Comprehensive Approaches to Managing Shingles Pain and Discomfort
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for alleviating shingles discomfort, including medications, natural remedies, and lifestyle tips. It emphasizes early antiviral treatment and holistic care to reduce pain, promote healing, and prevent postherpetic neuralgia, providing valuable insights for patients seeking relief from this painful condition.

Effective Methods for Alleviating Shingles Symptoms
Understanding and managing shingles discomfort
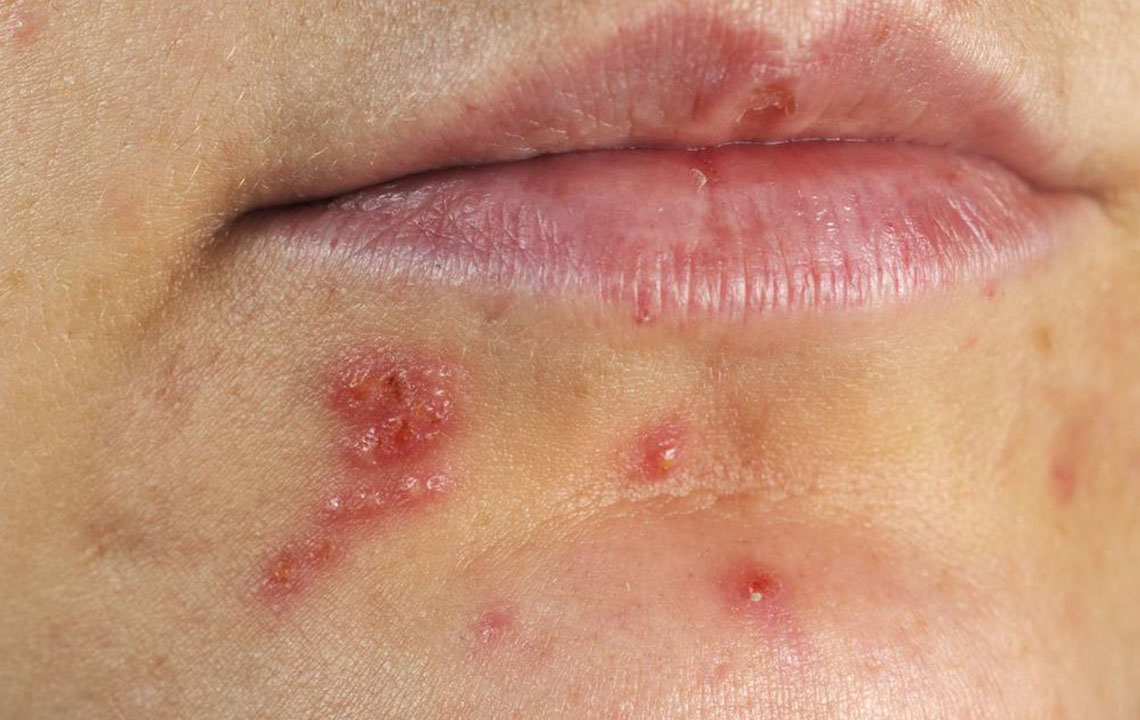
Shingles, medically known as herpes zoster, is a painful skin condition caused by the reactivation of the varicella zoster virus—the same virus responsible for chickenpox. This reactivation results in a distinctive, often intensely painful rash, which appears along nerve pathways and can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. While many people find that the rash and associated pain diminish over time, a subset of patients endure prolonged discomfort, a condition known as postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). Managing shingles effectively is essential not only to reduce immediate suffering but also to prevent long-term complications such as chronic nerve pain.
Strategies to manage shingles pain effectively
Many individuals affected by shingles seek reliable methods to ease the intense pain and discomfort caused by the virus. Collectively, a combination of medications, natural remedies, and lifestyle adjustments can provide significant relief, improve healing times, and reduce the risk of complications. Below, we explore the most proven strategies for managing shingles symptoms and enhancing patient comfort.
Pharmacological pain management
Effective pain relief plays a crucial role in shingles treatment. Various medications are used to alleviate symptoms, ranging from over-the-counter options to prescription drugs. For mild to moderate pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetaminophen are commonly recommended. In some cases, healthcare providers may suggest antidepressants like amitriptyline or nortriptyline, which help modulate nerve pain. Topical anesthetics such as calamine lotion or capsaicin creams can soothe itching and reduce localized discomfort.
Antiviral medications
The cornerstone of shingles treatment is antiviral therapy. Common antiviral drugs include valacyclovir (Valtrex), acyclovir (Zovirax), and famciclovir (Famvir). These medications are most effective when administered within 72 hours of rash onset, as they can significantly reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. For immunocompromised patients or severe cases, intravenous antivirals might be necessary. Early intervention with antivirals not only shortens the course of the disease but also decreases the likelihood of developing postherpetic neuralgia.
Addressing persistent pain: Opioids and nerve-specific treatments
For ongoing nerve pain persisting after the rash resolves, opioids like morphine or oxycodone might be prescribed, but their use is carefully monitored due to addiction risks. Additionally, nerve-specific medications such as pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin) are often recommended to target neuralgia directly. These drugs can be highly effective in reducing nerve pain and improving quality of life for chronic sufferers.
Natural and home remedies for shingles relief
Besides pharmaceuticals, several natural therapies can support symptom management and promote healing. Incorporating these into daily routines can provide extra comfort and aid recovery:
Cool baths and soothing soaks: Taking a cool bath with colloidal oatmeal can soothe inflamed skin and decrease itching. For optimal relief, baths of about 20 minutes daily are recommended, providing a cooling effect that eases pain and prevents infection.
Cold compresses: Applying a cold, damp cloth or ice pack wrapped in a cloth to affected areas can diminish pain and swelling. Reapplying cold compresses multiple times a day helps reduce inflammation, but if pain worsens or skin becomes more irritated, discontinuation is advised.
Topical creams and lotions: Use gentle, skin-calming creams such as capsaicin or those containing a small amount of lidocaine. Although initial application may cause a burning sensation, these products can help decrease nerve firing and reduce both pain and itching over time.
Nutritional support: A balanced diet rich in vitamins A, B complex, C, E, and the amino acid lysine may help strengthen the immune system and promote faster healing. Foods like leafy greens, citrus fruits, lean proteins, eggs, fish, whole grains, and dairy are particularly beneficial.
Stress management and lifestyle adjustments: Chronic stress can impair immune response, potentially exacerbating shingles symptoms. Engaging in relaxing activities such as meditation, yoga, and adequate sleep can bolster immune health and facilitate recovery.
Integrating medical treatments with natural therapies and lifestyle modifications offers a comprehensive approach to shingles management. With patience and careful adherence, most individuals can experience symptom relief and a faster return to normalcy, minimizing long-term complications and enhancing overall well-being.