Comprehensive Guide to Aging Gracefully and Maintaining Health in Later Years
Aging gracefully requires proactive health management. This comprehensive guide emphasizes regular exercise, balanced nutrition, routine screenings, and lifestyle choices to maintain physical and cognitive health. Understanding age-related body changes helps tailor preventive strategies, ensuring a comfortable and active life in later years. Engage in cardiovascular, mental, and physical activities, manage diet meticulously, and avoid harmful habits to optimize aging and enjoy independence for years to come.

Comprehensive Strategies for Aging Gracefully and Staying Healthy in Your Golden Years
As individuals grow older, many face concerns related to declining health, physical endurance, and cognitive functions. However, with proactive and strategic preparations, aging can be a smoother, more comfortable process. The secret to maintaining vitality and independence in later years lies in adopting a holistic approach to health early on. This involves a combination of regular physical activity, proper nutrition, routine health screenings, and lifestyle choices that promote overall well-being. By understanding how aging affects different bodily systems, you can implement preventive measures that help mitigate age-related health issues and enhance quality of life in your senior years.
Awareness of which body parts and systems slow down with age enables tailored preventive care. Recognizing these changes allows for targeted strategies that support healthy aging.
Heart and Circulatory System
With age, blood vessels can stiffen, and the heart's muscle mass may decrease, making it work harder to pump blood efficiently. This increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, heart attack, and stroke. Engaging in regular cardiovascular exercises like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming strengthens the heart, improves blood circulation, and helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels. Additionally, managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding excessive salt intake are crucial for cardiovascular health.
Brain Function and Cognitive Health
Age-related cognitive decline is common but can be slowed significantly through mental activities and a healthy lifestyle. Memory lapses, slower processing speeds, and difficulty concentrating are typical signs, but staying mentally active through puzzles, reading, learning new skills, or social interactions can help preserve cognitive functions. Maintaining friends and social networks also combats loneliness and depression, which are linked to cognitive decline. Proper sleep hygiene and managing chronic conditions like hypertension and diabetes are vital for brain health.
