Comprehensive Guide to Male Hair Thinning: Causes, Stages, Detection, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive article explores male hair thinning, detailing its causes, stages, diagnosis, and effective prevention strategies. Understanding these aspects can help men take timely actions to maintain healthy hair and prevent extensive baldness. It emphasizes early intervention and professional consultation to manage this common condition effectively.
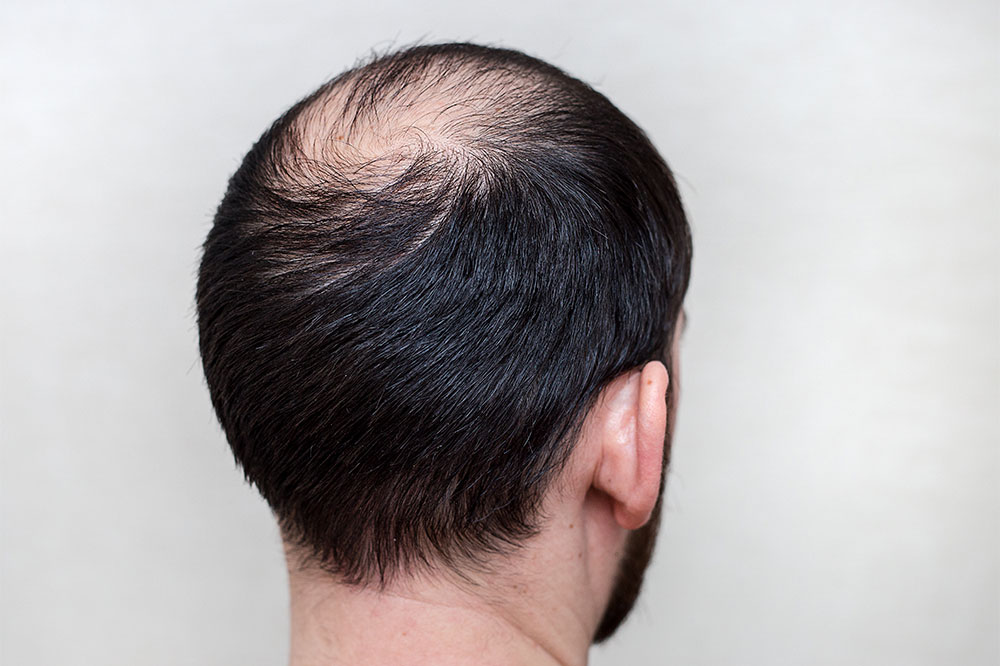
Comprehensive Guide to Male Hair Thinning: Causes, Stages, Detection, and Prevention Strategies
Hair plays a vital role in defining an individual's appearance, confidence, and overall health. Covering most areas of the human body, hair is primarily made up of keratin, a durable protein produced within hair follicles. Human scalp usually hosts approximately 100,000 to 150,000 hairs, and it's normal to shed around 100 hairs daily as part of the natural hair cycle. However, when shedding becomes excessive, it signals potential underlying health or genetic issues that need attention. Male hair thinning, also known as male pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia, is among the most common hair loss conditions affecting men worldwide.
Understanding the progression of male hair thinning involves recognizing its various stages, which can help in identifying the condition early and taking appropriate preventive or therapeutic measures. This comprehensive guide explores the causes behind male hair thinning, the different stages of hair loss progression based on established classification systems, methods for diagnosing the condition, and effective prevention and treatment strategies to maintain a healthy scalp and hairline.
Progression and Stages of Male Hair Loss
Hair loss, scientifically termed alopecia, exhibits a wide range of severity and onset times among men. The Norwood Scale, a clinically recognized classification system, segments male pattern baldness into seven distinct stages, illustrating the progressive nature of hair loss from minimal recession to extensive baldness. Factors impacting these stages include genetic predisposition, hormonal changes, lifestyle choices, overall health conditions, and environmental influences.
Stage 1
No visible hair loss; hairline appears intact and normal.
Stage 2
Slight recession begins around the temples, giving the hairline a more mature look.
Stage 3
Noticeable hairline recession forming an M, U, or V shape; moderate thinning appears at the crown.
Stage 4
Significant hair loss occurs at the crown area with receding temples; hair connecting the sides reduces significantly.
Stage 5
The bald areas at the crown and sides expand, leaving a narrow band of remaining hair.
Stage 6
The connecting band of hair disappears, merging balding regions on the crown and temples.
Stage 7
The most advanced stage—only a thin band of hair persists around the sides and back of the scalp, with extensive baldness covering the top of the scalp.
Diagnostic Methods for Hair Loss
Blood Tests
Detect underlying medical issues such as thyroid disorders, hormonal imbalances, or deficiencies that may contribute to hair thinning.
Pull Test
Gentle tugging strands of hair to assess their shedding rate, providing clues about active hair loss phases.
Scalp Biopsy
Removing small samples of scalp tissue to examine hair follicle health and detect inflammation or other scalp conditions.
Microscopic Examination
Analyzing hair and scalp samples under a microscope to study hair root structure and identify potential causes of shedding.
Effective Prevention and Management Strategies
Preventing or delaying male pattern baldness involves early lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions. Basic steps include avoiding hot showers that can weaken hair follicles, using gentle and nourishing hair care products, and minimizing stress through relaxation techniques. Regular scalp massages can enhance blood circulation, encouraging healthier hair growth. For more advanced prevention or treatment, options such as hair transplants—where hair follicles are moved from dense areas to balding spots—or laser therapy devices that stimulate hair growth are recommended. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol intake can further support healthy hair and scalp conditions.
Early detection and proactive management are crucial in controlling the progression of male hair thinning. Consulting with a dermatologist or trichologist can help develop personalized treatment plans that may include medications like minoxidil or finasteride, which have shown efficacy in reducing hair loss and promoting regrowth. Overall, understanding the causes, recognizing the stages, and adopting preventive measures can significantly improve the quality of life for men experiencing hair thinning or baldness.





