Comprehensive Guide to Breast Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Approaches
This comprehensive guide explores breast cancer, detailing its causes, early symptoms, risk factors, and the latest treatment options. Emphasizing early detection and personalized approaches, it aims to educate women and healthcare professionals about effective management strategies, ensuring better outcomes and improved quality of life.
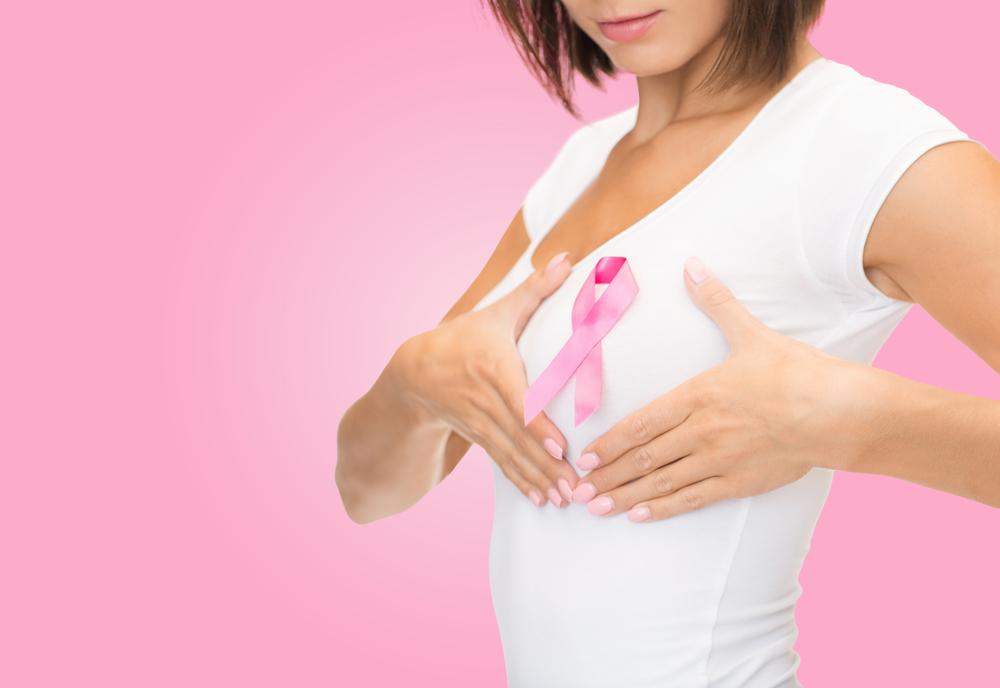

Comprehensive Guide to Breast Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Modern Treatment Approaches
Breast cancer ranks among the most common and impactful cancers affecting women globally, posing significant health challenges worldwide. Its prevalence underscores the importance of awareness, early detection, and advances in treatment options. Understanding the intricate details of breast cancer, including what causes it, how to recognize its symptoms early, and the latest available treatments, can significantly influence outcomes and survival rates.
