Maximizing Elderly Health: The Vital Role of Magnesium for Senior Wellbeing
This comprehensive article highlights the essential role of magnesium in promoting overall health in seniors. It covers dietary sources, the importance of supplementation, and the numerous health benefits including bone, cognitive, sleep, and inflammation support. Ensuring adequate magnesium intake can significantly improve quality of life for aging populations, addressing common deficiencies and age-related health concerns. Proper guidance from healthcare professionals is emphasized to maximize benefits and ensure safety when using supplements. A must-read for seniors and caregivers focused on health and wellness.

The Essential Mineral Magnesium and Its Impact on Aging Health
Magnesium is an indispensable mineral that plays a critical role in supporting numerous bodily functions. It is involved in over 300 essential biochemical reactions within the human body, affecting everything from regulating blood pressure and strengthening bones to controlling blood sugar levels and maintaining a healthy heart rhythm. As people age, the importance of maintaining adequate magnesium levels becomes increasingly apparent. Proper magnesium intake can significantly influence the health and quality of life of seniors, helping to prevent age-related health issues and promote overall wellbeing. Achieving sufficient magnesium levels can be accomplished through diet and, when necessary, through supplementation.
Why Magnesium Is Crucial for Aging Populations
Statistics reveal that a substantial majority of seniors—approximately 70% to 80%—fail to meet the recommended daily intake of magnesium. This deficiency can lead to a host of symptoms including persistent fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, muscle cramps, and overall muscular weakness. Individuals with compromised immune systems are particularly vulnerable to magnesium deficiency, which can further exacerbate health challenges associated with aging. Ensuring adequate magnesium intake is essential not only for physical health but also for enhancing energy levels, cognitive function, and emotional wellbeing among older adults.
Sources of Essential Magnesium for the Elderly
1. Nutrient-Dense Foods for Magnesium Intake
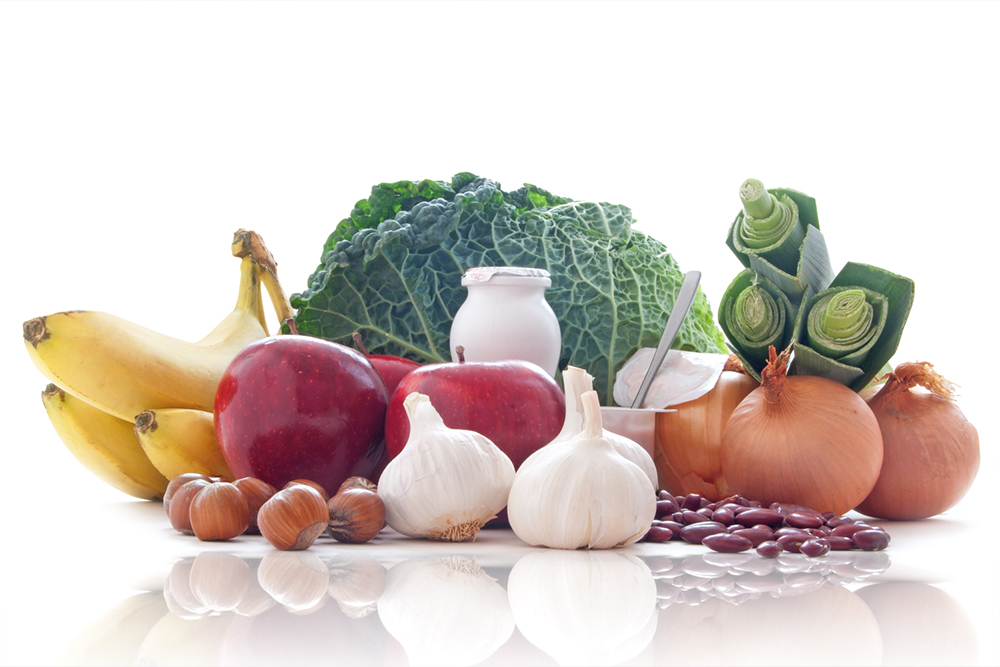
Incorporating a variety of magnesium-rich foods into daily diets is an effective way to prevent deficiencies and support bodily functions. Foods such as pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, leafy greens like spinach, almonds, cashews, black beans, edamame, and peanut butter provide high levels of magnesium. Whole grains like brown rice and oats, as well as fatty fish such as salmon and halibut, are also excellent sources. Avocados add healthy fats and magnesium, making them a nutritious choice for seniors aiming to boost their intake. Regular consumption of these foods can significantly improve magnesium levels naturally, contributing to a range of health benefits.
2. The Role of Dietary Supplements
As the body’s ability to absorb magnesium declines with age, dietary supplementation becomes an essential component of maintaining optimal magnesium levels. Supplements come in various forms, including glycinate, citrate, orotate, and carbonate. These are readily available on the market and typically exhibit good absorption rates. However, it is crucial for seniors to seek advice from healthcare professionals before starting any supplement regimen, particularly if they have underlying health conditions or take medications that may interact with magnesium supplements. Proper guidance ensures safe and effective supplementation tailored to individual needs.
Maintaining adequate magnesium intake supports vital processes such as energy production, protein synthesis, and muscle health. A deficiency can lead to various health problems, whereas proper supplementation can mitigate these issues. Overconsumption, however, can be harmful; hence, professional consultation is vital to determine appropriate dosages suited for seniors. Supplements should complement a balanced diet to optimize benefits without adverse effects.
Benefits of Magnesium Supplements for Seniors
Magnesium acts as a cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions, influencing energy metabolism, nerve transmission, muscle function, and overall cellular health. For older adults, supplementing with magnesium can offer a multitude of health advantages:
1. Promoting Bone Health and Nerve Function
Magnesium facilitates the activation of vitamin D, crucial for calcium absorption, which is vital for maintaining strong, healthy bones. It also helps alleviate muscle cramps and supports nerve health, reducing discomfort and promoting better mobility in seniors.
2. Supporting Cognitive and Brain Health
As cognitive decline is a common concern with aging, magnesium’s role in supporting nerve signal transmission becomes particularly important. Adequate magnesium levels have been linked to improved memory, cognitive function, and may help delay the progression of dementia. Furthermore, magnesium can positively influence mood, reducing anxiety and feelings of depression among seniors.
3. Mitigating Migraine Symptoms
Many individuals experience migraines that are exacerbated by magnesium deficiency. Supplementing magnesium or consuming magnesium-rich foods can decrease the frequency and severity of migraines, offering relief to affected seniors.
4. Enhancing Sleep Quality
Magnesium plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmitters like GABA, which are essential for restful sleep. Deficiency can lead to sleep disturbances, increased stress, and difficulty relaxing. Supplementing magnesium has been shown to reduce the time it takes to fall asleep and improve overall sleep quality, especially in older adults with sleep issues.
5. Supporting Physical Activity and Recovery
During physical exertion, magnesium levels naturally increase to support muscle recovery, reduce fatigue, and enhance strength. Supplementation can be highly beneficial for seniors leading active lifestyles, helping maintain mobility, stamina, and overall physical health.
6. Reducing Chronic Inflammation
Low magnesium levels are associated with elevated markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP). Chronic inflammation contributes to numerous age-related diseases. Magnesium supplements may help lower inflammation, potentially reducing the risk or severity of chronic illnesses.