Understanding the Health Risks and Complications Associated with Lupus: A Comprehensive Guide
This comprehensive article explores the various health risks and complications associated with lupus, including joint, skin, digestive, and cardiovascular issues. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, ongoing monitoring, and lifestyle management to mitigate serious health threats posed by this complex autoimmune disease. Learn about symptoms, potential organ involvement, and effective strategies for managing lupus-related health risks to improve overall quality of life.

Exploring the Health Challenges and Complications of Lupus
Lupus, medically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a complex autoimmune disorder that presents with a wide spectrum of symptoms affecting multiple organs and systems within the body. Its unpredictable nature often makes diagnosis and management challenging. Understanding the potential health risks and common complications associated with lupus is crucial for early detection, effective management, and improving quality of life for affected individuals. This comprehensive guide delves into the various health risks linked to lupus, including joint, skin, digestive, cardiovascular, and endocrine system complications.
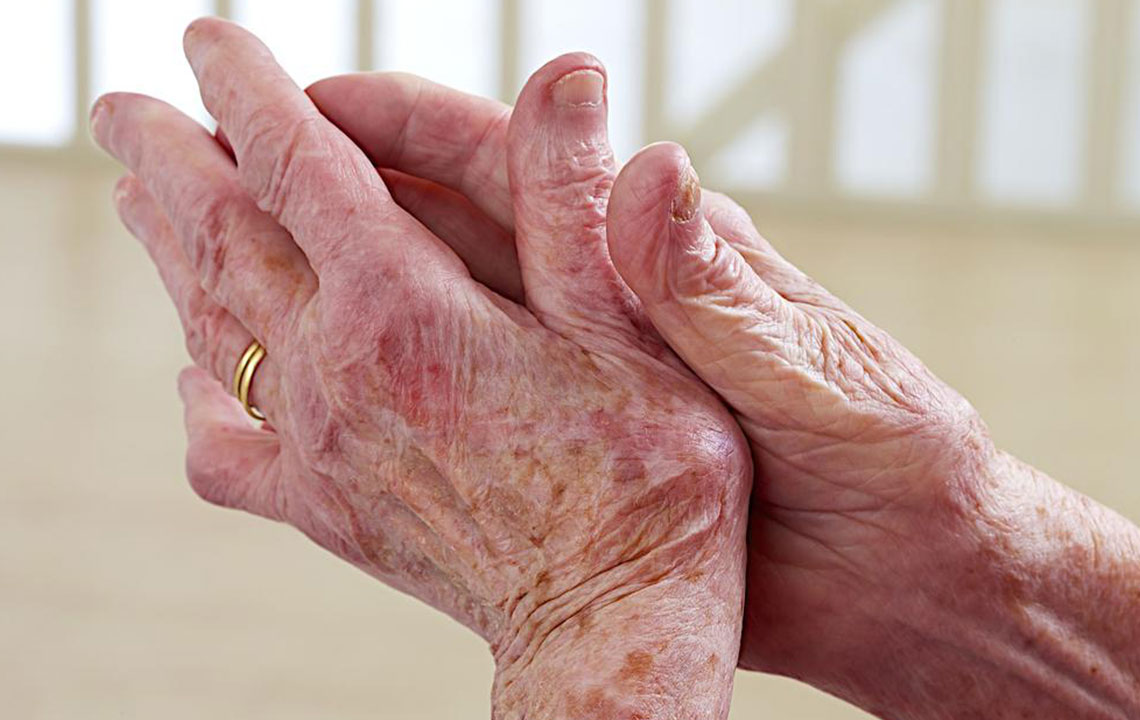
Lupus symptoms can vary significantly depending on which organs are affected. One of the most common initial manifestations involves the musculoskeletal system, particularly the small joints of the hands, wrists, and knees. These joints frequently experience pain, swelling, and morning stiffness, symptoms that may initially be mistaken for minor joint issues or conditions like osteoarthritis. However, persistent joint discomfort that does not improve with over-the-counter (OTC) medications warrants prompt consultation with a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis is vital to distinguish lupus from other rheumatologic conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis, and to initiate appropriate treatment.
