Effective Dietary Strategies for Managing Lupus Symptoms: Foods to Embrace and Avoid
Discover comprehensive dietary strategies to manage lupus symptoms effectively. Learn about anti-inflammatory foods, essential nutrients like omega-3s, calcium, and antioxidants, and identify foods to avoid, such as alfalfa sprouts and processed items. This detailed guide empowers lupus patients to make informed dietary choices that support immune health, reduce flare-ups, and improve overall well-being through a balanced nutritional approach.

Lupus, medically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is a complex autoimmune disorder that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Characterized by chronic inflammation, joint pain, fatigue, skin rashes, and organ involvement, lupus results from an overactive immune system attacking healthy tissues. While currently, there is no cure for lupus, lifestyle modifications, particularly dietary adjustments, can play a vital role in managing symptoms and reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups.
Understanding the connection between diet and lupus is essential for patients seeking to improve their health outcomes. An anti-inflammatory diet comprising specific foods can help suppress excess immune activity, reduce inflammation, and provide necessary nutrients to support overall well-being. Conversely, certain foods may aggravate symptoms and should be minimized or avoided.
Key Dietary Components for Managing Lupus
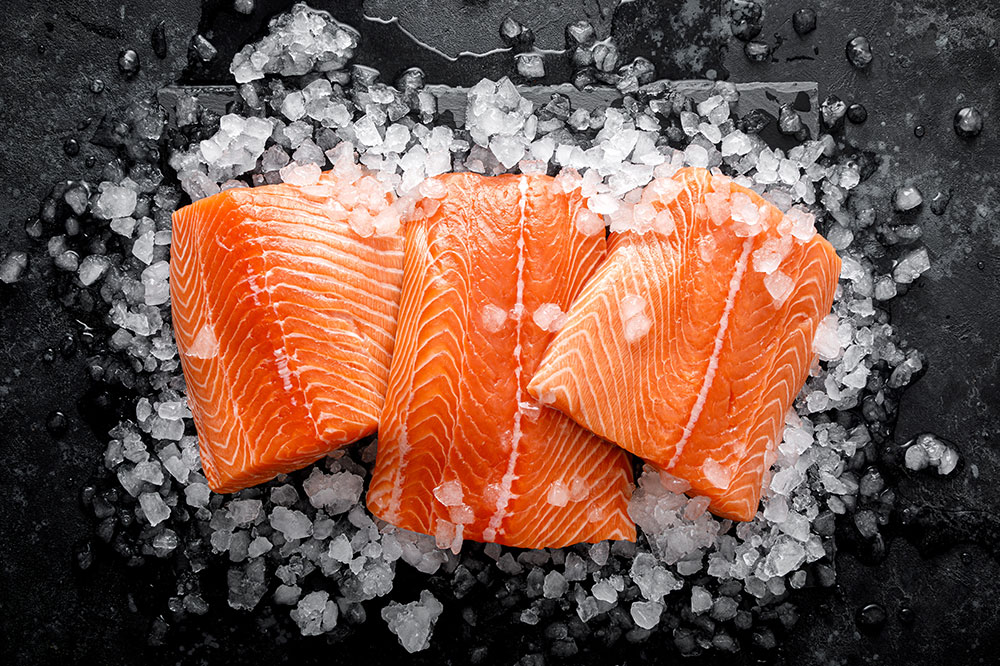
Incorporate Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are potent anti-inflammatory agents that can significantly aid in controlling lupus symptoms. These healthy fats are abundantly found in fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and albacore tuna. Including at least two servings of fatty fish per week can help reduce joint pain and stiffness associated with lupus. For those who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, plant-based sources like walnuts, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds can provide omega-3s. Dietary supplements, such as fish oil capsules, are also an option but should be taken under medical supervision to avoid interactions with medications.
Prioritize Calcium and Vitamin D
People with lupus are often at increased risk of osteoporosis, partly due to long-term medication use, limited sun exposure, and inflammation. To support bone health, it's vital to consume calcium-rich foods. Low-fat or fat-free dairy products like yogurt, milk, and cheese are excellent sources. Leafy greens such as kale, collard greens, and bok choy also contain calcium. Since vitamin D enhances calcium absorption and modulates immune responses, adequate sunlight exposure and foods like fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and fatty fish are recommended. In some cases, supplements may be needed, but only under healthcare provider guidance.
