Complete Guide to Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Proven Treatments for Better Joint Health
This comprehensive guide explores gout’s causes, symptoms, and effective treatments. It covers lifestyle modifications, dietary recommendations, and medical options to manage pain and prevent future attacks. Learn how to optimize joint health with expert-approved strategies and improve quality of life.
In-Depth Overview of Gout: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatment Strategies
Gout is a prevalent form of inflammatory arthritis that primarily affects adults, characterized by sudden and intense episodes of joint pain caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals within the joints. This condition, which can significantly impair mobility and quality of life, results from elevated levels of uric acid—a waste product formed when the body breaks down purines found in many foods. When the body fails to eliminate uric acid efficiently through the kidneys, it begins to crystallize in the joints, leading to painful inflammation and swelling. Gout can present as either primary, which develops independently without an underlying cause, or secondary, which arises as a complication of other medical conditions like kidney disease or metabolic syndromes.
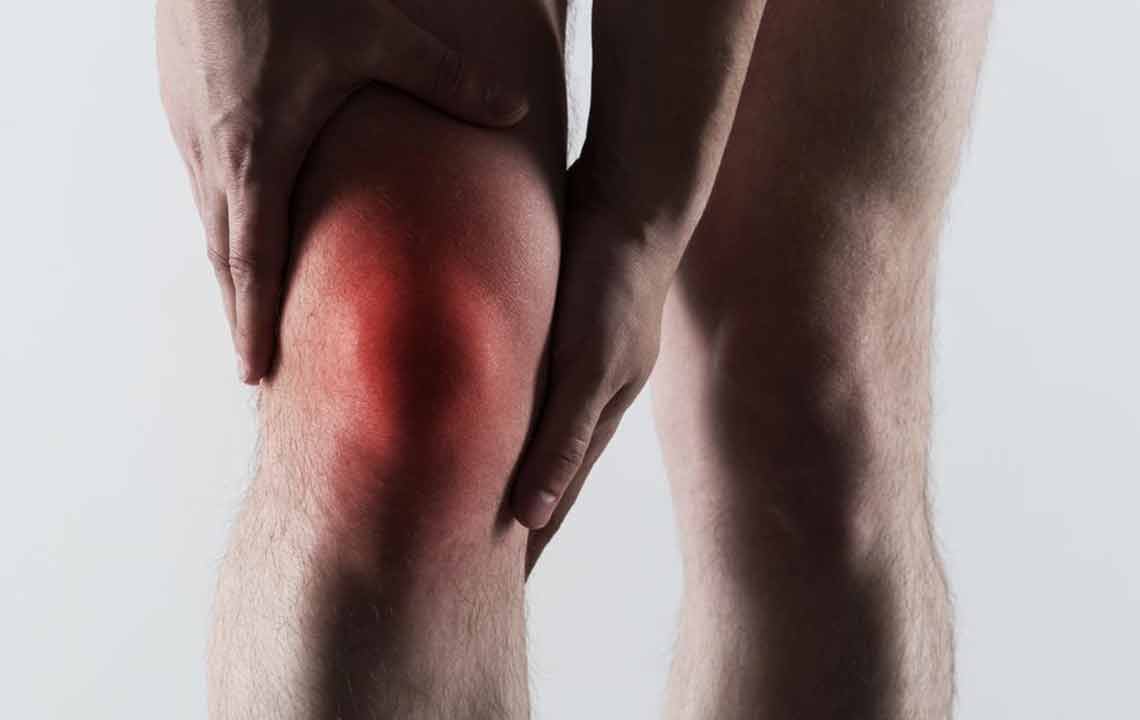
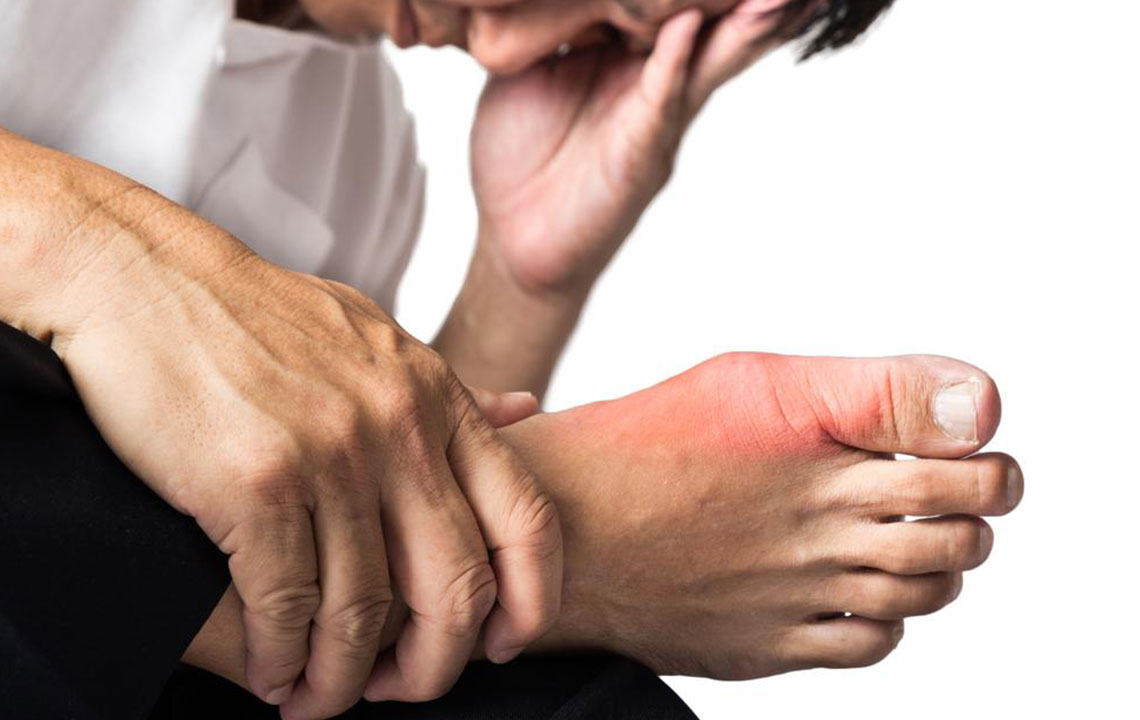
