Comprehensive Guide to Managing Gout Pain: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Effective Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores gout, emphasizing early symptom recognition, causes, and detailed management strategies. It covers medication options, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies to help sufferers control their condition effectively. Understanding these aspects is vital to prevent joint damage and improve quality of life with gout.

Effective Strategies for Managing Gout Discomfort: Recognizing Symptoms and Treatment Options
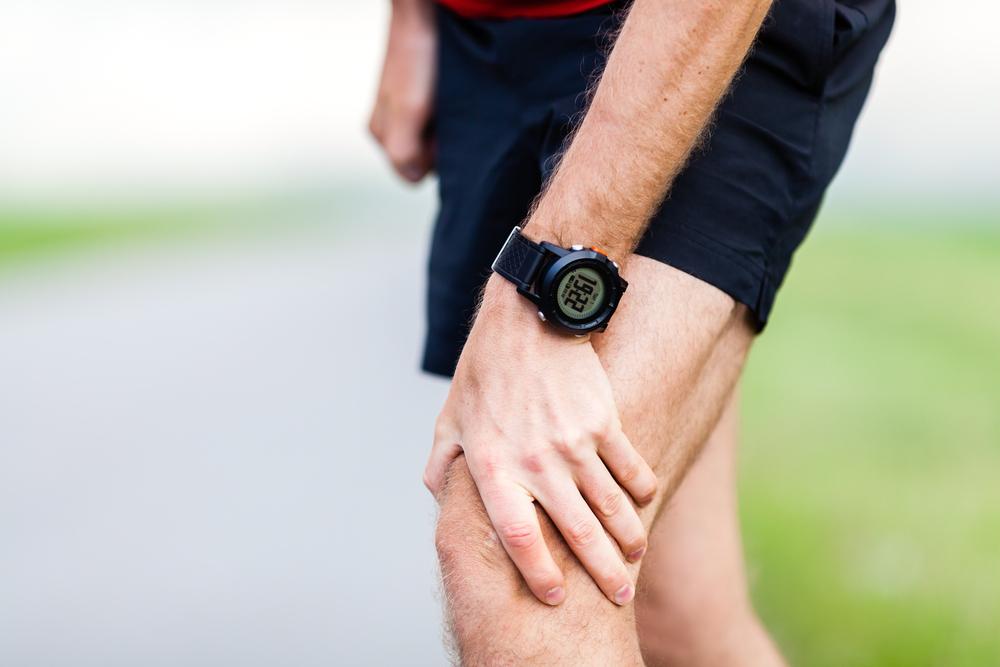
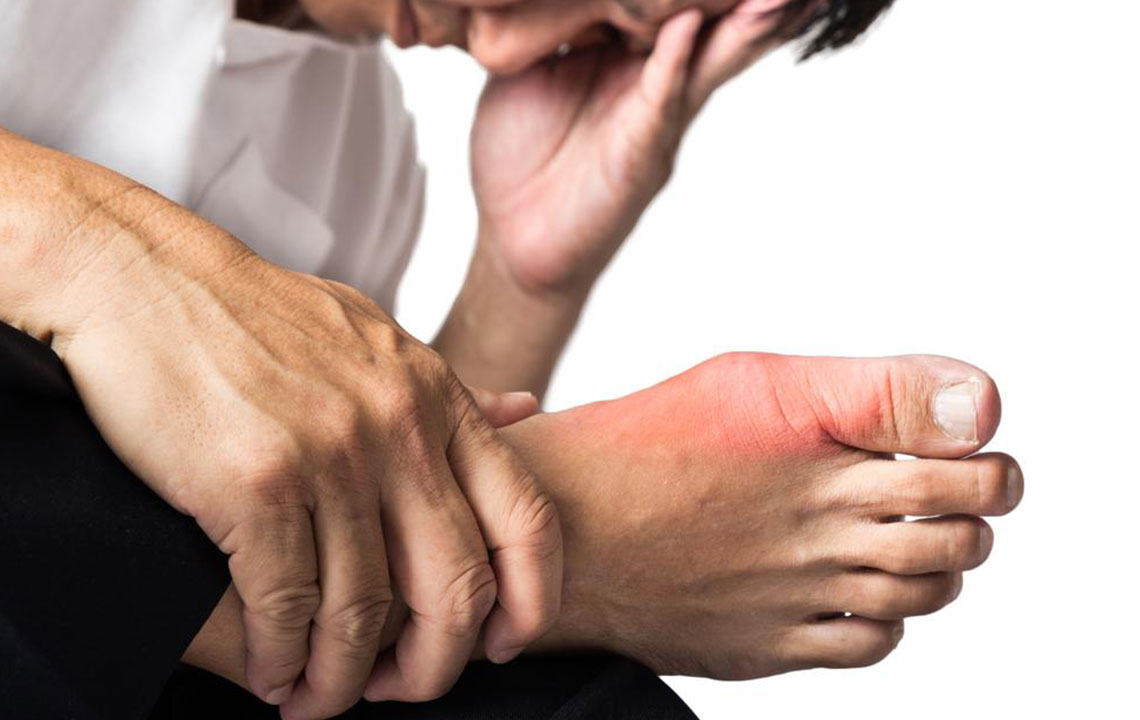
Gout is a painful form of arthritis characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, swelling, and redness in the joints. These episodes often occur unexpectedly and can affect anyone, though certain risk