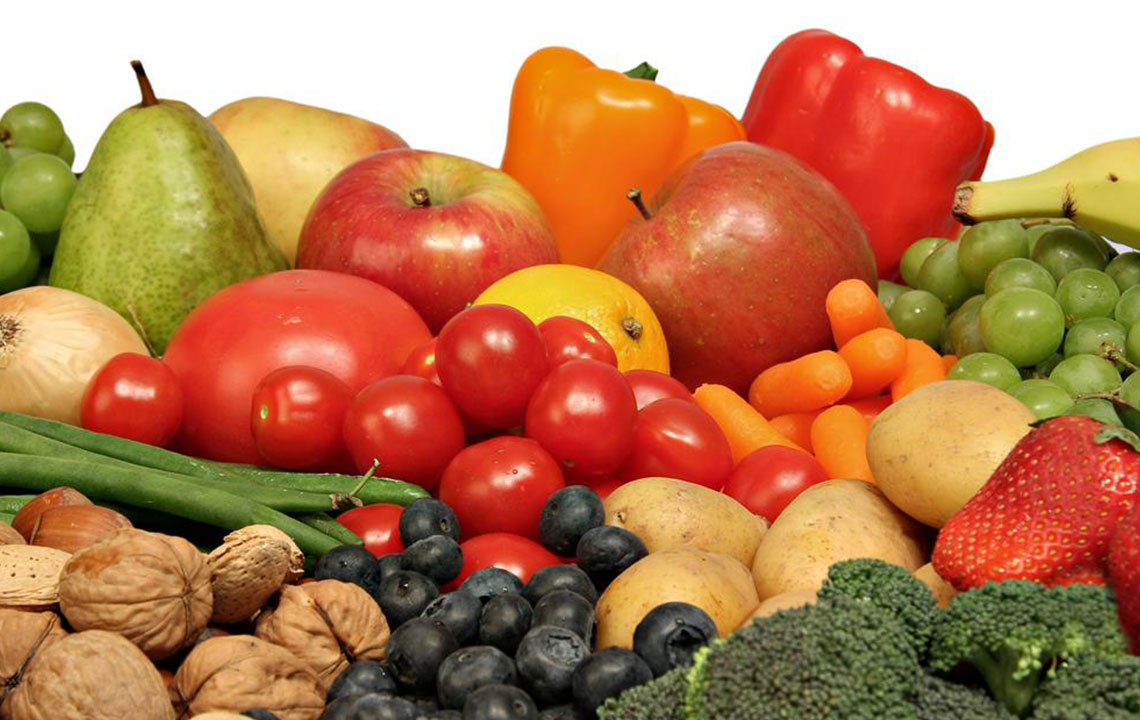
Emphasize Fruits and Vegetables Loaded with Antioxidants
Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, which play a role in promoting inflammation and tissue damage in lupus. Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet, emphasizing berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries), oranges, cherries, and vegetables like carrots, spinach, and broccoli. These foods contain vitamins C and E, selenium, and other phytochemicals that support immunity and reduce oxidative stress. Eating a rainbow of produce daily can enhance overall health, support immune function, and lessen lupus symptoms.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
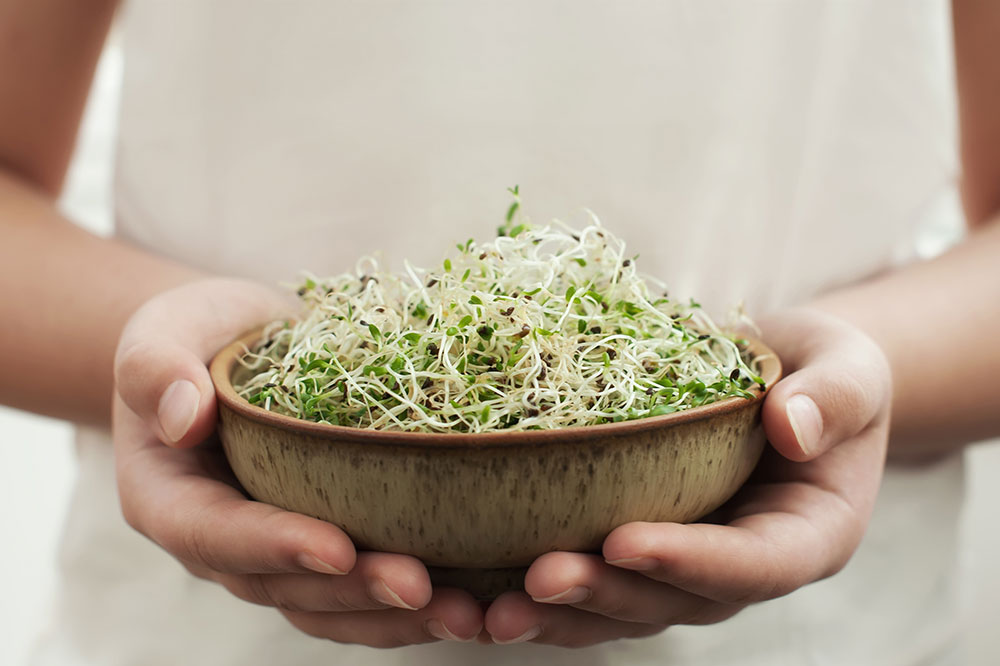
Alfalfa Sprouts
Alfalfa sprouts contain an amino acid derivative called L-canavanine, which has been linked to triggering lupus flare-ups and worsening symptoms. Patients are advised to avoid fresh alfalfa sprouts entirely to prevent potential immune system overstimulation.
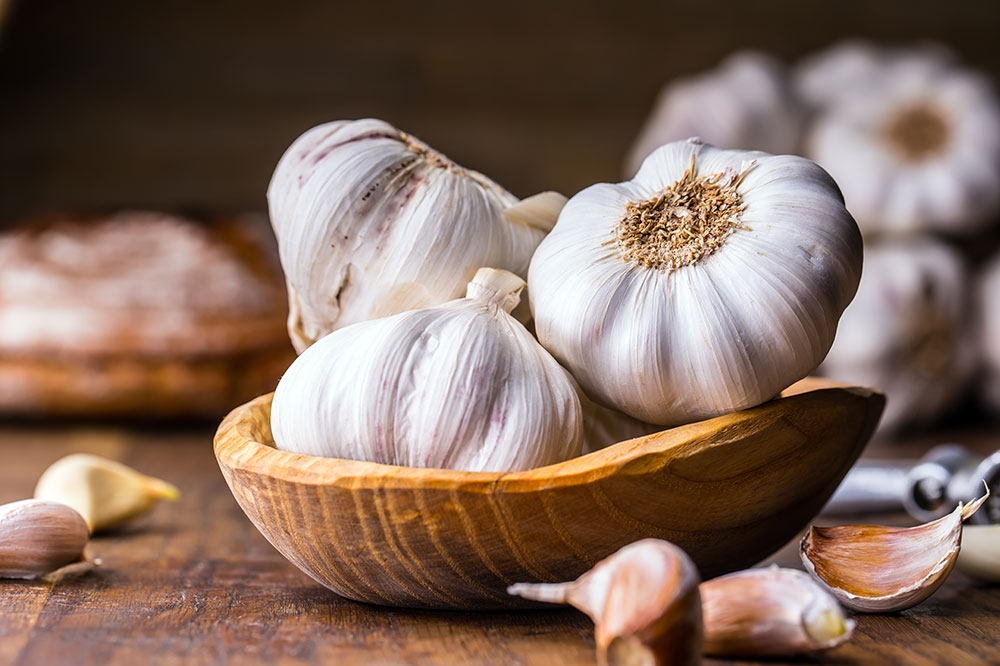
Limit Garlic and Certain Vegetables
While garlic is known for its heart-healthy properties, it can overstimulate the immune system in lupus patients, possibly triggering flare-ups. It’s best to consume garlic in moderation. Other vegetables that may exacerbate symptoms include onions and leeks; however, individual reactions vary, and it’s essential to monitor personal responses.
Processed and High-Fat Foods
Foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and processed ingredients can promote inflammation. Limit intake of fast food, fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks. Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed foods to reduce systemic inflammation and support overall health.
Maintaining a Balanced Diet for Long-Term Health
Adopting a balanced diet tailored to lupus management involves eating a diverse array of nutrient-dense foods. Incorporate lean proteins, complex carbohydrates like whole grains, and healthy fats. Hydration is equally important; drinking plenty of water helps flush toxins and maintain optimal bodily functions.
It's also critical to customize dietary choices based on individual responses and medical advice. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider can help develop an effective, personalized nutrition plan that complements medical treatment, enhances immune health, and reduces flare-ups.
Additional Lifestyle Tips Supporting Lupus Management
Beyond diet, regular moderate exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding smoking are crucial for managing lupus symptoms effectively. A comprehensive approach combining these lifestyle factors can enhance quality of life and minimize disease progression.
Conclusion
While diet alone cannot cure lupus, smart nutritional choices can significantly impact disease control and quality of life. Emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, fruits, and vegetables, while avoiding known triggers such as alfalfa sprouts and processed foods, provides a practical strategy for managing symptoms. Working with healthcare professionals to tailor dietary interventions ensures an optimal approach toward healthier living with lupus.