Comprehensive Guide to Identifying Insect Bites and Stings for Effective Treatment
This comprehensive guide provides detailed information on how to identify different insect bites and stings, their symptoms, treatment options, and preventive tips. Recognizing the insect responsible helps in proper treatment and avoiding serious health complications. From mosquitoes and ticks to spiders and fire ants, learn the key signs and when to seek medical help. Practical advice makes managing insect bites easier and safer, ensuring quick relief and reduced health risks. Protect yourself effectively by understanding insect behavior and bite patterns with this in-depth resource.
Insect bites and stings are common occurrences that can cause discomfort, allergic reactions, or even more serious health problems if not properly identified and treated. Being able to recognize the specific insect responsible for a bite or sting is crucial for providing appropriate first aid, preventing secondary infections, and seeking timely medical assistance when necessary. Different insects produce characteristic symptoms, bite patterns, and reactions, which can serve as clues to determine their identity. This detailed guide aims to help you understand how to distinguish between various insect bites and stings, what signs to look for, and when to consult healthcare professionals.
Why Accurate Identification Matters
Correctly identifying the insect that caused a bite or sting is vital because it influences treatment decisions. For example, a mosquito bite might only require soothing topical treatments, while a tick bite could pose the risk of Lyme disease, necessitating antibiotics. Similarly, venomous insects like bees, wasps, or certain spiders may cause severe allergic reactions that require emergency medical intervention. Proper identification also helps prevent misunderstandings about potential health risks, reducing anxiety and guiding appropriate responses.
Common Insects Responsible for Bites and Stings
Mosquitoes: Known for their itchy, swelling bites, mosquitoes are vector carriers of diseases like malaria, dengue, and Zika virus. Their bites usually appear as small, itchy bumps with surrounding redness.
Ticks: These arachnids attach themselves to the skin, often leaving a small, round, and sometimes bulls-eye-shaped rash. Ticks are notorious for transmitting Lyme disease and other illnesses.
Flies: Certain flies, like horseflies or deer flies, bite and can cause painful, swollen areas. Their bites often leave a single puncture wound and may be accompanied by itching.
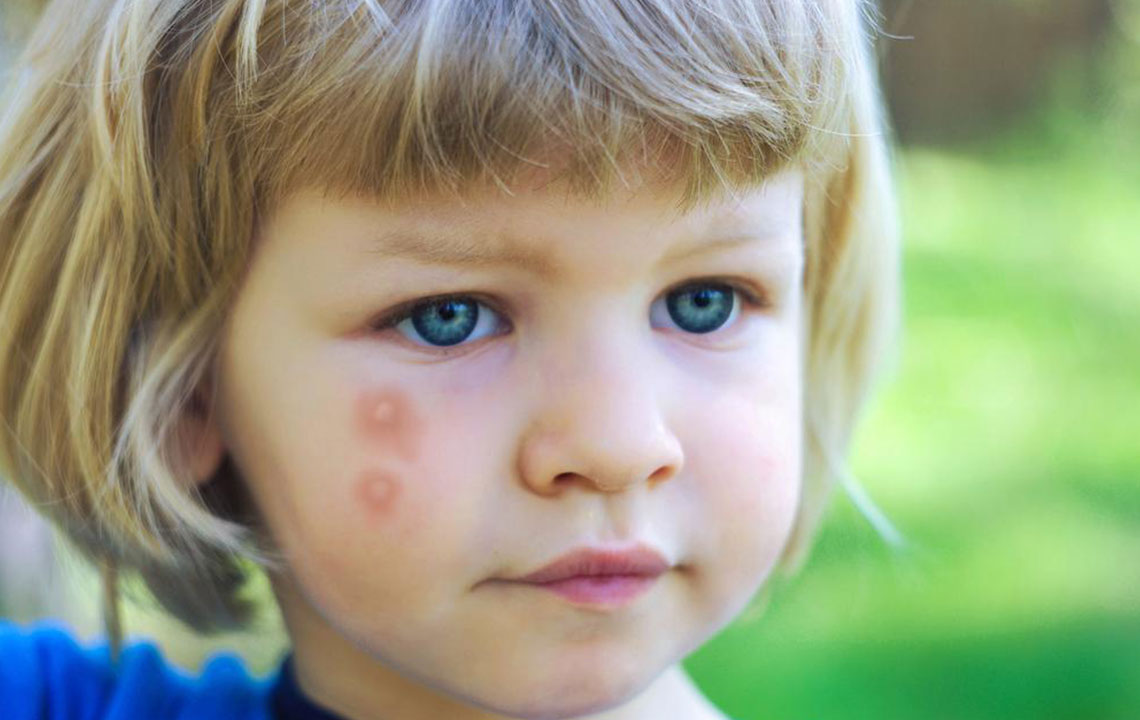
Bees and Wasps: These insects sting to defend themselves. Bee stings are more painful and tend to be left in the skin if the stinger remains, causing localized swelling and tenderness. Wasp stings can occur repeatedly and may provoke allergic reactions.
