Comprehensive Guide to Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus: Causes, Treatments, and Management Strategies
This comprehensive article offers in-depth insights into rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, exploring their causes, symptoms, advanced treatment options, and management strategies. It emphasizes early diagnosis and lifestyle modifications to improve patient outcomes. With ongoing research leading to innovative therapies, individuals can now take proactive steps toward controlling these chronic autoimmune diseases and maintaining a good quality of life.

Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus: Causes, Treatments, and Management Strategies
Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (commonly known as lupus) are complex, chronic conditions that affect millions worldwide. While these illnesses share some overlapping symptoms, they are distinct disorders that require tailored approaches to treatment and management. Despite the lack of a definitive cure, advances in medical research and personalized care strategies have enabled many patients to lead active, fulfilling lives. Gaining a thorough understanding of these diseases, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments, is essential for early diagnosis and effective management.
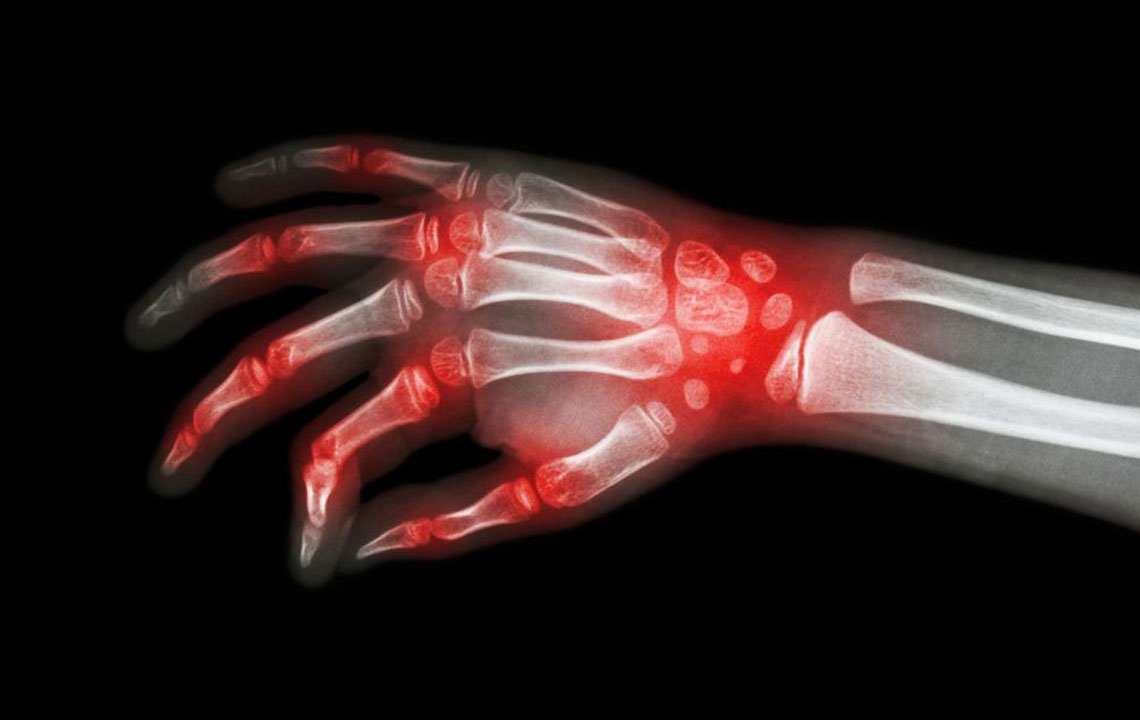
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition primarily attacking the joints, causing inflammation, pain, stiffness, and potential joint deformity if untreated. Conversely, lupus is a systemic autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs including the skin, kidneys, heart, and lungs, with symptoms that can fluctuate unpredictably. Due to their overlapping symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, and inflammation, accurate diagnosis is crucial for appropriate management.
This comprehensive guide will explore the causes of RA and lupus, available treatment options, lifestyle modifications that support disease control, and recent research aimed at uncovering their exact origins for targeted therapies. Furthermore, we will discuss how individuals can optimize their quality of life through personalized care plans, medication adherence, and healthy lifestyle habits.
Causes and Risk Factors
The precise causes of rheumatoid arthritis and lupus remain elusive. However, scientists believe that a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and hormonal factors contribute to the development of these intricate autoimmune disorders.
Genetics: Both diseases tend to run in families, suggesting that inherited genetic markers increase susceptibility. Certain genes related to immune regulation, such as the HLA (human leukocyte antigen) complex, are linked to higher risks.
Environmental Factors: External triggers such as infections, exposure to sunlight, smoking, and stress can activate immune responses in genetically predisposed individuals, leading to autoimmune attacks.
Hormonal Influences: Especially in women, hormonal fluctuations may influence disease onset or flares, explaining the higher prevalence of RA and lupus among females.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Early recognition of symptoms is vital for effective disease management. Common symptoms include persistent joint pain, swelling, fatigue, and skin rashes in lupus. RA often manifests with symmetrical joint swelling, morning stiffness lasting more than an hour, and joint deformities over time. Lupus symptoms can be highly varied, affecting the skin, joints, kidneys, and other organs, with periods of exacerbation and remission.
Diagnosis involves a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, imaging studies, and specialist assessments. Laboratory tests such as rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-CCP antibodies, ANA (antinuclear antibodies), and inflammatory markers help distinguish these conditions from other disorders.
Treatment Approaches
While there is no cure for RA or lupus, a wide array of treatments can effectively manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, prevent joint and organ damage, and improve overall quality of life.
Medications
Pharmacological treatments form the cornerstone of disease management. These include:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Help reduce pain and inflammation during flare-ups.
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): Such as methotrexate, are essential for controlling disease progression and preventing joint damage.
Biologic agents: Target specific immune pathways involved in inflammation, especially for patients unresponsive to traditional DMARDs.
Corticosteroids: Used to swiftly control severe inflammation, typically for short periods due to potential side effects.
Lifestyle Modifications
Complementing medical therapy, lifestyle changes significantly influence disease outcomes. Regular low-impact exercise, such as swimming or walking, enhances joint mobility and reduces stiffness. Maintaining a healthy weight decreases joint stress and inflammation levels. Ensuring adequate sleep, managing stress through mindfulness or therapy, and avoiding triggers like smoking or prolonged sun exposure are crucial for symptom control.
Surgical and Advanced Treatments
In severe RA cases, joint replacement surgeries might be necessary to restore function and reduce pain. For lupus with organ involvement, treatments may include plasma exchange or organ-specific therapies to prevent damage. Emerging treatments include targeted biologics and personalized medicine approaches, which promise better disease control with fewer adverse effects.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus
Effective disease management goes beyond medications. Patients are encouraged to adopt comprehensive health strategies that include:
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods such as omega-3 fatty acids, fruits, and vegetables.
Engaging in regular, moderate exercise tailored to individual capabilities.
Using stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or counseling.
Monitoring the disease regularly with healthcare providers to adjust treatments as needed.
Understanding the importance of early diagnosis and adopting a proactive approach can prevent complications and improve long-term outcomes. Support networks, patient education, and ongoing research offer hope for future therapies and better quality of life for those affected by these challenging autoimmune diseases.
In conclusion, rheumatoid arthritis and lupus require a multidisciplinary management approach combining medication, lifestyle adjustments, and regular medical care. Advances in understanding their causes and pathophysiology continue to drive innovative treatments, offering improved prognosis for patients worldwide. Empowering patients with knowledge and support remains pivotal in navigating these complex conditions effectively.