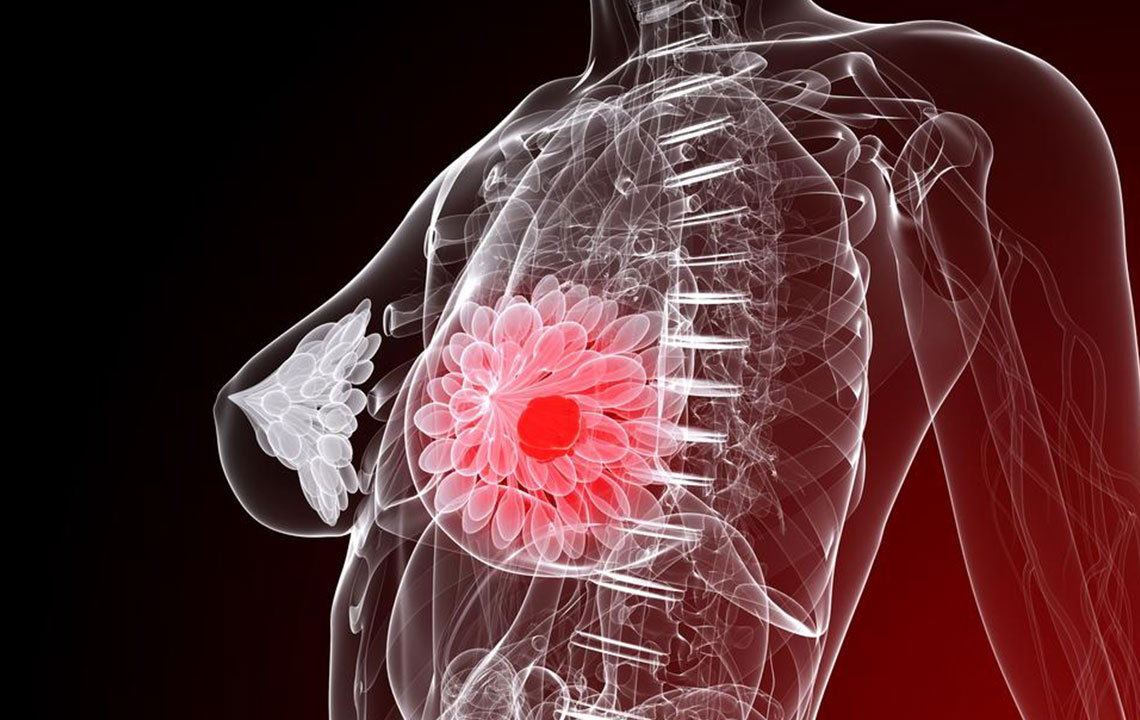
Breast cancer develops when cells within the breast tissue begin to grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors. These abnormal cell growths can invade surrounding tissues and sometimes spread to distant parts of the body through a process known as metastasis. Early detection of breast cancer is often facilitated by noticing subtle changes or abnormalities, such as a lump in the breast that persists over time. While lumps are common benign issues, persistent or unusual ones require prompt medical assessment. Besides lumps, other early warning signs include changes in breast size or shape, skin alterations, nipple discharges, or discomfort that doesn't resolve.
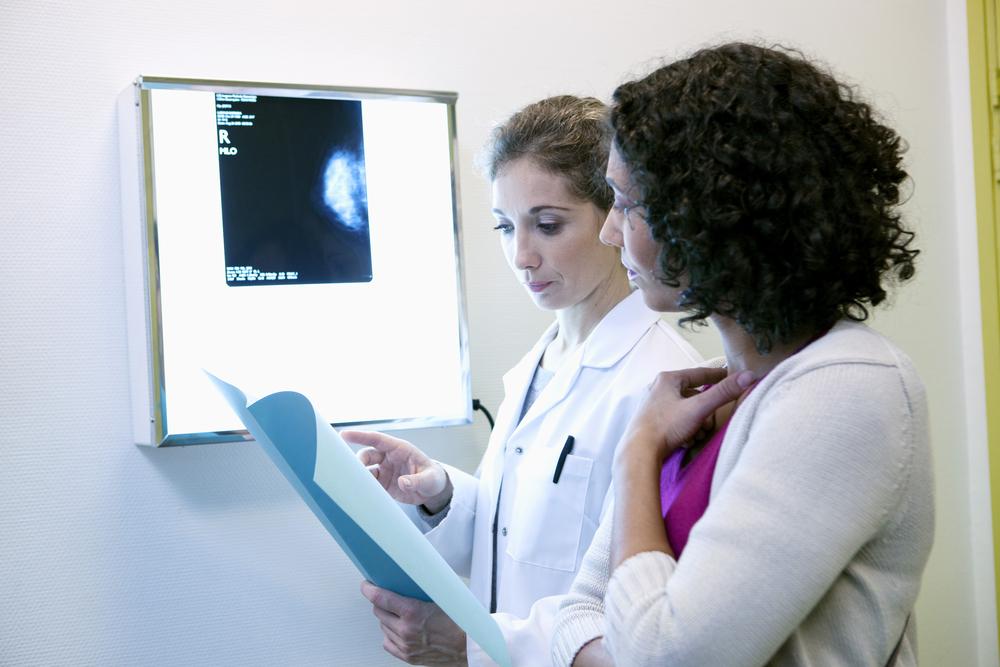
Regular self-examinations are crucial as they empower women to recognize potential signs early. Healthcare professionals recommend conducting monthly breast checks, ideally a few days after menstruation, for women of all ages. When irregularities are observed, medical evaluation, including imaging tests like mammograms, ultrasound, or MRI, becomes essential for accurate diagnosis. Identifying the specific type of breast cancer—such as ductal carcinomas, lobular carcinomas, or rarer variants like Paget’s disease—is vital for tailoring effective treatment strategies.
