditary and typically manifests after puberty. In men, it often begins with a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, progressing gradually over years. Women usually experience a diffuse thinning across the entire scalp, especially around the part line. The hormonal component, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), plays a significant role by shrinking hair follicles and shortening the hair growth phase. Post-menopausal hormonal changes can worsen this condition in women, leading to increased hair loss during aging. Understanding its genetic basis helps in exploring targeted treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, or hair transplant procedures.
Telogen Effluvium: The Stress-Related Hair Thinning
Telogen effluvium is characterized by a sudden and diffuse shedding of hair, often triggered by physical or emotional stressors. It occurs when an abnormal number of hair follicles prematurely enter the resting (telogen) phase, leading to noticeable hair thinning within months. Common triggers include severe illness, significant stress, major surgeries, childbirth, sudden weight loss, or certain medications. While this condition is typically reversible once the stressors are addressed, persistent or severe cases may result in more prominent hair thinning or patchy baldness. Managing underlying triggers is essential for recovery, and consults with healthcare providers can help develop appropriate treatment plans.
Autoimmune Disorders and Hair Loss: Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss. This condition can affect people of all ages, and it often appears suddenly as round or oval bald patches on the scalp, face, or other parts of the body. It is hereditary in some cases, but environmental and immune factors also contribute. While some individuals experience spontaneous hair regrowth, others may develop ongoing or recurrent hair loss. Treatments include corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy, and other immune-modulating therapies to help hair regrowth. Support groups and psychological counseling can also be beneficial to cope with the emotional impact of hair loss.
Thyroid Disorders: Hyperthyroidism and Hair Health
The thyroid gland regulates various metabolic processes, including hair growth. Both hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) significantly influence hair health. Hyperthyroidism causes rapid metabolism, which can result in brittle, thinning hair, and even hair loss in some cases. Conversely, hypothyroidism often leads to dry, coarse, and thinning hair due to slowed metabolic functions and disrupted hair growth cycles. Untreated thyroid issues not only impair hair health but can also cause fatigue, weight changes, mood disorders, and other serious health problems. Accurate diagnosis through blood tests, and appropriate hormone regulation treatments, are critical for managing these conditions and improving hair vitality.
In conclusion, addressing severe hair loss caused by medical conditions requires a comprehensive approach involving proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. If you experience sudden or persistent hair thinning, consulting healthcare professionals—dermatologists, endocrinologists, or trichologists—is essential. Early intervention can improve outcomes, restore hair health, and enhance overall quality of life. Modern medical advances continue to provide new hope for individuals struggling with hair loss due to underlying health issues, emphasizing the importance of professional care in managing this complex condition.