Comprehensive Guide to Breast Cancer: Types, Symptoms, and Early Detection
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of breast cancer, highlighting their characteristics, symptoms, and the importance of early detection. Understanding different classifications, such as ductal and lobular carcinoma, plus advanced stages like metastatic cancer, helps in recognizing signs and seeking prompt medical care. The article emphasizes the role of genetic factors like HER2 positivity and discusses detection methods to improve outcomes. Stay informed about breast health to increase the chances of early diagnosis and successful treatment, ultimately saving lives.

An In-Depth Overview of Breast Cancer Types, Symptoms, and Detection Strategies
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, but it can also occur in men. It originates from the cells lining the milk ducts or the lobules, which are the milk-producing glands within the breast tissue. Recognizing the different types of breast cancer, understanding their unique characteristics, and being aware of early warning signs are crucial steps in promoting early diagnosis and improving treatment outcomes. This comprehensive guide will explore the various classifications of breast cancer, their biological features, and practical tips for early detection.
The initial development of breast cancer usually begins in the lining of the milk ducts—a form known as ductal carcinoma. When the cancer starts in the milk-producing lobules themselves, it is classified as lobular carcinoma. These primary types can exhibit different behaviors, treatment responses, and prognoses. Additionally, breast cancers are classified based on molecular markers and receptor status, which help determine the most effective therapeutic approach.
Let's delve into the main types of breast cancer and their distinctive features:
Invasive Carcinoma: The most common type, invasive carcinoma, begins in the ducts or lobules and then spreads into surrounding breast tissues. This form has the potential to metastasize to other parts of the body if not detected early. It includes subtypes such as invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma.
Inflammatory Breast Cancer: An uncommon yet aggressive and rapidly progressing form characterized by swelling, redness, and warmth in the breast. Unlike other forms, it can develop without a distinct lump and often requires urgent medical attention.
Recurrent Breast Cancer: This occurs when breast cancer reappears after initial successful treatment, either in the same location or elsewhere in the body. It underscores the necessity for ongoing monitoring post-treatment.
Metastatic Breast Cancer: Also known as stage IV, this is the most advanced stage where cancer cells spread through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to other organs such as the brain, lungs, liver, or bones. Although treatable, it is rarely curable at this point.
Understanding the genetic and molecular aspects of breast cancer significantly aids in targeted therapy. One such genetic factor is HER2 (Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2). HER2-positive breast cancer involves overexpression of this gene, leading to rapid tumor growth. Patients with HER2-positive tumors often benefit from targeted treatments like trastuzumab (Herceptin) that specifically inhibit this receptor.
Recognizing symptoms associated with breast cancer is vital for early detection. These symptoms can be subtle and easily overlooked, but awareness can lead to prompt medical evaluation:
Persistent swelling in any part of the breast or underarm area
Lumps, thickening, or a noticeable mass in the breast tissue
Nipple abnormalities, such as inversion or discharge
Skin changes including redness, dimpling, or scaling near or around the nipple
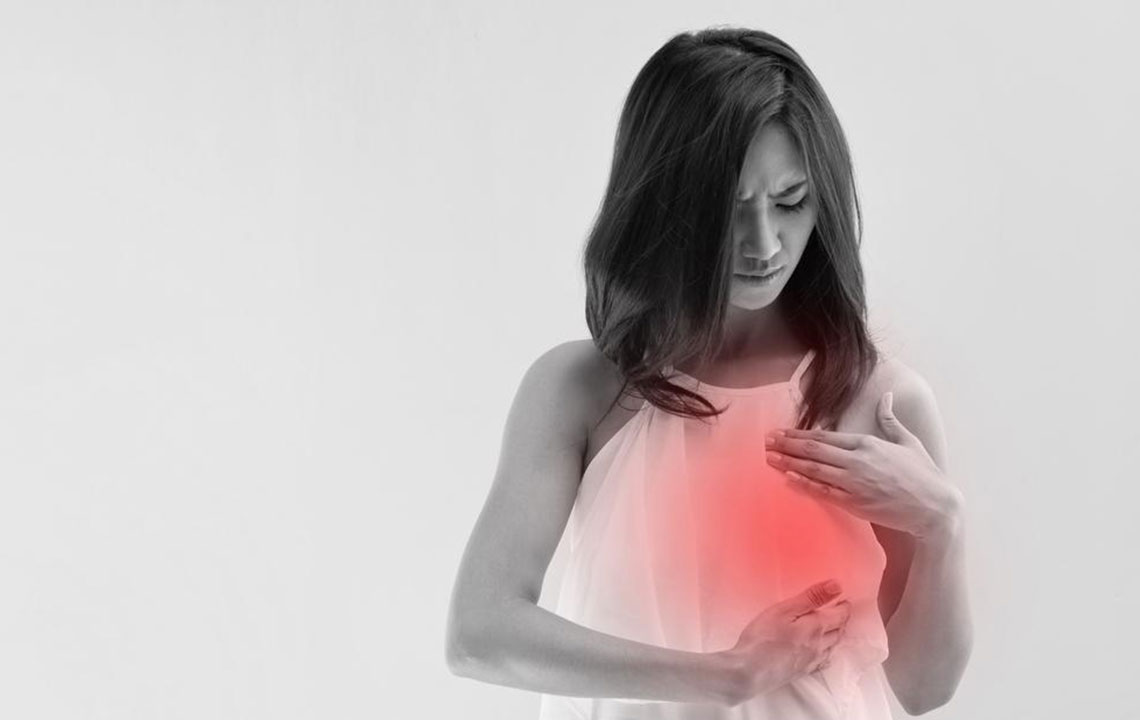
Unexplained pain in the breast or nipple
Changes in the size or shape of the breast, particularly asymmetry
Rashes, crusting, or peeling of the nipple or surrounding skin
While these signs can be indicative of breast cancer, they are also associated with benign conditions. Therefore, if any of these symptoms are observed, consulting a healthcare professional promptly is essential for diagnosis. Regular screening methods such as mammograms, clinical breast exams, and self-examinations are critical tools that facilitate early detection.
In conclusion, understanding the various types of breast cancer and their indicators enables individuals to take proactive steps toward early diagnosis and intervention. Advances in molecular biology and targeted therapies have significantly improved treatment options, but early detection remains key to better survival rates. Staying informed and vigilant about breast health can make a life-saving difference.