Comprehensive Guide to Alleviating Knee Pain and Discomfort
This comprehensive guide explores effective strategies for relieving knee discomfort, highlighting causes, treatments, and preventative measures. It covers immediate injury responses, managing chronic conditions like arthritis and gout, surgical options, and lifestyle modifications. Understanding these methods can help individuals reduce pain, improve joint health, and restore mobility. Early intervention and personalized care are key for long-term knee health, whether through conservative management or advanced procedures like knee replacement. Prioritizing knee care ensures a better quality of life and sustained activity levels.
Comprehensive Strategies for Alleviating Knee Pain and Discomfort
The knee joint is a complex and crucial part of the human body, enabling mobility and supporting weight during various activities like walking, running, jumping, and squatting. Due to its pivotal role, the knee is often subjected to stress, strain, and injuries that can lead to discomfort or dysfunction. As the body's second-largest weight-bearing joint, the knee's susceptibility to damage increases with age, overuse, or trauma. This frequently results in discomfort that prompts many individuals to seek medical advice. Understanding the common causes and effective treatments of knee pain can significantly improve quality of life and mobility.
Persistent knee discomfort can lead to further joint deterioration if left unmanaged. It’s essential to address symptoms early with appropriate interventions to prevent long-term damage and restore joint function.
Effective Treatments for Knee Discomfort
Immediate Response to Injury: When faced with sudden knee injury, it's crucial to initiate first aid measures promptly. Applying a cold pack or ice to the affected area helps constrict blood vessels, reducing blood flow and minimizing swelling and inflammation. Resting the joint and keeping the leg elevated can further decrease swelling and alleviate pain. Avoiding weight-bearing on the injured knee during this period is essential. Over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can be used to manage pain and decrease inflammation. However, if pain persists beyond a few days, intensifies, or if swelling doesn’t subside, consulting a healthcare professional becomes necessary for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Chronic Conditions Affecting the Knee: Several medical conditions can cause persistent knee pain. Rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and osteoarthritis are common culprits. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder leading to joint inflammation, while gout involves the accumulation of uric acid crystals, causing acute pain episodes. Osteoarthritis, the most prevalent form among older adults, results from cartilage breakdown leading to joint degeneration.
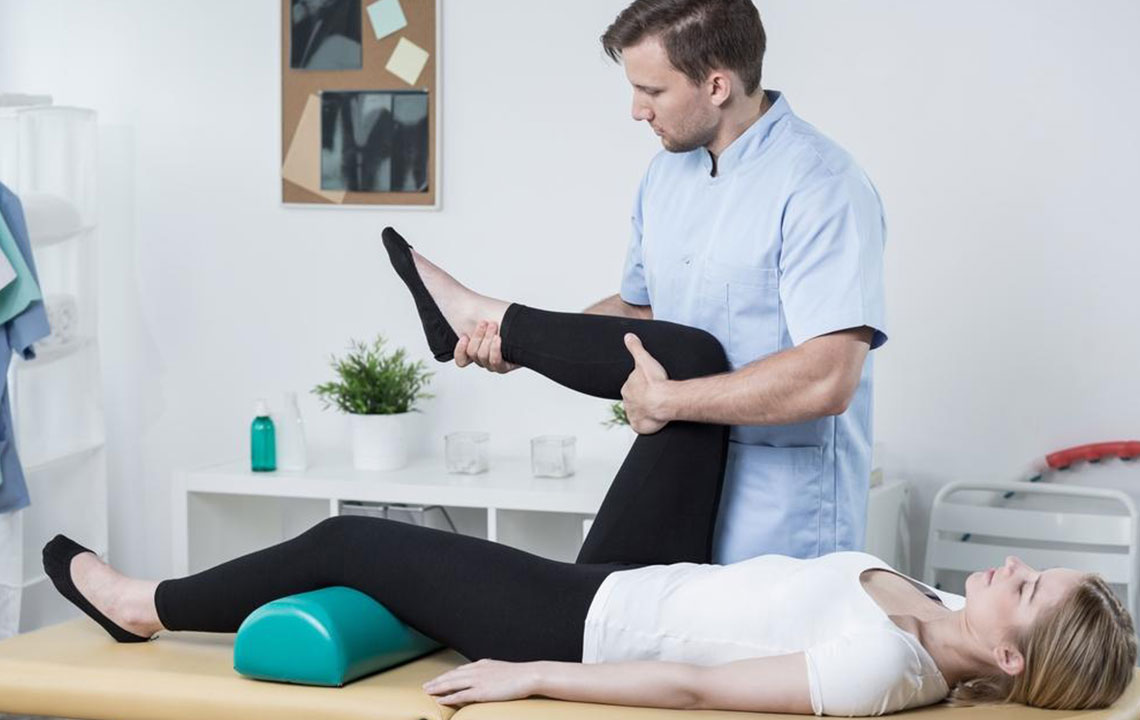
Managing these conditions typically involves both medication and lifestyle changes. Corticosteroid injections are commonly administered to reduce inflammation and relieve pain during flare-ups. For gout, medications that lower uric acid levels are prescribed, along with dietary modifications to prevent crystal formation. For osteoarthritis, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs are used, alongside physical therapy and weight management strategies.
Intra-articular injections have become a popular treatment modality for managing knee pain. Hyaluronic acid injections work by supplementing the joint’s natural lubricant, easing friction, and providing temporary pain relief in cases of osteoarthritis. These injections can improve joint mobility and reduce discomfort for some patients.
Surgical Interventions: When conservative treatments prove insufficient, surgical options may be necessary. Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, allows surgeons to examine and repair internal knee structures, such as cartilage damage, tears in ligaments, or removing loose debris that hampers joint function. Arthroscopy entails small incisions and the use of a fiber-optic camera to visualize the joint and perform repairs efficiently.
In advanced cases where joint damage is extensive, more invasive procedures like partial or total knee replacement surgery are considered. During knee replacement, damaged cartilage and bone are replaced with metal, plastic, or ceramic components, restoring function and reducing pain. This procedure can significantly improve quality of life for individuals with severe osteoarthritis or joint degeneration.
Additional Therapies and Preventative Measures
Supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate have been explored for their potential to support joint health. While research results are mixed, some patients report relief and improved joint function.
Strengthening exercises targeting muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves, can provide better joint stabilization and reduce stress on the knee. Increased flexibility through stretching, along with proper biomechanics, can prevent injury.
Alternative therapies like acupuncture may help some individuals manage chronic knee pain. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the knee joint, delaying or preventing degenerative changes.
Adopting a comprehensive approach to knee health — combining medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and preventive strategies — is essential for alleviating discomfort and maintaining mobility. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized diagnosis and treatment plans ensures optimal recovery and joint preservation.