Comprehensive Guide to Eliminating Skin Parasites Effectively
This comprehensive guide offers effective strategies to eliminate skin parasites like mites with medical treatments, natural remedies, and preventive hygiene tips. Learn how to recognize symptoms, choose proper treatments, and maintain skin health for a parasite-free life. Essential for those experiencing persistent skin discomfort or looking to protect themselves from infestations, this article emphasizes safety, hygiene, and professional consultation as key to successful eradication.
Comprehensive Strategies for Eliminating Skin Parasites and Protecting Your Skin Health
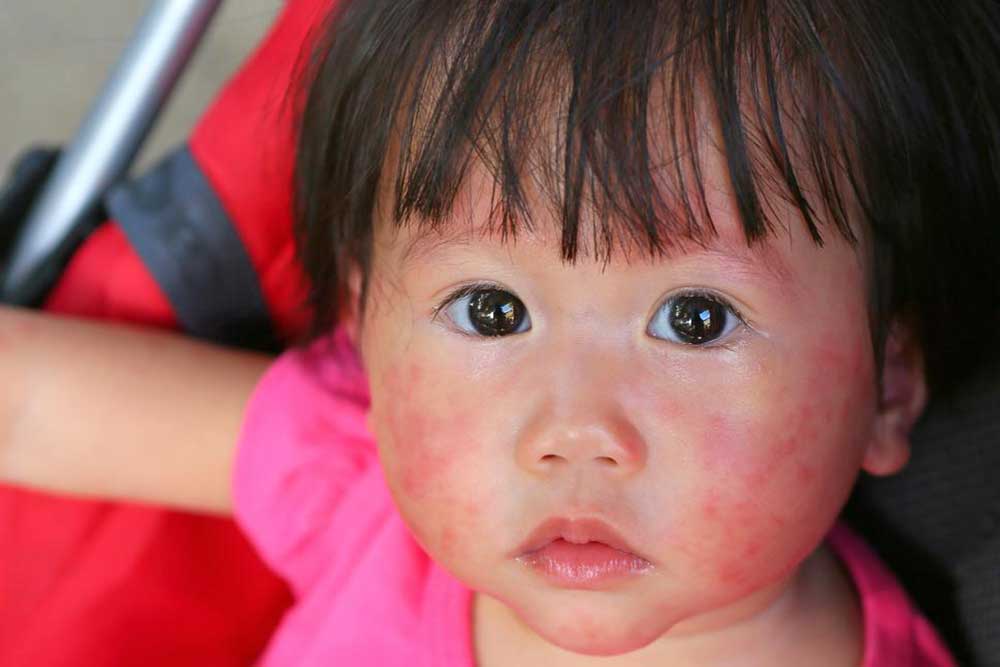
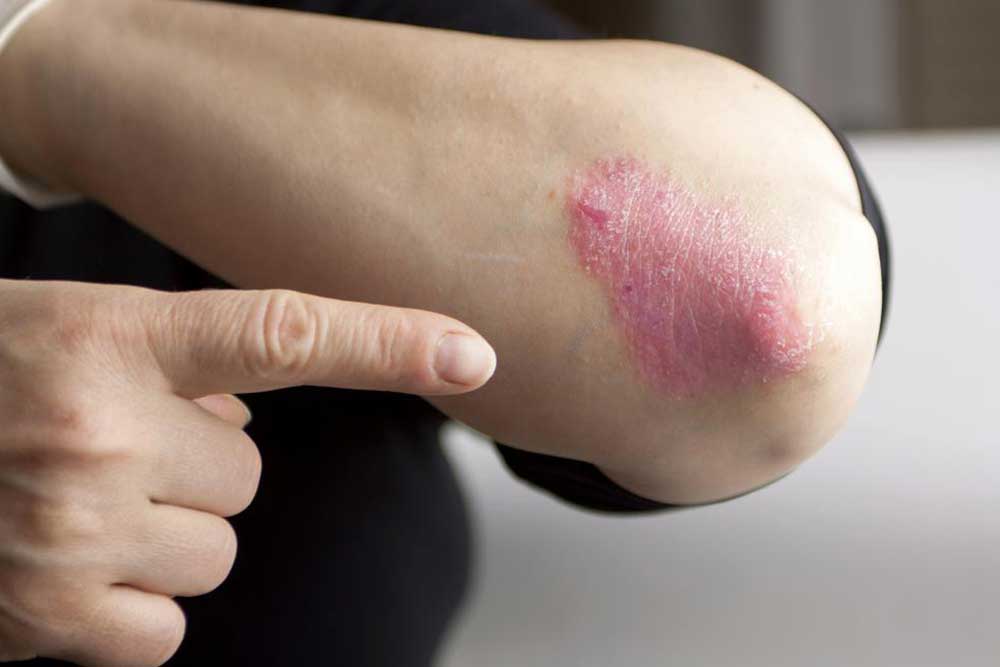
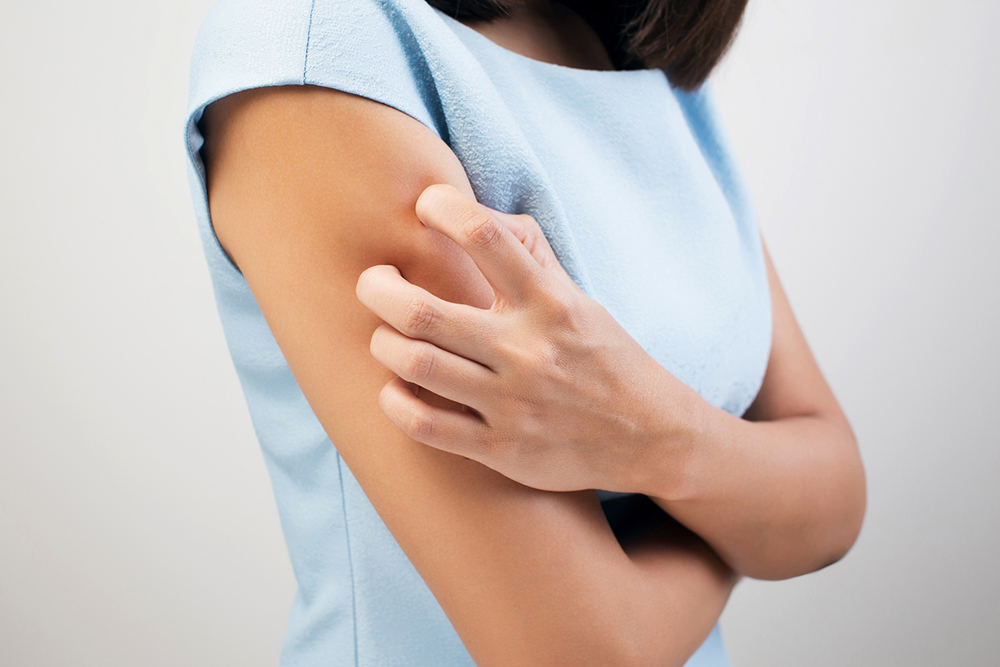
Skin parasites, including various mites, are microscopic creatures that can invade the skin of humans and cause a range of dermatological issues if not treated promptly and properly. Among these, Demodex mites and Sarcoptes scabiei are among the most notorious, capable of embedding, biting, or burrowing into the skin tissue. These infestations can lead to conditions such as demodicosis—caused by Demodex—and scabies, which is caused by Sarcoptes scabiei. Recognizing the symptoms early and understanding the cure options are essential steps toward effective management to prevent long-term skin damage or discomfort. Common symptoms of skin parasite infestations include persistent burning sensations, intense itching, redness, swelling, and noticeable changes in the texture of the skin, often accompanied by a rash or bumps. Consulting a healthcare professional early on is vital to obtain a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan, ensuring that infestations are eradicated safely and effectively.
Standard Treatment Methods for Skin Parasites
Most individuals coexist peacefully with tiny mites on their skin without developing symptoms, owing to a healthy immune system and natural defenses. However, when the immune system is compromised or hygiene practices are inadequate, these parasites can multiply rapidly, leading to uncomfortable or even dangerous skin conditions. When symptoms manifest or worsen, medical intervention becomes necessary. The primary treatments include topical applications—such as prescribed creams and gels—along with medicated washes that contain active ingredients capable of killing or removing mites. These treatments usually involve compounds such as permethrin, crotamiton, or ivermectin. In severe cases, oral medications might be prescribed by healthcare providers to control the infestation from within. The goal of these treatments is to eliminate the parasites, reduce inflammation, and promote skin healing, all while minimizing the risk of reinfestation.
