Comprehensive Guide to Detecting and Preventing Scabies Skin Rash Effectively
This comprehensive guide provides in-depth strategies for detecting and preventing scabies skin rash. It covers symptoms recognition, accurate diagnosis, effective treatment options, and essential hygiene practices. Proper management involves professional medical interventions and thorough environmental cleaning to eliminate mites and prevent re-infestation. Early diagnosis and preventive measures are vital to controlling the spread of this contagious skin condition and ensuring complete recovery. Follow expert advice and adopt strict hygiene routines for effective scabies management.

The Ultimate Guide to Detecting and Preventing Scabies Skin Rash
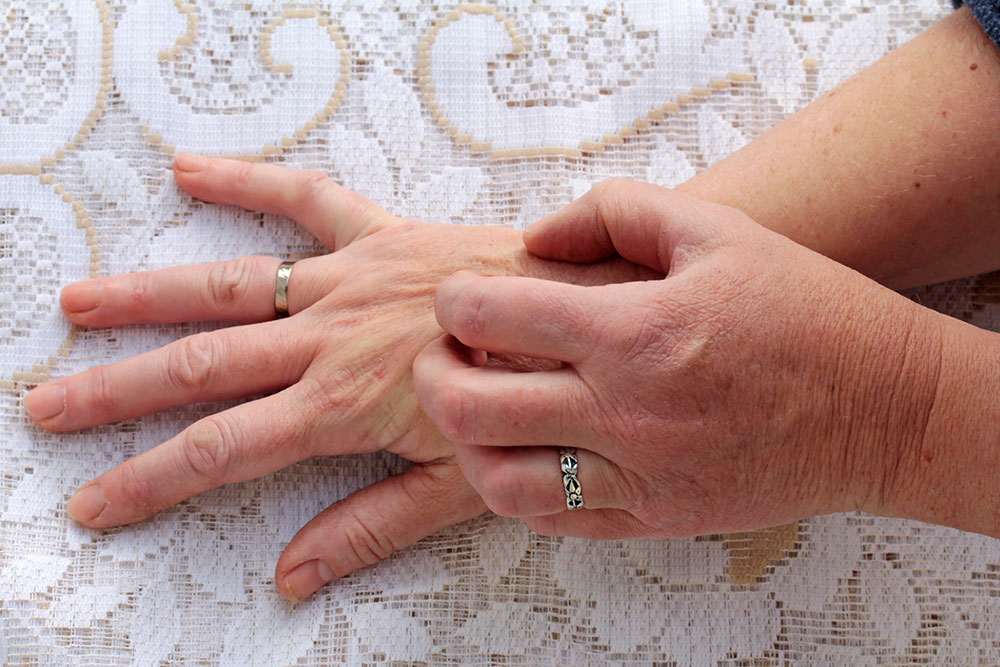
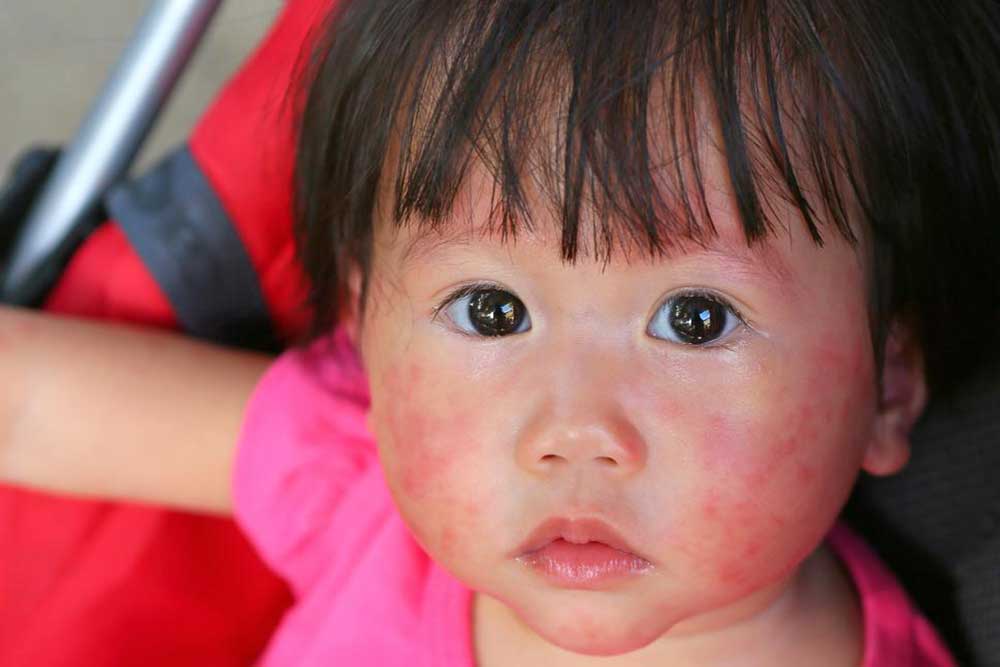
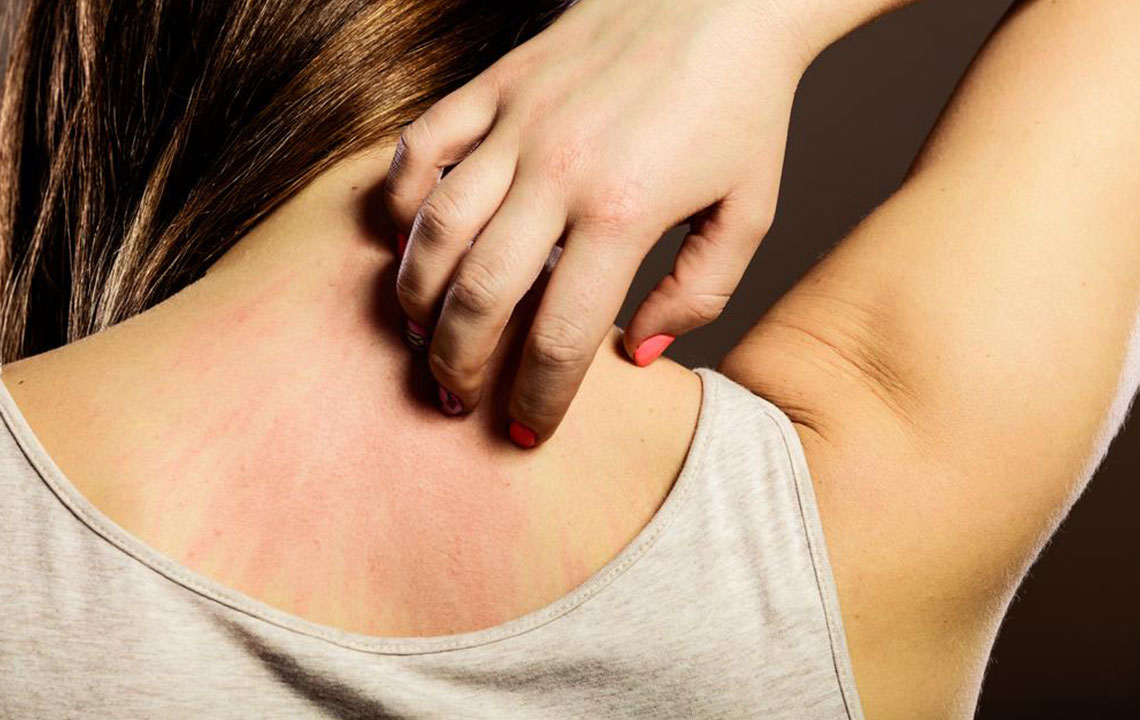
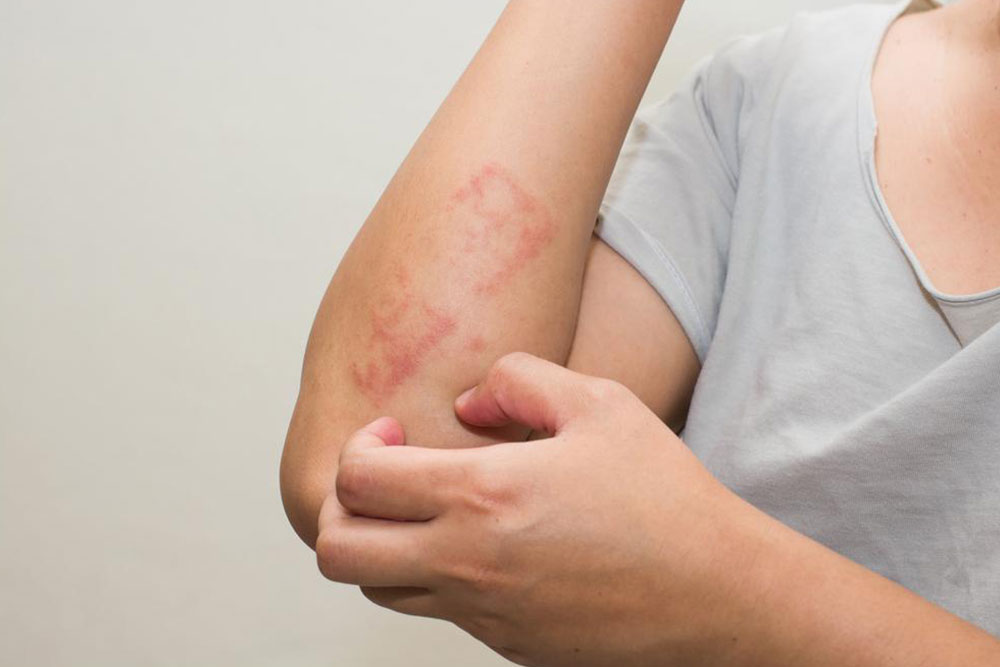
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, leading to intense itching and distinctive skin changes. It often presents as small, red, itchy bumps and blisters that can be mistaken for other skin ailments like allergic reactions or bacterial infections. Accurate diagnosis is crucial since misidentification can delay proper treatment and facilitate the spread of the infestation. Recognizing the signs early and understanding effective prevention strategies are key to managing scabies effectively.
