Comprehensive Guide to Adult-Onset Asthma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies
Adult-onset asthma is an increasingly common respiratory condition affecting many adults worldwide. This comprehensive guide explores its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and the most effective management strategies. Understanding triggers, recognizing symptoms early, and adopting lifestyle changes are crucial for effective control. Modern treatments, personalized plans, and ongoing monitoring can help individuals maintain a good quality of life despite this chronic condition. Staying informed and proactive is essential for managing adult-onset asthma and preventing severe attacks, ensuring healthier, more comfortable lives for those affected.

Comprehensive Guide to Adult-Onset Asthma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management Strategies
Asthma has long been perceived as a disease predominantly affecting children; however, recent years have seen a noticeable rise in cases of adult-onset asthma. This form of respiratory condition can develop at any stage of adulthood, often catching individuals unaware due to the misconception that asthma is solely a childhood disease. Understanding adult-onset asthma, its underlying causes, common symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and the latest management strategies is essential for those affected and their caregivers.
Adult-onset asthma is characterized by the development of asthma symptoms in individuals over the age of 20, though symptoms can sometimes appear later in life. This condition differs from childhood asthma in various ways—including triggers, severity, and the impact of age-related physiological changes. Unlike childhood asthma, which often improves over time, adult-onset asthma may persist or worsen if not diagnosed and properly managed promptly.
Asthma, in general, involves hyperreactive airways that overreact to various environmental and internal triggers. This results in airway inflammation, narrowing, and difficulty in airflow, leading to typical respiratory symptoms. What makes adult-onset asthma particularly concerning is that its symptoms can be subtle at first, often dismissed as other respiratory issues such as chronic bronchitis or allergic reactions, leading to underdiagnosis or delayed treatment.
Within the respiratory system, the muscles surrounding the bronchial tubes tighten, causing a narrowing of the air passages. Simultaneously, inflammation causes swelling of the airway lining, and excessive mucus production further obstructs airflow. These physiological changes manifest through various symptoms that can significantly impact daily life.
Classification of Adult-Onset Asthma Severity
Mild intermittent asthma: Symptoms occur less than twice a week, and nighttime symptoms less than twice a month, with minimal impact on daily activities.
Mild persistent asthma: Symptoms occur more than twice a week but not daily, with nighttime symptoms occurring more than twice a month.
Moderate persistent asthma: Symptoms are daily, with nighttime symptoms more than once a week, affecting daily routines.
Severe persistent asthma: Symptoms happen throughout the day, with frequent nighttime episodes, severely impairing quality of life.
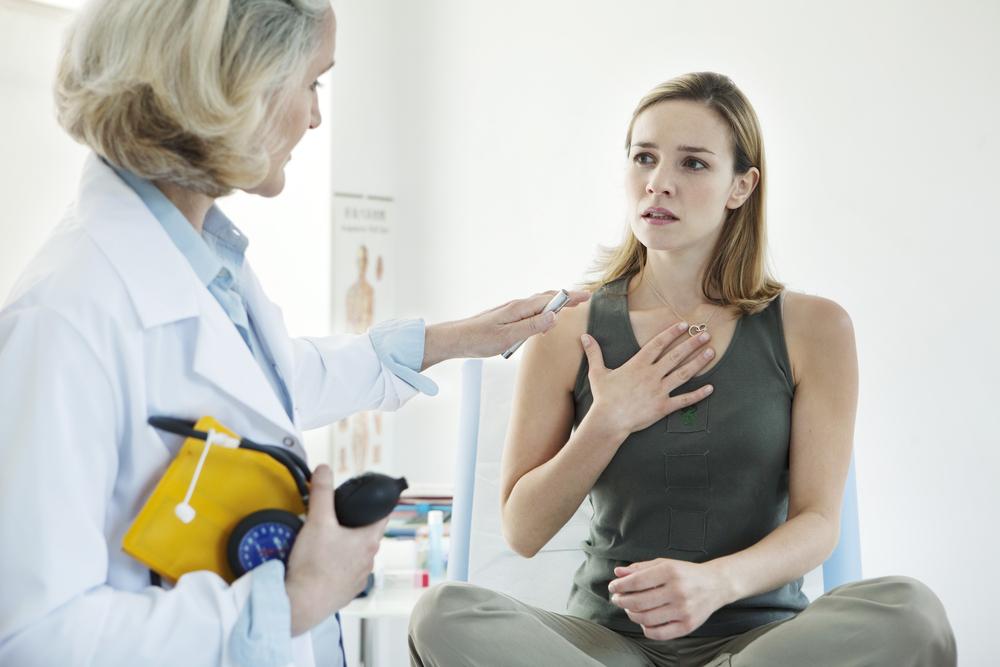
As individuals age, physiological changes such as stiffening of the chest walls and diminished muscle strength contribute to decreased lung capacity and airflow limitations. These age-related factors can mask the presence of asthma, complicating diagnosis. Hence, healthcare providers often rely on detailed medical histories, symptom assessments, and specific lung function tests, such as spirometry, to confirm the diagnosis.