In addition to medical treatments, adopting effective preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of infection and reinfestation. For skin mites that predominantly dwell on the face, ears, or eyelashes, maintaining strict hygiene routines is essential. Daily washing of hair, eyelashes, and face with mild, sulfate-free shampoos can keep mite populations in check. Avoiding oily or greasy skincare products that can provide a favorable environment for mites is recommended. Regular exfoliation helps remove debris and potential mites from the skin surface, while resisting the urge to scratch minimizes skin irritation and prevents secondary infections. Ensuring that personal hygiene items such as towels, bedding, and pillowcases are washed frequently—preferably in hot water—can decrease the chance of mites spreading within the household. Good hygiene is a cornerstone of prevention.
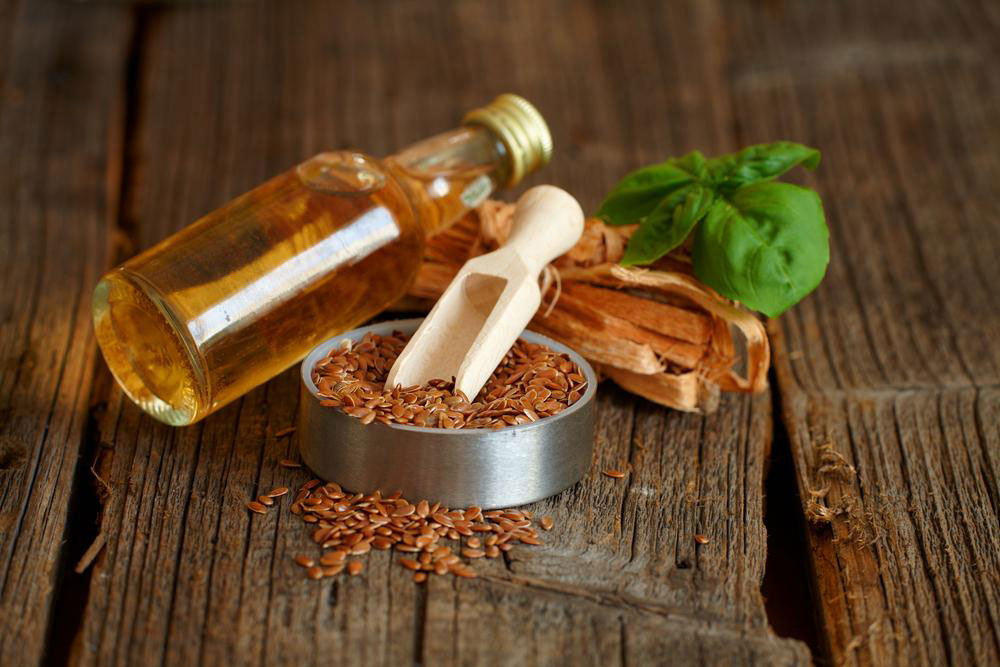
Natural remedies have gained popularity for managing mite infestations owing to their soothing properties and minimal side effects. Oatmeal baths, for example, can provide relief from itching and help reduce inflammation caused by mites. Essential oils such as tea tree oil, neem oil, and clove oil have antimicrobial and antiparasitic properties, making them effective adjuncts in treatment regimens—applied topically in diluted form. Aloe vera gel offers soothing relief for irritated skin, while cayenne pepper and cold compresses can also ease discomfort. It's advisable to avoid harsh soaps and chemical irritants, as they can exacerbate skin sensitivity and prolong recovery. Combining these remedies with good hygiene practices can help manage symptoms and contribute to the eventual eradication of skin mites.
To further prevent the spread of mites, regular laundering of clothes, bedding, and towels in hot water (at least 130°F or 54°C) is highly effective. Vacuuming upholstery, carpets, and mattress seams can remove mites and their eggs from surfaces. Ensuring that all household members are included in treatment plans—even those without visible symptoms—is crucial to preventing reinfestation. If symptoms persist despite the use of home remedies and preventive measures, seeking professional medical advice is essential. Healthcare providers can perform skin scrapings, microscopic examinations, and prescribe stronger, more targeted treatments if necessary. Adhering to prescribed therapies and preventive hygiene practices can help you regain healthy, parasite-free skin and prevent long-term complications caused by these microscopic invaders.