Comprehensive Guide to Persistent Asthma: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Management Strategies
Discover comprehensive insights into persistent asthma, including symptoms, causes, and management strategies. Learn how to identify warning signs early and adopt effective treatment plans to control this chronic respiratory condition. This detailed guide explores risk factors, triggers, and personalized approaches to improve quality of life for asthma sufferers.

Understanding Persistent Asthma: Symptoms, Causes, and Management Strategies
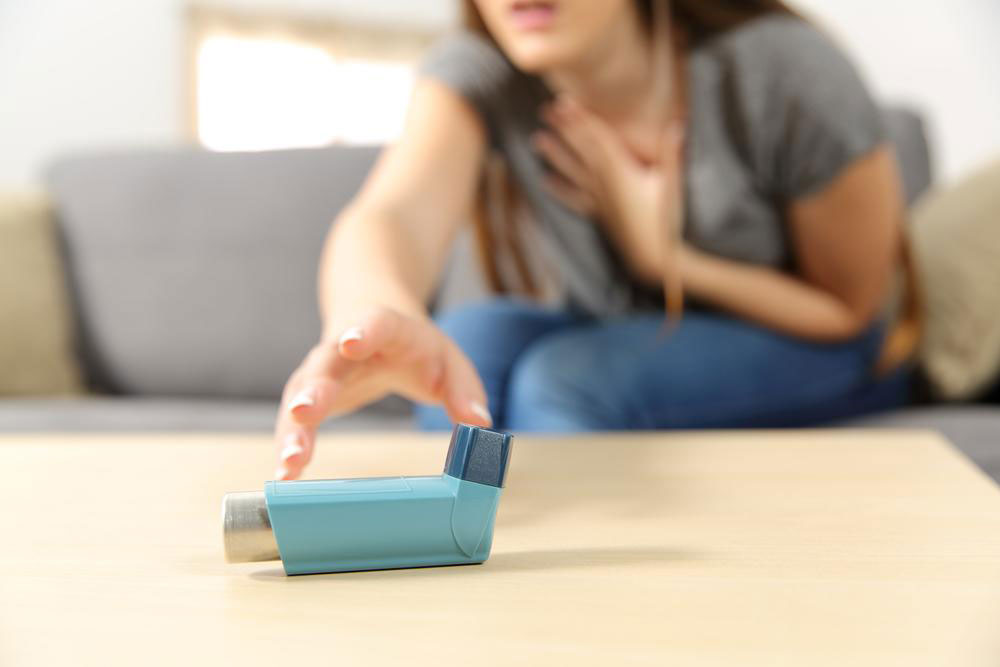
Persistent asthma is a long-term respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Unlike occasional asthma episodes, persistent asthma involves continuous inflammation of the airways, which results in chronic breathing difficulties and reduced lung function. This persistent inflammation causes the airways to become swollen and narrow, producing excess mucus that further obstructs airflow. Though there is no definitive cure for asthma, modern management techniques enable individuals to control their symptoms effectively, allowing them to lead active and fulfilling lives. Recognizing the signs early, understanding the underlying causes, and employing effective management strategies are vital steps toward improving quality of life for asthma sufferers.
Identifying the Symptoms of Persistent Asthma
Symptoms of persistent asthma can vary significantly among patients. Some individuals experience mild but constant symptoms, while others face severe episodes that interfere with daily activities. Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for prompt intervention and better disease control.