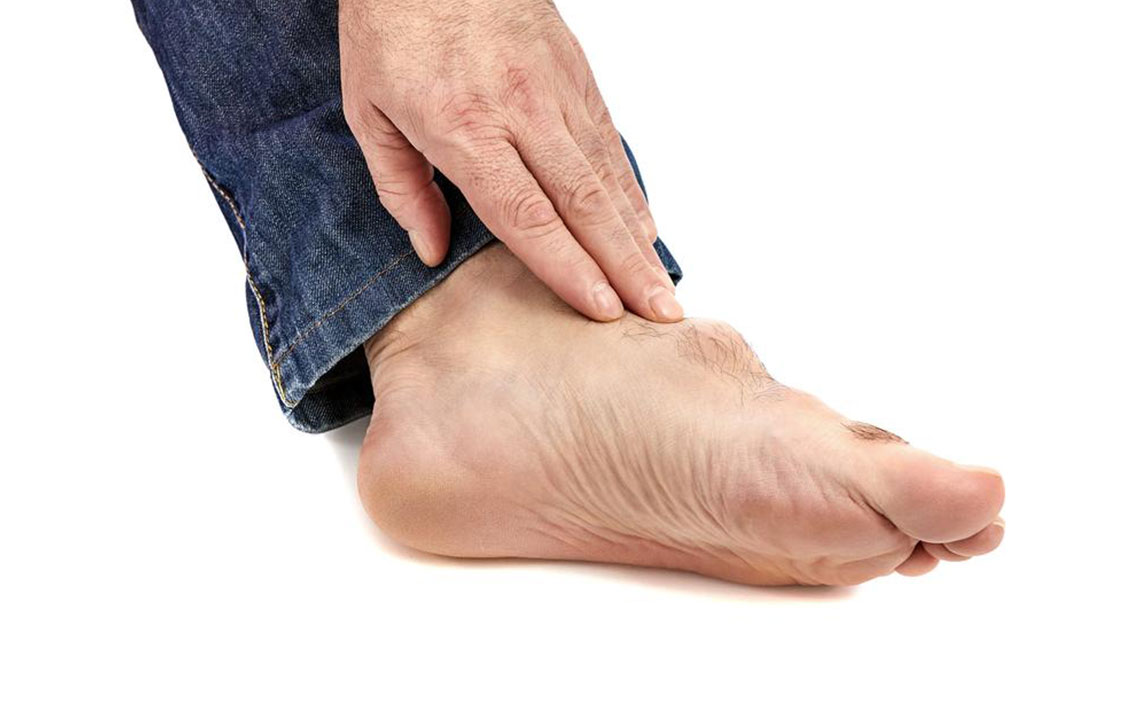
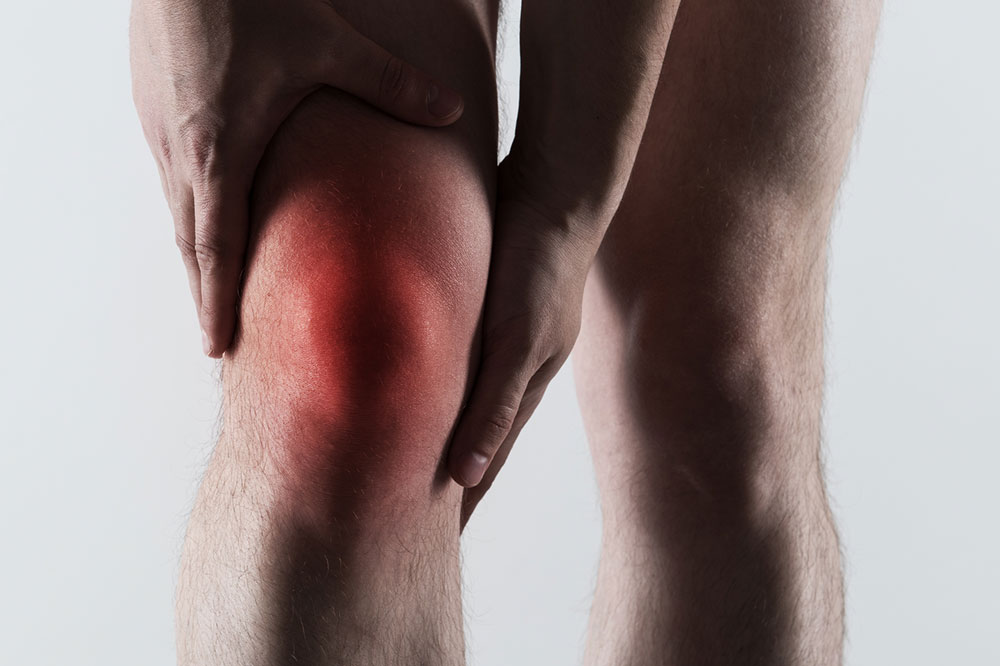
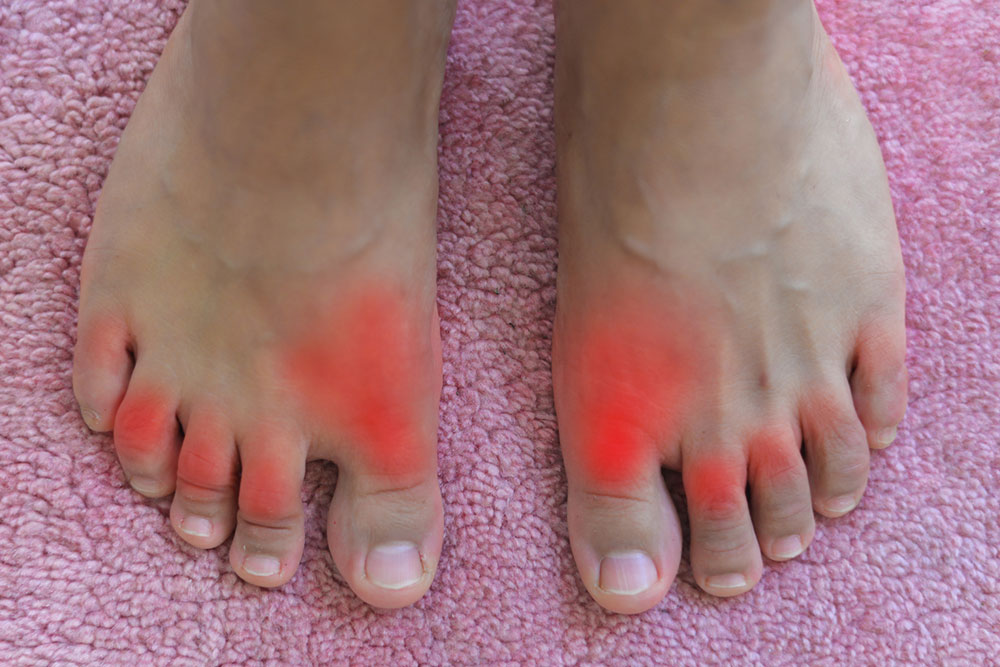
Gout predominantly affects middle-aged and older men, especially those over 40 years old, although it can also occur in women, particularly after menopause. The hallmark symptom of gout is a sudden, severe attack of joint pain that often arises unexpectedly, usually at night. The pain is usually localized in the affected joint and can be accompanied by redness, swelling, warmth, and tenderness. The most common site for gout attacks is the big toe—known as podagra—but the condition can also impact other joints such as the ankles, knees, wrists, fingers, and elbows.
Beyond the acute pain episodes, individuals might experience persistent discomfort and joint stiffness during intermission periods. Repeated gout attacks can cause joint deterioration and deformities if left untreated. Typical symptoms include sharp, intense joint pain that seems to come on suddenly, discoloration or purplish skin over the affected joints, and tenderness that makes movement painful. Attacks usually last from several hours to days, with some episodes spanning a week or more, depending on the severity and treatment measures taken.