Common symptoms include extreme itching, especially at night, reddish skin patches, fine gray lines (burrows), and widespread rashes on various parts of the body. Due to their similarity with other dermatological conditions, self-diagnosis is discouraged. Instead, seeking medical evaluation ensures correct identification and timely treatment. Over-the-counter remedies generally prove ineffective because scabies requires targeted prescription medication.
Professional treatment options involve applying medicated creams or lotions containing acaricidal agents such as permethrin or sulfur ointments. These treatments are usually applied from the neck down, ensuring coverage of all affected areas, often overnight or as per physician instructions. It is vital to follow the treatment plan precisely and to repeat application if recommended to eliminate all mites thoroughly.
Preventive measures are equally critical in controlling the spread of scabies and preventing reinfection. Avoiding direct skin contact with infected individuals, especially during the contagious phase, significantly reduces transmission risk. Additionally, meticulous hygiene practices—such as washing all clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water at a minimum temperature of 50°C (122°F)—are vital. Items should be soaked or washed thoroughly, then dried on high heat for at least 10 minutes. Vacuuming furniture and carpets, and cleaning surfaces regularly, further reduces the likelihood of mites surviving in the environment.
To effectively manage and control scabies outbreaks, it is important to treat all close contacts simultaneously, even if asymptomatic, to prevent reinfection. Comprehensive cleaning routines, vigilant hygiene, and adherence to prescribed medication regimens collectively ensure effective control. Remember, early diagnosis coupled with strict preventive practices can significantly reduce the spread and duration of scabies infestations.
In cases of persistent or severe symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. They may prescribe additional medications or suggest alternative treatment strategies. Following medical advice and maintaining good hygiene creates a robust defense against this highly contagious skin condition, leading to quicker recovery and smoother skin health.