Digestive System
The digestive tract tends to become less efficient with age, causing issues such as indigestion, constipation, and reduced nutrient absorption. Incorporating high-fiber foods—fruits, vegetables, whole grains—into daily diets supports digestive health. Staying well-hydrated and limiting processed foods, sugary snacks, and excessive fatty foods further aids digestion. Regular physical activity stimulates bowel movements, reducing constipation risks. Consulting healthcare providers for personalized nutritional advice is also recommended.
Urinary System
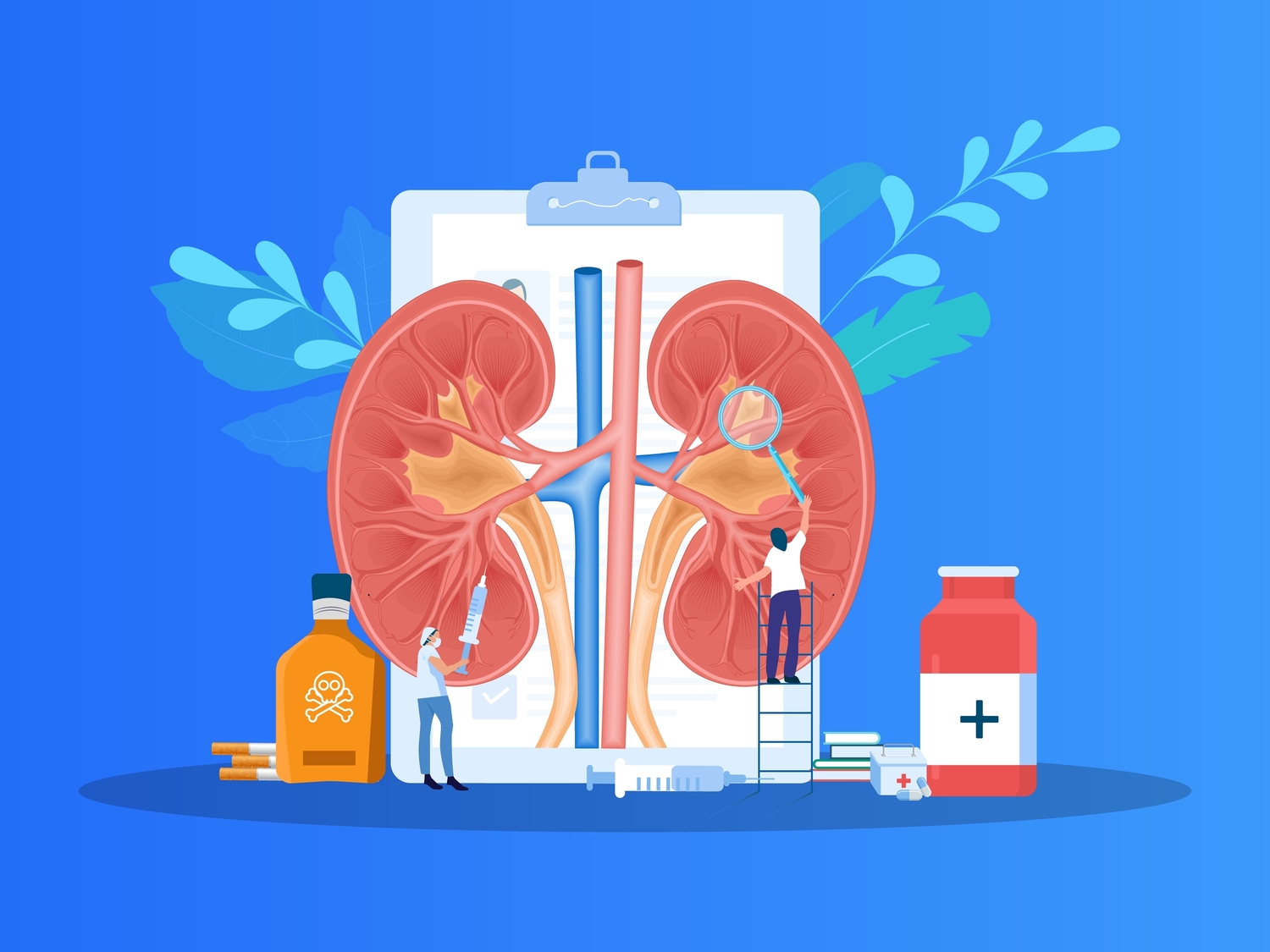
As we age, the bladder's elasticity decreases, often leading to symptoms like frequent urination, urgency, or incontinence. Pelvic floor exercises, such as Kegels, can strengthen muscles supporting the bladder. Staying hydrated but avoiding excessive fluid intake before bedtime helps manage urinary symptoms. Monitoring and controlling conditions like diabetes and urinary infections are essential, and seeking medical advice for persistent issues ensures proper management.
Sensory Organs
Vision, hearing, and smell tend to decline with age, impacting safety and daily activities. Protecting eyesight by wearing UV-protective sunglasses and regular eye exams helps detect issues like cataracts or macular degeneration early. Hearing loss can be mitigated through regular hearing assessments and using assistive devices if needed. Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding exposure to loud noises also preserves sensory functions. Addressing sensory impairments promptly can significantly enhance quality of life and safety.
To optimize aging healthily, it is crucial to incorporate habits that support these systems. Regular physical activity tailored to individual capacity—such as walking, swimming, yoga, or light jogging—boosts overall strength, flexibility, and cardiovascular health. Routine health screenings are vital, especially after 40 years of age, to identify and address emerging health issues early. A nutritious diet that emphasizes fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains ensures vital nutrient intake, while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive alcohol minimizes health risks. Avoiding smoking altogether and moderating alcohol consumption further contributes to longevity and well-being in old age.