Diagnosing gout involves a combination of physical examination and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers typically analyze synovial fluid extracted from the affected joint under a microscope to identify uric acid crystals, which confirm the diagnosis. Blood tests to measure serum uric acid levels are also conducted; however, elevated uric acid isn’t always present during an acute attack. Imaging techniques such as X-rays or ultrasound can be useful to observe joint damage and crystal deposits.
Managing gout effectively requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and medication. The primary goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation during attacks and lower uric acid levels to prevent future episodes. Patients are advised to limit or avoid foods rich in purines, such as certain types of seafood (like sardines, shellfish), organ meats (liver, kidneys), red meats, and sugary beverages—including fruit juices and soft drinks with high fructose content. Instead, a gout-friendly diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, legumes, and low-fat dairy products, which can help reduce uric acid production and promote overall health.
In addition to dietary changes, medications play a critical role. Anti-inflammatory drugs like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or colchicine are used to manage pain during acute attacks. Long-term management often involves uric acid-lowering therapies, such as allopurinol or febuxostat, which reduce uric acid synthesis, and uricosuric agents like probenecid that enhance uric acid excretion. Regular monitoring of uric acid levels and kidney function is important to optimize treatment and avoid potential side effects.
Home remedies and lifestyle practices can also greatly improve outcomes for gout sufferers. Resting the affected joint, applying cold packs to reduce swelling, staying well-hydrated to facilitate uric acid excretion, and avoiding weight-bearing activities during attacks are simple but effective strategies. Maintaining a healthy body weight through regular exercise and balanced nutrition not only lowers uric acid levels but also reduces the risk of developing gout altogether. Patients should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized management plan that takes into account their overall health, comorbidities, and treatment responses.
Understanding gout comprehensively is vital for effective management. While it can be an intensely painful and sometimes debilitating condition, advancements in diagnosis and treatment options allow patients to control symptoms, prevent future attacks, and protect joint health. Timely intervention, lifestyle changes, and adherence to medical advice are the keys to living well with gout and minimizing its impact on daily life.