Beyond joint involvement, lupus also influences the digestive system. Patients commonly report symptoms such as acid reflux, heartburn, and indigestion, which may be related to inflammation or medication side effects. Managing gastrointestinal symptoms involves lifestyle modifications, including the use of antacids, consuming smaller and more frequent meals, and avoiding lie-downs immediately after eating. Chronic gastric issues should be evaluated by healthcare providers to rule out other gastrointestinal diseases, such as peptic ulcers or GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease).
One of the more serious aspects of lupus is its ability to target vital organs, leading to potentially life-threatening complications. The liver and pancreas, for instance, can be affected, resulting in conditions like hepatitis or pancreatitis. Furthermore, lupus can cause pathological leakage of proteins from the intestines, leading to a condition known as protein-losing enteropathy or protein-losing atrophy. This condition causes patients to experience symptoms such as diarrhea, fatigue, and nutritional deficiencies due to the loss of essential proteins.
Salivary and lacrimal gland involvement are also common in lupus, often related to Sjogren’s syndrome, an autoimmune disorder frequently seen alongside lupus. Patients may experience persistent dryness of the mouth, eyes, or vaginal tissues, leading to discomfort, increased risk of infections, and difficulties in swallowing or sexual activity. Recognizing these symptoms early helps in tailoring treatment strategies to alleviate dryness and prevent secondary infections.
Furthermore, lupus increases susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disorders, which can significantly impact metabolic health. Hypothyroidism, caused by autoimmune destruction of the thyroid gland, results in decreased metabolism, leading to fatigue, weight gain, depression, and cold intolerance. Conversely, hyperthyroidism can cause an elevated metabolism, manifesting as rapid heartbeat, weight loss, heat intolerance, and excessive sweating. Both conditions require careful management, as they can exacerbate overall health deterioration if left untreated.
Cardiovascular complications constitute some of the most serious health risks associated with lupus. Patients are at heightened risk for conditions such as pericarditis, which involves inflammation of the lining around the heart, causing chest pain and shortness of breath. Additionally, many individuals with lupus develop antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), an autoimmune disorder characterized by abnormal blood clot formation. APS significantly elevates the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis, strokes, miscarriages, and pulmonary embolism. Blood clots resulting from APS can travel (embolize), leading to critical events like heart attacks, strokes, or limb ischemia, which may necessitate amputations in severe cases.
Given these risks, regular cardiovascular monitoring and blood tests are essential for lupus patients. Preventive strategies include anticoagulant therapy, lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation, maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Early recognition and treatment of cardiovascular issues dramatically improve outcomes and reduce the risk of fatal events.
Another vital aspect of lupus-related health complications is its impact on blood and immune system function. Patients often develop hematological abnormalities such as anemia, leukopenia, or thrombocytopenia, which can compromise immune defenses and increase infection risks. Additionally, chronic inflammation can lead to a heightened risk of developing certain cancers, underscoring the importance of ongoing medical surveillance.
In conclusion, lupus is a multifaceted autoimmune disease with the potential to cause diverse and severe health complications. From joint pain and skin rashes to life-threatening cardiovascular and organ-specific issues, understanding these risks is key to effective disease management. Patients should work closely with healthcare providers to monitor symptoms, undergo regular screenings, and adopt lifestyle changes aimed at minimizing complications. A comprehensive approach to lupus care can enhance quality of life and reduce the long-term impact of this complex disease.
Managing lupus requires awareness of its myriad health risks and proactive intervention. Early diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and regular health assessments are essential for minimizing complications and ensuring better health outcomes. If you or someone you know is living with lupus, seek expert medical advice and adopt strategies to safeguard your health today.