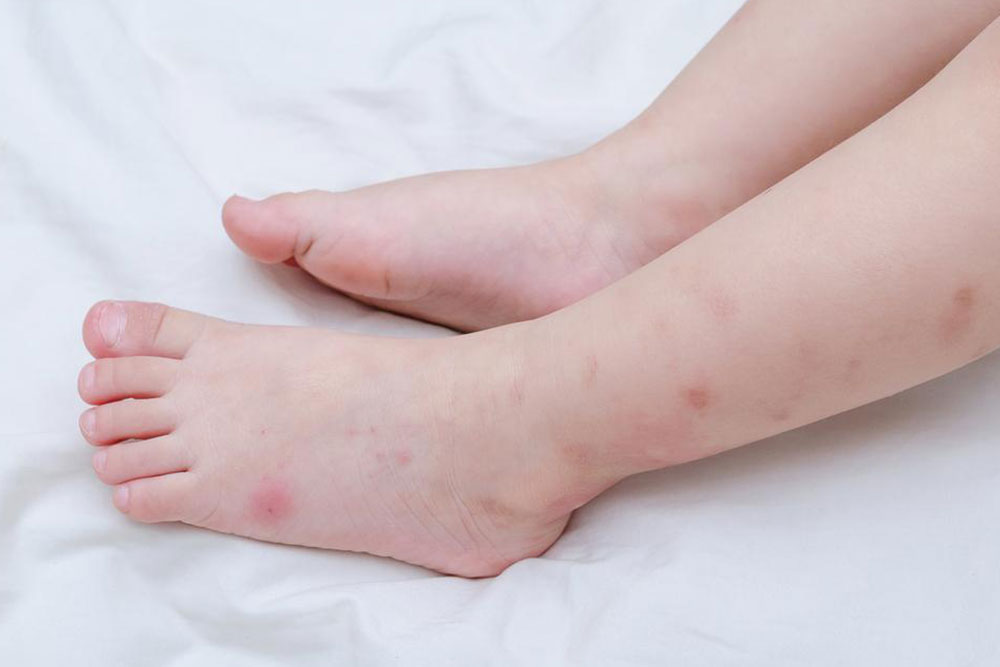
Fleas: Flea bites generally appear as small, clustered red bumps on the skin, often around the ankles or legs. They can cause itching and may transmit certain infections.
Bedbugs: Bedbug bites often occur in clusters or rows and are typically found on exposed skin areas like arms or legs, causing itchy welts.
Fire Ants: Fire ant stings cause painful pustules or bumps, sometimes with a burning sensation, and can lead to allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Scorpions: Scorpion stings are extremely painful, with symptoms including swelling, numbness, and in some cases, more severe neurological responses.
Spiders: Not all spiders bite, but those that do can cause various reactions ranging from mild redness to serious necrotic wounds, especially if the spider is venomous like the black widow or brown recluse.
How to Recognize Insect Bite Characteristics
Each insect leaves behind distinct signs and symptoms that can help in identification:
Swelling and Redness: Most insect bites cause localized swelling and redness. The degree varies depending on the insect and individual's reaction.
Pattern of Bites: Some insects bite repeatedly in rows or clusters (e.g., bedbugs), while others leave a single mark (e.g., mosquitoes).
Lesion Appearance: Bites from fire ants can develop into pustules, while spider bites might cause necrotic ulcers. Bee and Wasp stings often leave a stinger embedded in the skin.
Itching and Pain: Mosquito and flea bites are typically itchy, whereas fire ant bites and wasp stings tend to be painful.
Additional Symptoms: Allergic reactions may include hives, swelling beyond the bite site, or difficulty breathing. Systemic symptoms like fever or rash need urgent medical attention.
When to Seek Medical Help
While many insect bites and stings can be treated at home, certain signs indicate the need for professional medical evaluation:
Persistent or worsening swelling and redness
Signs of infection such as pus, warmth, or increased pain
Severe allergic reactions, including difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or dizziness
Fever or chills following a bite
Presence of a bull's-eye rash from a tick bite
Multiple bites over a large area or systemic symptoms
First Aid and Treatment Tips
For most insect bites and stings, prompt and proper care can alleviate symptoms and prevent complications:
Clean the bite area thoroughly with soap and water to reduce infection risk.
Apply cold compresses or ice packs wrapped in a cloth to reduce swelling and numbing pain.
Use over-the-counter antihistamines or hydrocortisone cream to relieve itching and inflammation.
Take pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen if needed.
Remove embedded stingers carefully using tweezers, scraping the stinger out rather than squeezing.
Avoid scratching the bite to prevent secondary infections.
If allergic reaction occurs, administering an epinephrine auto-injector and seeking emergency care is critical.
Preventing Future Insect Bites
Prevention is the best strategy to minimize insect bite risks:
Wear protective clothing such as long sleeves, pants, and closed shoes when outdoors.
Use insect repellents containing DEET or picaridin, especially during peak insect activity times.
Avoid standing water and damp areas where insects like mosquitoes breed.
Keep living spaces clean and reduce clutter to deter pests like cockroaches and bedbugs.
Seal cracks and gaps in windows and doors to prevent insect entry.
Be cautious around nests or hives and avoid disturbing insects.
Summary
Recognizing the difference between various insect bites and stings is essential for effective management and treatment. Understanding common insects, their bite patterns, and associated symptoms enables individuals to respond promptly, reducing health risks and complications. When in doubt or if severe allergic reactions or infections occur, consult healthcare professionals without delay. Incorporating preventive measures can greatly decrease the likelihood of future bites, ensuring safety and comfort during outdoor activities or in infested environments.