Common Triggers for Adult-Onset Asthma
Triggers vary among individuals but commonly include environmental and lifestyle factors. Weather changes—particularly cold, dry air—are potent triggers. Physical exertion, especially in cold environments, can induce symptoms. Hormonal fluctuations, notably in women during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can influence airway reactivity. Exposure to indoor allergens like dust mites, pet dander—especially from cats—mold, and exposure to irritants such as tobacco smoke or air pollution also play significant roles in triggering asthma episodes.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Adult-Onset Asthma
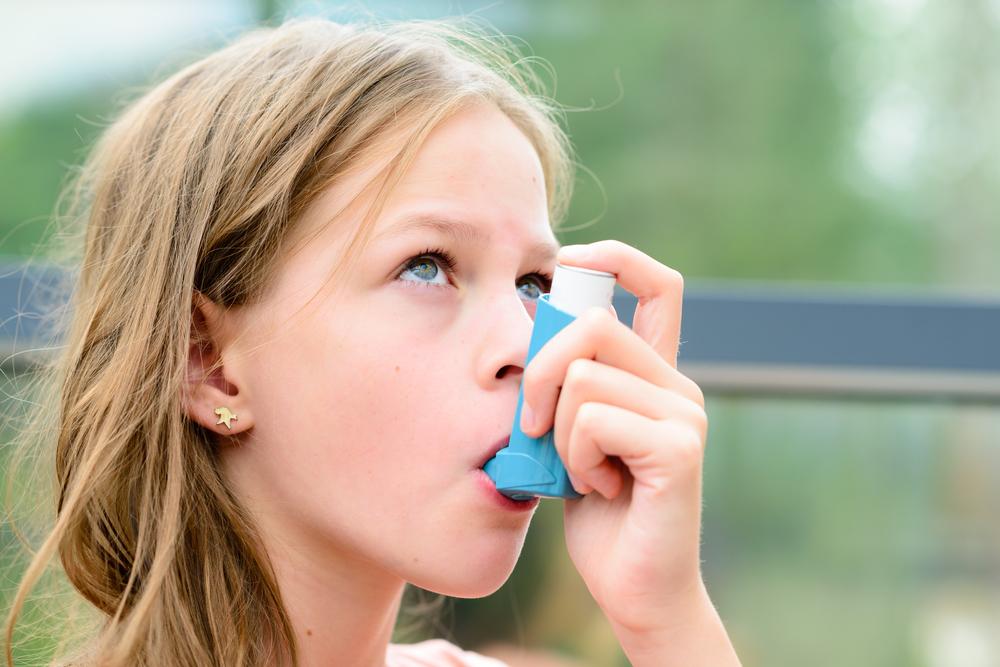
Common symptoms include persistent wheezing, a tight feeling in the chest, shortness of breath, persistent cough—especially at night or early mornings—and increased mucus production. Many individuals initially overlook these signs or attribute them to other health issues, leading to delays in diagnosis. Recognizing early symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly are crucial steps in managing the disease effectively.
Understanding the Causes of Adult-Onset Asthma
Multiple factors contribute to the development of asthma in adults. Allergic reactions are a primary cause, with pet allergies—particularly to cats—being responsible for approximately 30% of cases. Hormonal changes in women, such as those during pregnancy, menopause, or due to oral contraceptives, can influence airway hyperreactivity. Additionally, respiratory infections, especially persistent cold or flu episodes, can act as triggers, especially in genetically predisposed individuals. Environmental pollutants, occupational exposures, and lifestyle choices like smoking also contribute heavily to the risk of developing adult-onset asthma.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Adjustments
Preventing adult-onset asthma involves proactive measures. Maintaining a clean living environment—regular dusting, controlling exposure to indoor allergens, and ensuring proper ventilation—can significantly reduce risk. Avoiding known triggers such as cigarette smoke and pollution, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are also beneficial. If allergic, minimizing contact with pets or using air purifiers can help prevent episodes. Regular health check-ups and allergy testing are vital, especially for individuals with a family history of respiratory conditions.
Effective Management and Treatment Options
While a cure for adult-onset asthma remains elusive, effective management is entirely possible through a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and ongoing medical supervision. Early diagnosis is critical to prevent long-term lung damage and improve quality of life. Common treatments include inhaled corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, bronchodilators for immediate relief during asthma attacks, leukotriene modifiers, and biologic therapies for severe cases. Personalized treatment plans are developed in consultation with healthcare providers, focusing on symptom control and reducing flare-ups.
Regular lung function monitoring, adherence to medication regimens, and avoiding known triggers are essential. Patients are advised to carry emergency inhalers and develop action plans for managing exacerbations. Additionally, breathing exercises, physical activity tailored to individual capacity, and maintaining an optimal weight can contribute to better overall respiratory health.
In conclusion, adult-onset asthma is a complex but manageable condition that requires awareness, early detection, and diligent management. Understanding the triggers, recognizing symptoms early, and adhering to treatment regimes can significantly improve life quality for affected individuals. Advances in asthma research continue to enhance treatment options, promising better control and outcomes for adult patients worldwide.