Comprehensive Guide to Managing Urticaria: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention Strategies
This comprehensive guide delves into urticaria, explaining its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of identifying triggers, using appropriate medications, and adopting lifestyle changes like stress reduction. The article also covers advanced treatments for persistent cases and provides practical advice for relief. Perfect for those seeking to understand and control this common skin condition, the guide aims to improve quality of life through awareness and proactive care.

Understanding Urticaria: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Urticaria, more commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of red, itchy, swollen bumps or welts on the surface of the skin. These lesions are often transient, typically lasting anywhere from six to twelve hours, though they can sometimes persist longer if untreated. The appearance of these bumps can vary greatly—they may be small or large, round or irregular, and can appear anywhere on the body. The condition is a common dermatological issue that affects individuals of all ages, from children to adults, and can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life if not managed properly.
Hives are primarily caused by an allergic response, though in many cases, the exact trigger remains elusive. When the body encounters an allergen—such as certain foods, medications, insect bites, or environmental factors—it triggers the immune system to release histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream. This release causes the blood vessels in the skin to expand and become more permeable, resulting in fluid accumulation that manifests as swelling and redness. Identifying the specific triggers is fundamental to preventing future outbreaks and managing the symptoms effectively.
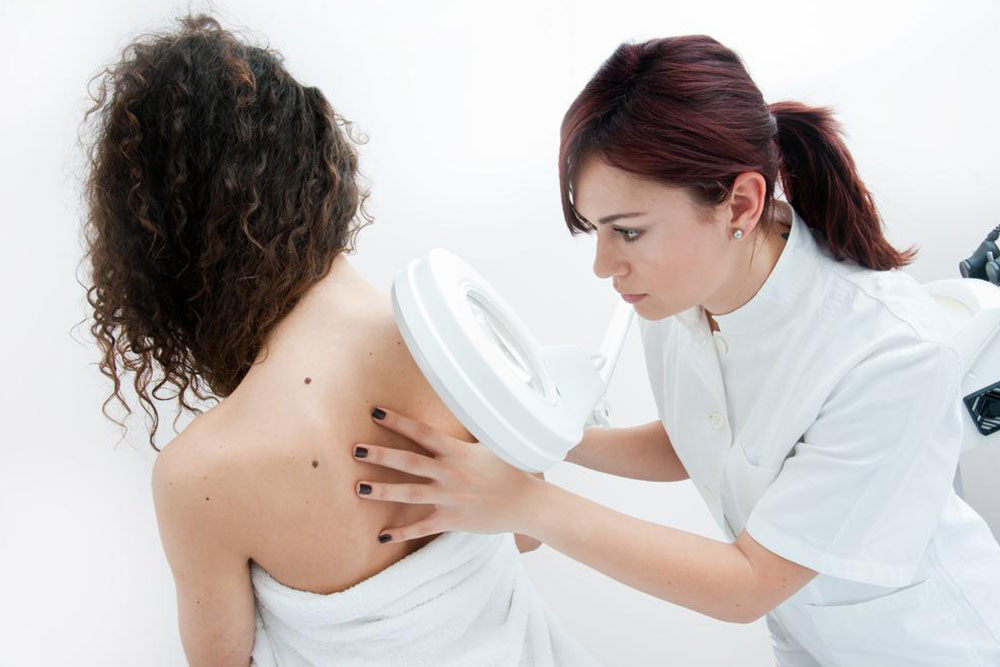
While allergic reactions are a common cause, other factors can also contribute to the development of urticaria. These include stress, infections, exposure to extreme temperatures, or even certain chronic medical conditions. Stress, in particular, has been shown to exacerbate the severity and frequency of hives, as it can influence immune system activity. Furthermore, some cases are idiopathic, meaning no identifiable cause can be found despite extensive testing. That’s why a thorough evaluation powered by medical professionals is critical for tailored treatment plans.
Treatment and Management of Urticaria: Strategies and Recommendations
Managing urticarial symptoms effectively involves a combination of identifying and avoiding triggers, administering appropriate medication, and adopting lifestyle changes. The first step in treatment is conducting a thorough allergen assessment, often with the help of an allergist or dermatologist. Once a trigger is identified—such as certain foods like shellfish, nuts, or eggs; medications; or environmental factors—patients should make every effort to minimize contact with these substances. For mild cases, simple measures like cold compresses or baths can provide relief by constricting blood vessels and reducing swelling. Cold water helps soothe itching and can diminish the histamine response.
Topical treatments also play a significant role in alleviating the discomfort caused by hives. Over-the-counter antihistamine creams or corticosteroid ointments can temporarily reduce inflammation and soothe irritated skin. For more persistent or severe cases, oral antihistamines such as loratadine or cetirizine are often prescribed by healthcare providers to block histamine's effects throughout the body. These medications usually provide fast relief and help decrease both itchiness and swelling.
Management extends beyond medications. Stress reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises are highly recommended since stress can trigger or worsen urticarial episodes. Keeping a detailed diary that records daily food intake, environmental exposures, and symptom occurrences can help identify hidden triggers that might not be immediately obvious.
In cases where hives last longer than six weeks—classified as chronic urticaria—or if they are particularly severe or recurrent, seeing a specialist is crucial. Dermatologists may recommend additional tests to uncover underlying causes or coexisting conditions, such as autoimmune diseases. Advanced treatments may include immunotherapy or biologic agents, which target specific immune pathways involved in allergic reactions. Ultimately, a comprehensive approach that combines trigger avoidance, medication, and lifestyle modifications offers the best outcomes for managing urticaria effectively.
Persistent urticaria can significantly impact an individual's emotional and psychological well-being, making it important to incorporate mental health support and patient education into the treatment plan. Open communication with healthcare professionals ensures personalized care tailored to each patient's unique circumstances and needs.
In summary, urticaria is a manageable condition when proper identification of triggers and appropriate treatments are employed. While minor cases may resolve naturally, chronic or severe instances often require medical intervention and lifestyle adjustments. Being proactive and attentive to bodily changes, along with seeking professional help when necessary, can lead to effective management and improved quality of life.