factors can predispose individuals to developing this condition. The most commonly affected joint is the big toe, but gout can also impact other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers. Understanding the symptoms and early signs of gout is crucial for timely intervention and effective management to prevent long-term joint damage.
Gout attacks typically develop rapidly and reach a peak within just a few hours. An initial episode usually lasts about 10 days, with the most intense pain occurring during the first three days. If left untreated, gout can spread to adjacent joints and lead to chronic joint issues, making management and prevention strategies vital for patient health and quality of life.
Recognizing the early symptoms of gout and understanding its causes are essential steps toward effective control. Gout results from excess uric acid in the bloodstream, which crystallizes and deposits in joints, leading to inflammation and pain. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on uric acid levels and the duration of crystal accumulation. Key indicators of gout advancement include:
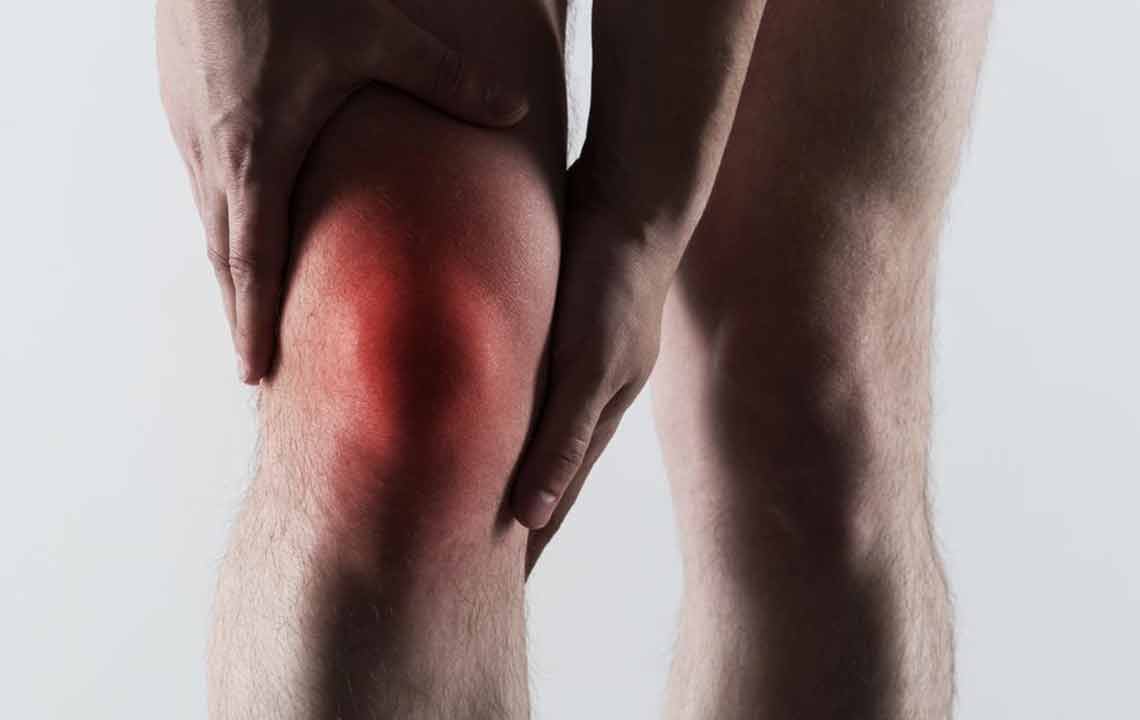
Extreme joint pain: Most notably in the big toe, but it can also affect ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
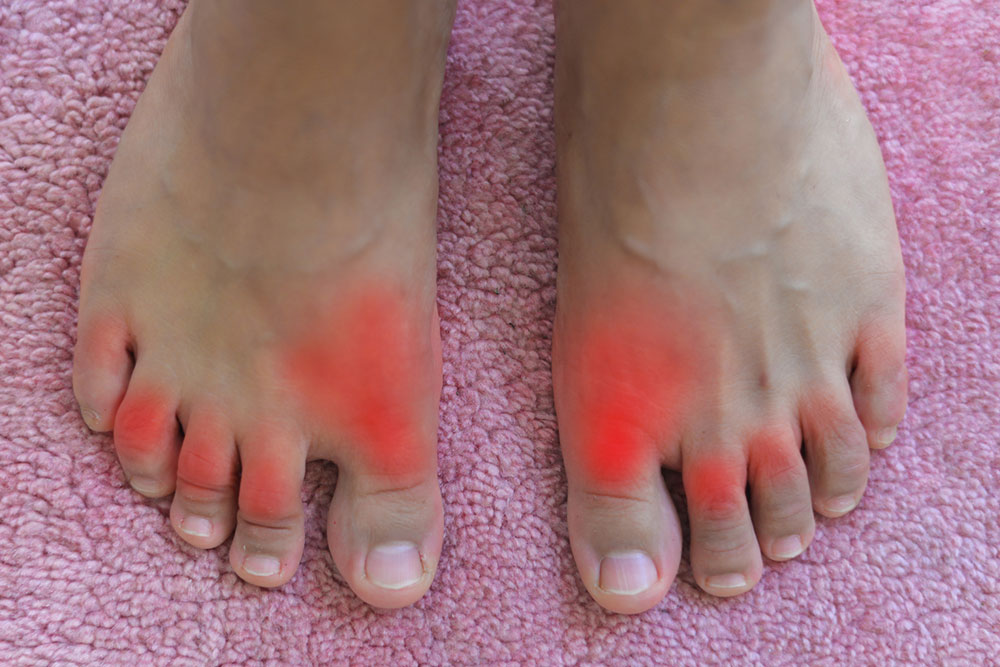
Swelling and visible nodules: Uric acid deposits cause swelling around affected joints and sometimes form firm nodules beneath the skin, known as tophi.
Persistent discomfort after an attack: Mild residual pain or sensitivity may last weeks, with future attacks often becoming more frequent and intense if untreated.
Inflammation & redness: Joints appear red, tender, and warm due to inflammatory responses caused by uric acid crystals.