The statistics from the American Cancer Society highlight the gravity of the issue, with nearly 2 million women diagnosed annually worldwide. Several risk factors contribute to the development of breast cancer, some of which are modifiable while others are genetic or age-related. Post-menopausal obesity, exposure to ionizing radiation, increasing age, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapies, high-dose contraceptives, early menstruation, and dense breast tissue all elevate risk levels. Understanding these factors enables better risk assessment and preventive measures.
Recognizing symptoms early is essential for improving prognosis. Common indicators include a persistent lump that doesn't go away, unexpected breast pain, skin changes such as redness or dimpling, alterations in breast size or shape, swelling particularly near the armpit, and unusual skin discoloration. Some women also experience nipple retraction or unusual discharges. Timely identification of these symptoms facilitates earlier diagnosis, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
Treatment options for breast cancer are diverse and depend heavily on the type, stage, and patient's overall health. The primary treatment modality involves surgery, which might range from minimally invasive procedures to complete removal of the affected breast (mastectomy). Surgeons aim to excise the tumor along with some surrounding healthy tissue to ensure clear margins. In certain cases, lymph node removal is also performed to assess metastasis.
In addition to surgery, chemotherapy plays a significant role in managing breast cancer. Chemotherapy can be administered preoperatively—known as neoadjuvant therapy—to shrink tumors and facilitate less invasive surgeries. Post-surgery, adjuvant chemotherapy aims to eradicate residual cancer cells, reducing the risk of recurrence. Radiation therapy may also complement surgical and chemotherapeutic approaches, especially when cancer involves nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
More recently, targeted therapies and hormonal treatments have revolutionized breast cancer care. Drugs such as HER2 inhibitors and hormone receptor blockers (like tamoxifen) are employed to attack specific cancer cell pathways, improving survival rates and minimizing side effects. The selection of treatment protocols is highly personalized, considering the tumor's molecular profile, stage at diagnosis, and the patient's preferences and overall health.
Living with breast cancer requires not only medical treatment but also psychological and emotional support. Advances in reconstructive surgery have offered options for women wishing to restore breast appearance post-mastectomy. Support groups, counseling, and patient education are integral to comprehensive care. Regular follow-up appointments allow for monitoring recurrences and managing side effects of treatments.
Preventive strategies, such as maintaining a healthy weight, limiting alcohol intake, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding unnecessary radiation exposure, can reduce risk. For women at high risk, chemoprevention and screening protocols are tailored to facilitate early diagnosis and prevention.
In conclusion, breast cancer remains a formidable health challenge but one that benefits greatly from early diagnosis, personalized treatment, and ongoing research. By staying informed and proactive about breast health, women can improve their chances of successful treatment and recovery. Awareness campaigns, regular screenings, and advances in medical science continue to enhance survival rates and quality of life for patients worldwide.