Comprehensive Dietary Strategies to Alleviate Hiatal Hernia Symptoms and Improve Quality of Life
This comprehensive guide provides effective dietary strategies and lifestyle modifications to help manage hiatal hernia symptoms. It highlights food choices to avoid and healthier alternatives, along with cooking tips and lifestyle advice to improve digestion and reduce reflux episodes. Whether you're seeking immediate relief or long-term management, these expert tips aim to enhance your quality of life and minimize discomfort associated with hiatal hernia. Implementing these changes can lead to better health outcomes and increased comfort in everyday activities.

Effective Dietary Management for Hiatal Hernia Relief
A hiatal hernia is a condition where a part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, leading to uncomfortable symptoms like acid reflux, heartburn, and indigestion. Managing this condition effectively involves a combination of dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes medical intervention. Nutrition plays a vital role in controlling and alleviating symptoms associated with hiatal hernia, providing individuals with a better quality of life and reducing the need for medication or surgical procedures.
Adopting a strategic diet plan tailored for hiatal hernia patients can significantly reduce episodes of acid regurgitation, heartburn, and abdominal discomfort. It’s crucial to understand which foods exacerbate symptoms and to select healthier alternatives that promote digestion and reduce reflux. This comprehensive guide offers insights into dietary choices, cooking techniques, and lifestyle adjustments that can help manage and mitigate the effects of hiatal hernia effectively.
Foods to Avoid:
Chocolate and cocoa products
Fruits high in citric acid, including oranges, grapefruits, lemons, and certain berries
Garlic and onions, which can trigger reflux episodes
Caffeinated beverages like coffee, tea, and decaffeinated drinks
Mint-flavored products, including peppermint and spearmint
Alcoholic beverages, especially wines and spirits
High-fat dairy products such as cheese, creams, butter, and ice cream
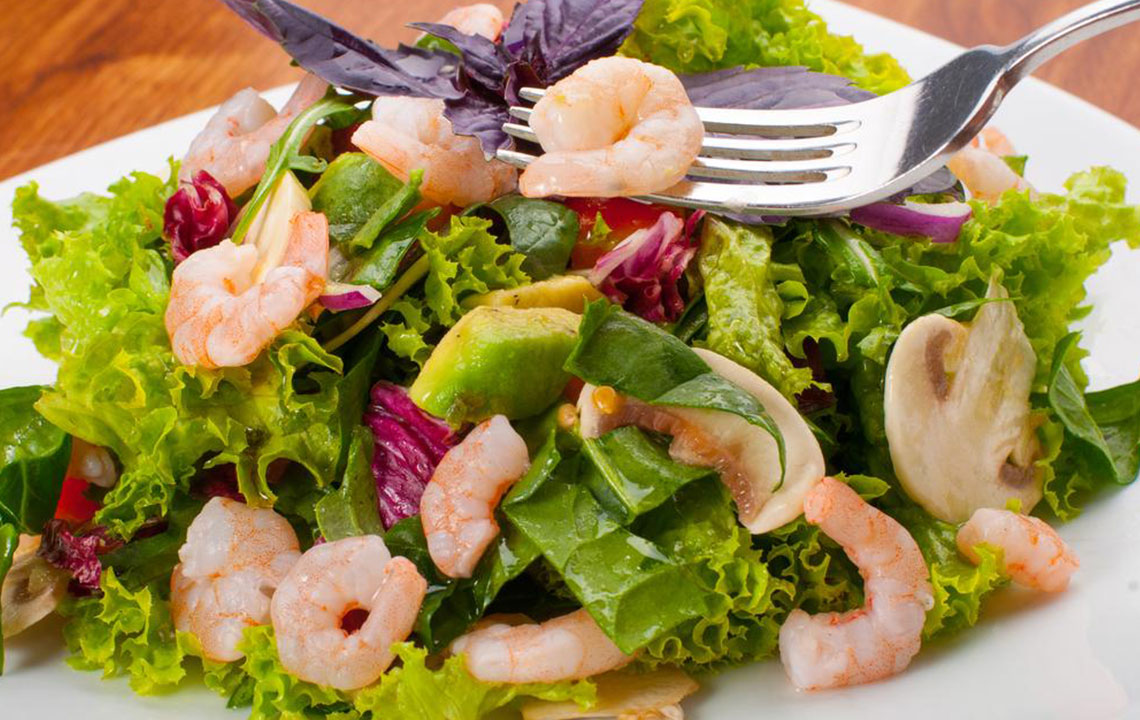
Healthier Dietary Options:
Fruits like bananas, apples, and pears, which are less likely to trigger reflux
Vegetables such as carrots, broccoli, spinach, and leafy greens
Low-fat or plant-based milk alternatives, including almond, soy, or oat milk
Lean proteins like chicken, turkey, fish, and lean cuts of beef or pork
Plenty of water to stay hydrated and aid digestion
Healthy snacks such as rice crackers, baked potato chips, or unsalted nuts
Low-fat, non-chocolate, and non-mint sweets for a satisfying treat
Cooking methods also influence symptoms. Favor baking, steaming, boiling, or grilling over frying to keep foods light and less greasy. Removing skin from meats, trimming excess fats, and using minimal oil can help prevent acid reflux. Enhancing dishes with herbs (avoiding spicy or highly seasoned options) adds flavor without aggravating symptoms. Incorporate plenty of vegetables prepared with little or no oils, and select low-fat dairy products to keep the diet gentle on your stomach.
In addition to dietary changes, lifestyle modifications play a critical role in managing hiatal hernia symptoms. Eating smaller, more frequent meals prevents overdistension of the stomach. Avoid lying down immediately after eating—waiting at least two to three hours can help minimize reflux. Engaging in light activity and avoiding strenuous exercises post-meal can further reduce symptoms. It’s also beneficial to quit smoking, maintain a healthy weight, and wear loose-fitting clothing to reduce pressure on the abdomen. In some cases, medications such as proton pump inhibitors or antacids may be prescribed to control acid production. For severe cases unresponsive to conservative measures, surgical options like hernia repair might be considered under medical guidance. Consistent implementation of these strategies is vital for effective management, fostering better health and greater comfort for those living with hiatal hernia.