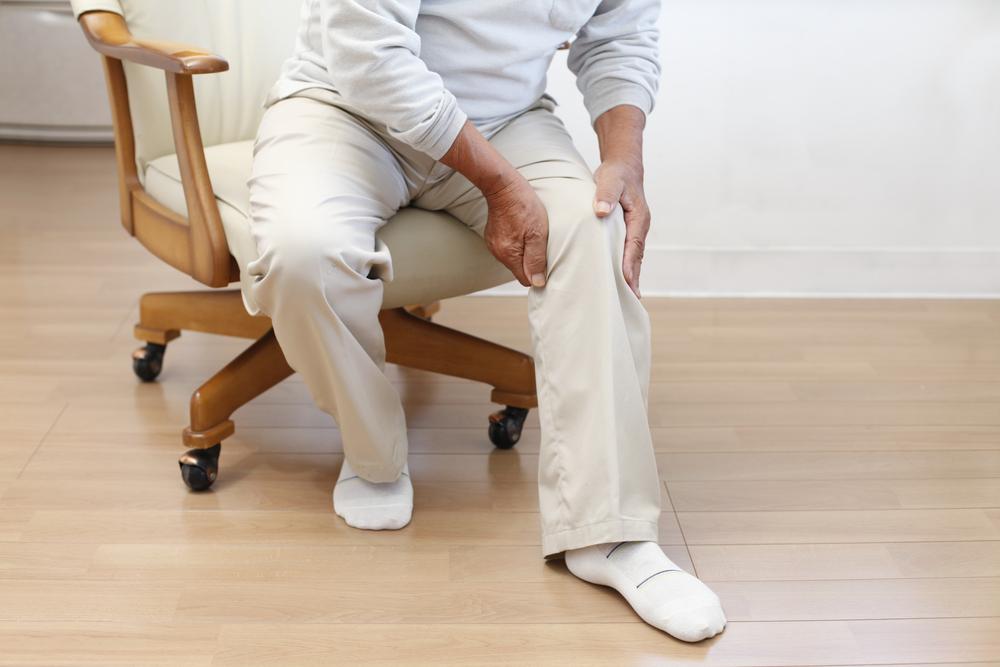
Reduced joint mobility: Swelling and pain limit movement, affecting walking and daily activities.
Balance and gait issues: Pain and swelling can hinder walking, sometimes leading to balance problems.
Fever and chills: Severe gout attacks may be accompanied by fever, signaling possible joint infection or systemic inflammation.
Strategies for Managing Gout Attacks and Preventing Future Flares
Timely intervention is key in managing gout symptoms and preventing long-term joint damage. While early treatment can often resolve symptoms within ten days, severe attacks accompanied by fever or signs of infection necessitate immediate medical attention. Management involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and supportive care.
Pharmacological treatments: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen, corticosteroids, and colchicine are commonly prescribed to alleviate pain and inflammation. Long-term uric acid-lowering medications, including allopurinol and febuxostat, help prevent the formation of uric acid crystals, reducing the frequency of attacks.
Home and supportive therapies: Applying cold packs to the affected joint can reduce swelling and numb pain. Resting the joint and elevating it can promote drainage of inflammatory fluids. Wearing comfortable, supportive footwear minimizes pressure on the affected joint and aids recovery.
Dietary and lifestyle interventions: Adopting a diet low in purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and certain fish reduces uric acid production. Staying well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps dilute uric acid and facilitates its excretion. Avoiding alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, as well as caffeine, can significantly decrease attack risk. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and balanced nutrition minimizes stress on joints and lowers uric acid levels.
Alternative and complementary therapies: Some individuals find relief through herbal supplements such as turmeric and bromelain, which possess anti-inflammatory properties. Acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine techniques may also help reduce pain and inflammation. Applying hot or cold compresses offers additional comfort by promoting circulation and reducing swelling when appropriate.
Effective gout management requires an integrated approach involving medication adherence, lifestyle changes, and early recognition of symptoms. Ignoring gout can result in recurrent attacks, irreversible joint damage, tophi formation, and potential kidney complications due to uric acid buildup. Therefore, it is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan.