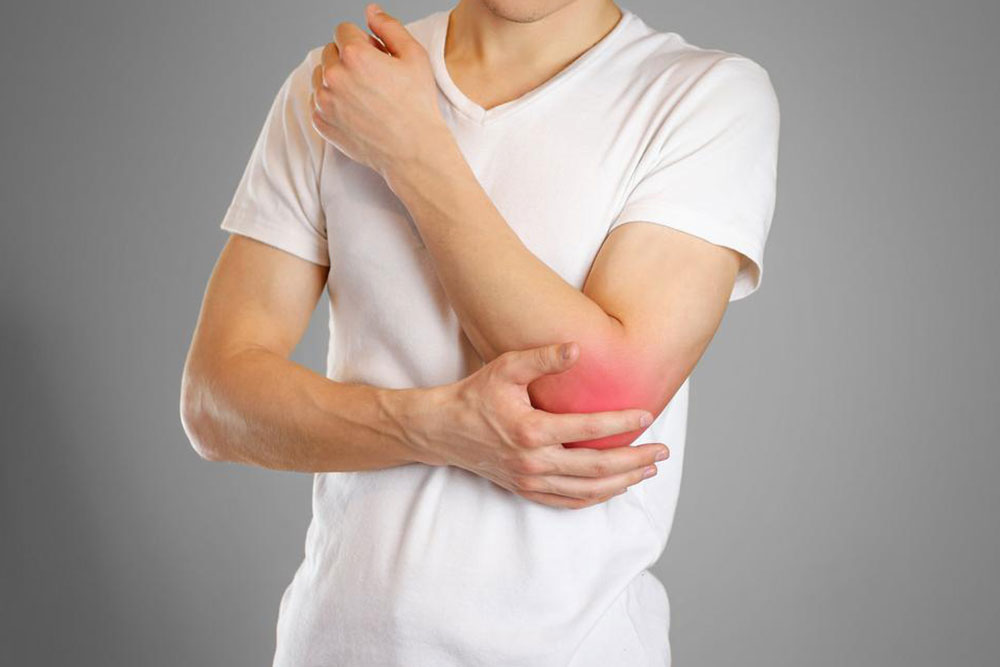
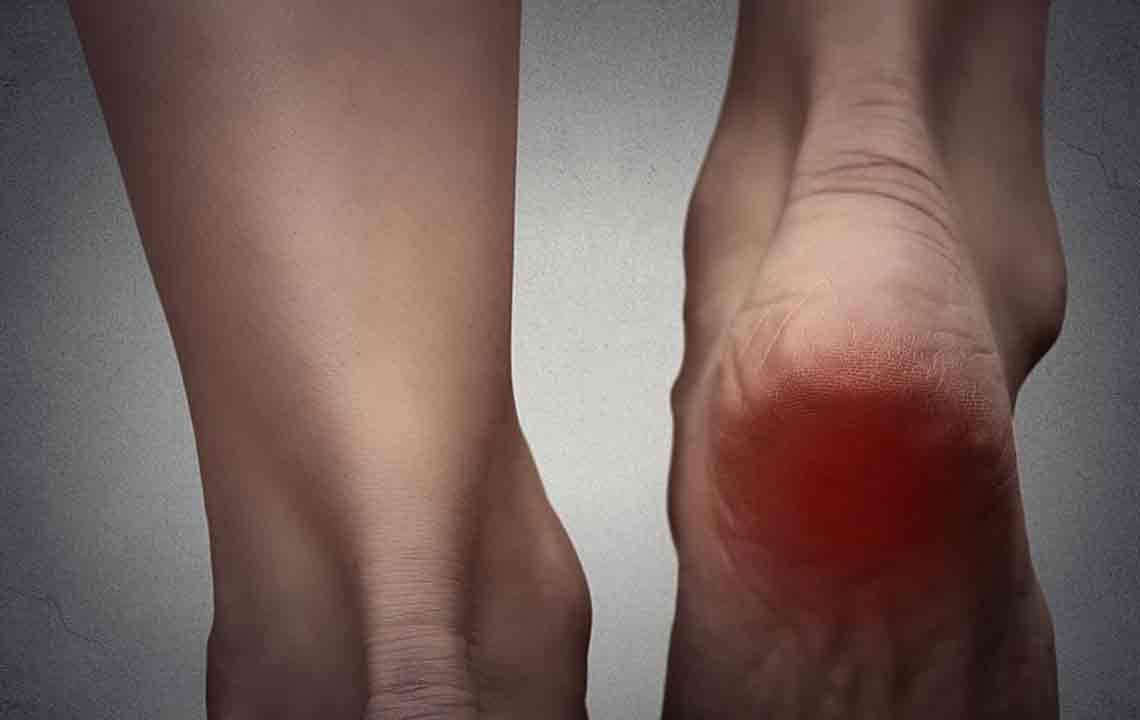
Comprehensive Guide to the Primary Causes and Prevention of Bursitis
Bursitis is a painful joint condition caused by various factors such as repetitive movements, injuries, infections, and systemic diseases. Understanding these causes can help in prevention and effective management. This comprehensive guide explores the primary reasons behind bursitis, offers preventive strategies, and discusses treatment options to maintain joint health and mobility.
