Comprehensive Approaches to Managing and Healing Shingles Through Proper Care, Nutrition, and Alternative Therapies
This comprehensive guide covers effective strategies for managing and healing shingles through medical treatment, proper daily care, nutrition, and alternative therapies. It emphasizes early intervention, soothing skin care routines, anti-inflammatory foods, and safe use of natural remedies to enhance recovery and reduce discomfort effectively.

Comprehensive Approaches to Managing and Healing Shingles Through Proper Care, Nutrition, and Alternative Therapies
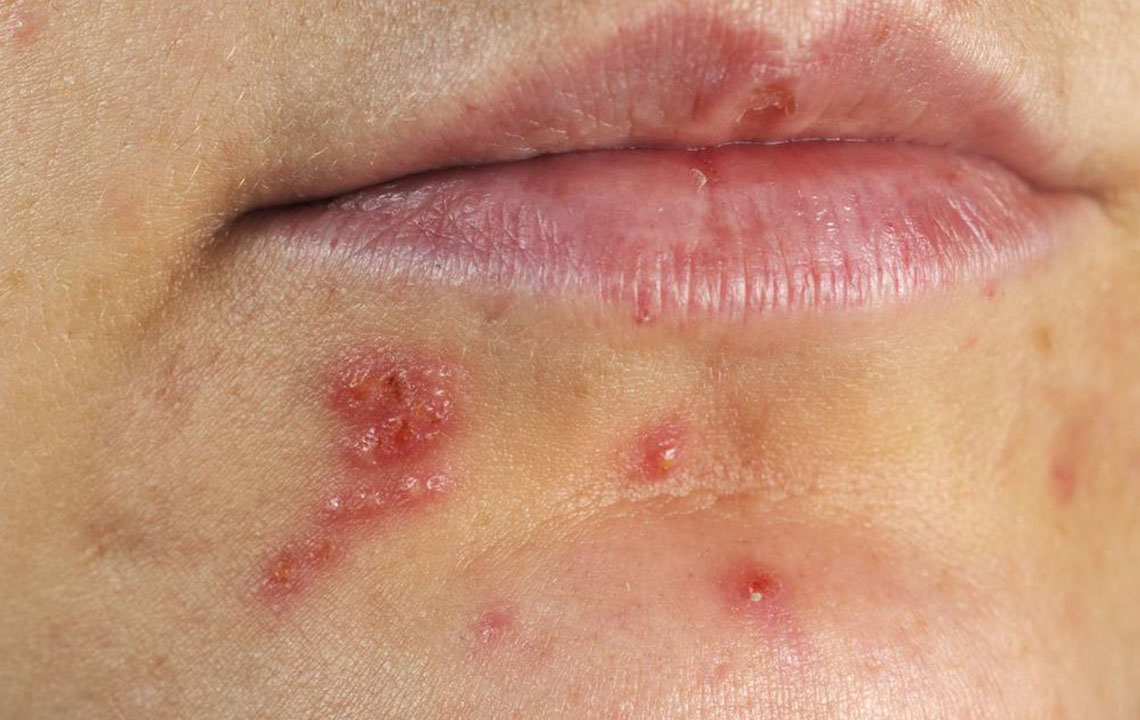
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster, is a painful condition caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus, which also causes chickenpox. When symptoms first appear, prompt medical intervention is crucial to effectively control the virus, reduce pain, and shorten the duration of illness. Timely diagnosis and treatment with antiviral medications can significantly influence recovery outcomes. Moreover, adopting supportive care practices, along with proper nutrition and alternative therapies, can enhance healing and improve quality of life during the course of shingles.
The importance of early treatment cannot be overstated. Antiviral drugs, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, are most effective when initiated within 72 hours of rash onset. These medications work by suppressing viral replication, which can lessen the severity and duration of symptoms. Alongside pharmacological treatment, supportive care measures are vital to managing discomfort and preventing complications.
Daily habits for optimal recovery:
Practice meticulous hygiene by cleansing the affected area gently with mild soap and water. Avoid using perfumed or harsh products that may irritate sensitive skin.
Applying cold compresses to the rash can effectively reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and diminish itching. Keep the compress on the area for 15-20 minutes several times a day, ensuring the skin remains moist and comfortable.
Use soothing topical agents like petroleum jelly or calamine lotion to moisturize the skin and form a protective barrier. This can help prevent cracking and secondary infections.
For itching relief, apply a paste made of two parts cornstarch mixed with one part water directly on the blisters. Leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing gently. This remedy can help soothe irritated skin.
Wearing loose, breathable clothing—preferably made from natural fibers—reduces friction, keeps the area dry, and promotes a faster healing process. Avoid tight-fitting garments that can cause irritation or trap heat.
Exploring alternative treatments for shingles:
Applying natural remedies like manuka honey or clover honey on the rash can provide antimicrobial properties, reduce inflammation, and support tissue repair. Honey has been used traditionally for its healing benefits and can be gently spread on the affected area.
A mixture of raw honey combined with leek juice and aloe vera offers a natural soothing effect, helping to alleviate pain and promote skin regeneration. The anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties of these ingredients can be beneficial during recovery.
Essential oils such as tea tree, lemongrass, peppermint, and geranium (germander) have been reported to ease shingles pain. When using essential oils, always perform a patch test by diluting two drops in a quarter teaspoon of coconut oil to check for allergies. You can also diffuse these oils in your living space to benefit from their aromatic therapeutic effects. Aromatherapy provides a calming environment, reduces stress, and may enhance overall well-being.
In some cases, acupuncture has shown promising results in reducing nerve pain associated with shingles. Consulting with a licensed acupuncturist might offer additional relief from discomfort and help support the body's healing process.
Nutritional strategies to bolster shingles recovery:
Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration assists the immune system in fighting the virus and facilitates detoxification.
Incorporate foods rich in Vitamin B complex, such as low-fat dairy products, eggs, organic chicken, and wild-caught fish. These nutrients support nerve health and reduce inflammation.
Consume raw garlic and onions regularly, as they contain potent antiviral compounds that can support your immune defenses. Including these in your diet may help limit the spread and severity of shingles.
Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables high in Vitamin C, which boosts immune function and accelerates tissue repair. Green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and arugula provide additional antioxidants that protect cells from damage.
While dietary and alternative methods can offer significant support, always remember they are adjuncts to, not replacements for, prescribed medical treatment. It is critical to consult your healthcare provider before combining any alternative therapies with your medical regimen to ensure safety and effectiveness.
In conclusion, managing shingles effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes timely medical intervention, proper daily self-care, nutritional support, and safe use of alternative therapies. By following these strategies, patients can reduce discomfort, promote faster healing, and minimize the risk of complications such as postherpetic neuralgia. Always seek medical advice for personalized treatment plans and ensure that any complementary therapies are used safely under professional supervision.