Difficulty breathing or a sensation of shortness of breath, especially during physical activity or at night
Persistent chest tightness, discomfort, or pressure that persists over time
Wheezing, which is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing, particularly during exhalation
Recurrent coughing episodes, often worse at night or early morning
Frequent episodes of breathlessness, especially during cold weather or respiratory infections
Sleep disturbances caused by coughing fits or difficulty breathing during sleep
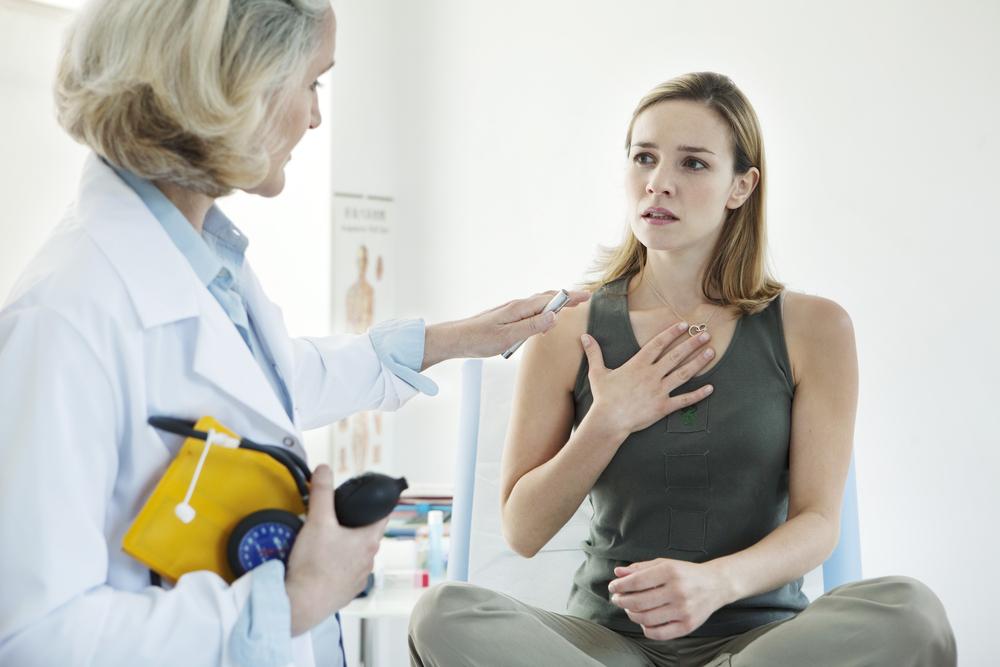
If these symptoms become more frequent, persistent, or severe, they may indicate worsening asthma, which necessitates immediate medical evaluation and tailored treatment plans to prevent potential attacks and long-term damage to the lungs.
Understanding the Causes and Triggers of Persistent Asthma
The precise cause of asthma remains elusive, but extensive research points to a complex interplay between genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of asthma or allergies are at higher risk of developing the condition. Additionally, certain environmental exposures can activate or worsen symptoms, making each patient's experience unique.
Common triggers that initiate or exacerbate asthma symptoms include:
Airborne allergens such as dust mites, mold spores, pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds, pet dander, or residues from insects like cockroaches
Physical exertion, especially in cold or dry environments
Environmental pollutants, including vehicle emissions, industrial fumes, and cigarette smoke
Chemical irritants encountered in household cleaning agents, perfumes, or workplace chemicals
Psychological stress and emotional upheavals, which can influence breathing patterns
Exposure to cold air, which can trigger airway constriction
Respiratory infections, such as influenza or the common cold, which can worsen inflammation
Dietary preservatives and sulfites found in wine, dried fruits, and processed foods
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), where stomach acids irritate the esophagus and lungs, potentially worsening symptoms
These factors can vary widely among individuals, emphasizing the importance of personalized management plans and awareness of specific triggers.
Who Is Most at Risk for Severe or Difficult-to-Control Asthma?
While asthma can affect anyone, certain populations are more susceptible to severe or uncontrolled forms of the disease. Awareness of risk factors helps in early identification and proactive management.
Individuals with a history of allergies, including allergic rhinitis and eczema
People with a family history of asthma or other respiratory conditions
Individuals with an unhealthy body mass index (BMI), especially those who are overweight or obese
Workers exposed to harmful fumes, chemicals, or pollutants in industrial or agricultural settings for prolonged periods
People who smoke or are exposed to secondhand smoke regularly
Understanding these risk factors can guide clinicians and patients in developing comprehensive strategies to manage and possibly decrease the severity of asthma symptoms. Regular medical checkups, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to prescribed treatments are critical components of managing persistent asthma effectively.
In conclusion, persistent asthma is a manageable yet complex respiratory condition that requires awareness, early diagnosis, and tailored treatment strategies. Advances in inhaler technology, medication options, and lifestyle adjustments have significantly improved the outlook for individuals living with this chronic disease. Ultimately, with proper management, most people with persistent asthma can enjoy a high quality of life without significant restrictions on their daily activities.