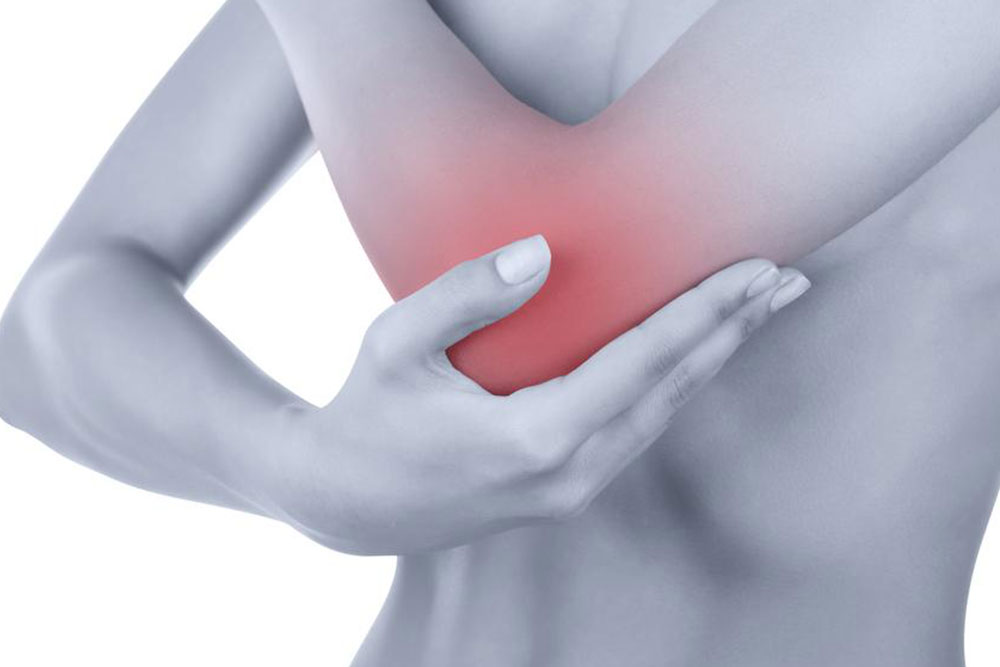
Comprehensive Guide to the Primary Causes and Prevention of Bursitis
Bursitis is an enduring and often painful condition characterized by inflammation of the bursae, which are small, fluid-filled sacs situated in various joints throughout the body. These sacs serve as cushions to reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles during movement. When inflamed, bursae cause pain, swelling, redness, and restricted mobility, significantly impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. Understanding the multifaceted causes of bursitis is essential for effective prevention, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment.
Several factors contribute to the development of bursitis, ranging from external injuries to internal health conditions. Repetitive movements and overuse of specific joints are among the most common causes, especially in individuals engaged in physically demanding occupations or sporting activities. Additionally, infections that invade the bursae may result in septic bursitis, which requires prompt medical intervention. Certain systemic diseases like gout and rheumatoid arthritis also predispose individuals to bursitis, complicating its management. This comprehensive overview aims to detail these causes and provide insights into preventive measures to safeguard joint health.
Key Causes of Bursitis
Repetitive Movements and Overuse: Activities involving repeated motion or sustained pressure on joints, such as kneeling, lifting, or swinging a racket, can irritate the bursae and lead to inflammation.
Physical Injuries: Impact injuries or acute trauma, including falls or blows, may damage the bursae directly, initiating an inflammatory response.
Infections: Bacterial or viral infections can infiltrate bursae, especially following skin injuries or punctures, resulting in septic bursitis that requires antibiotics or drainage.
Underlying Medical Conditions: Diseases like gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or other autoimmune disorders often cause systemic inflammation that predisposes bursae to swelling and discomfort.
Prolonged Pressure or Posture: Persistent pressure on specific joints, such as prolonged kneeling or leaning, can cause bursitis over time by irritating the bursae.
Preventive Strategies and Management
Preventing bursitis involves maintaining good joint health and avoiding actions that overstress or injure the bursae. Proper ergonomics, adequate rest, and the use of padding during repetitive tasks can significantly reduce risks. For athletes and manual workers, incorporating joint-strengthening exercises, stretching routines, and protective gear is advisable. Recognizing early symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention can prevent the progression of bursitis into chronic or septic forms. Treatments may include rest, anti-inflammatory medications, ice applications, or in severe cases, surgical interventions.