The Ultimate Guide to Hernia Treatment: Prevention, Management, and Surgical Options
This comprehensive guide explores hernia types, symptoms, risk factors, and effective treatment options, including lifestyle changes and surgical procedures. Early detection and professional advice are emphasized to prevent complications and ensure optimal management of hernias.
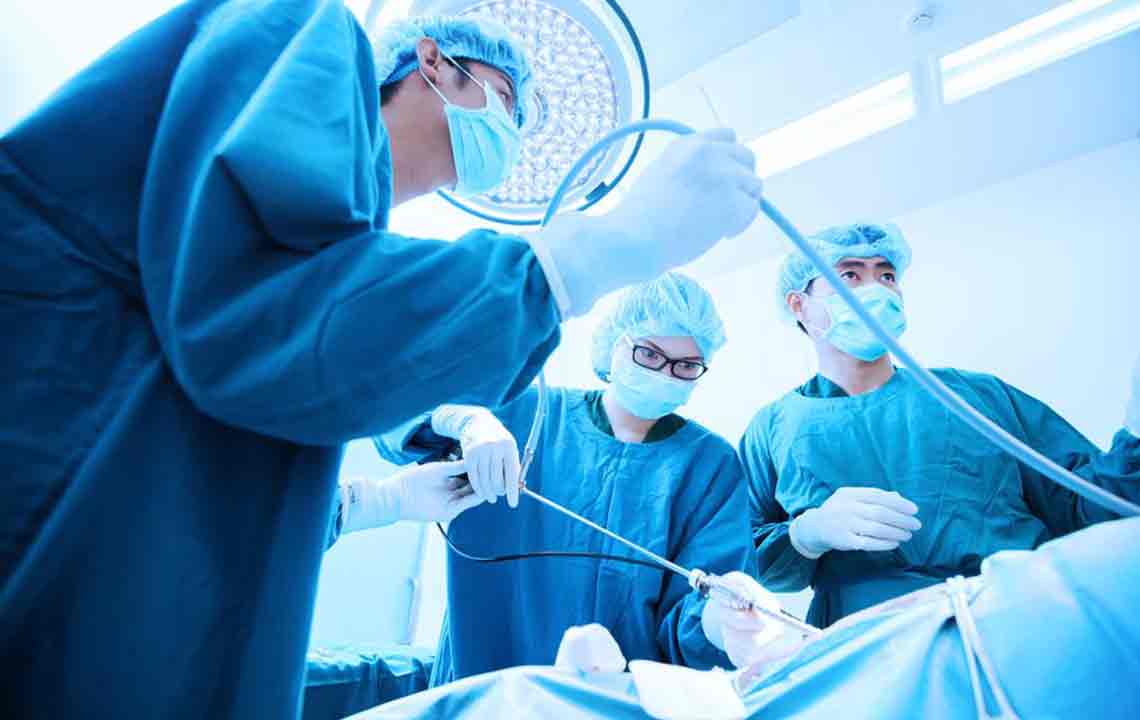

Comprehensive Approaches to Hernia Relief and Management
A hernia occurs when internal organs or tissues push through a weak spot in the muscles or connective tissue that normally contain them. It commonly develops in the abdomen but can also appear in other areas like the groin, belly button, or upper thigh. Recognizing the different types of hernias and understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options are crucial for effective management.
Understanding the Types of Hernias
Hernias are categorized based on their location and the affected tissue. The most common types include:
Inguinal Hernia: The most prevalent hernia form, occurring when part of the intestine protrudes through a weak spot in the inguinal canal in the groin. It largely affects men and can cause noticeable swelling or discomfort in the groin area.
Hiatal Hernia: Develops when part of the stomach pushes upward into the chest cavity through the diaphragm. This type often leads to symptoms related to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), such as heartburn and acid regurgitation.
Umbilical Hernia: Common among infants under six months but can also affect adults, where intestine or fatty tissue protrudes through the abdomen near the navel. It is often noticeable as a swelling or lump near the bellybutton.
Incisional Hernia: Occurs at the site of a previous surgical incision, where scar tissue weakens, allowing internal organs to push through the surgical wound.
Femoral Hernia: Typically affects women and involves the protrusion of fatty tissue or bowel through the femoral canal in the upper thigh, often presenting as a bulge just below the groin.
Identifying Hernia Symptoms and Risk Factors
Common signs include a visible swelling or lump, discomfort or pain at the hernia site, especially during activities like coughing, lifting, or bending, and in some cases, nausea or bowel obstruction. Factors increasing hernia risk comprise heavy lifting, chronic coughing, obesity, pregnancy, and previous abdominal surgeries.
Effective Hernia Treatment Strategies
Proper management of hernias is vital to prevent complications such as incarceration or strangulation of the herniated tissue. Various treatment options range from conservative lifestyle modifications to surgical interventions.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Implementing dietary changes, avoiding heavy or greasy meals, refraining from lying down immediately after eating, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking can significantly reduce symptoms and prevent hernia progression.
Medication Use: While medications don't cure hernias, drugs such as antacids or acid reducers can alleviate symptoms like acid reflux associated with hiatal hernias. These medications can improve quality of life but do not address the hernia itself.
Targeted Exercise Programs: Engaging in gentle core strengthening exercises andAvoiding strenuous activities help support abdominal muscles. Activities like water therapy, gentle abdominal massage, and specific breathing techniques may assist in hernia management. Consulting a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen is essential.
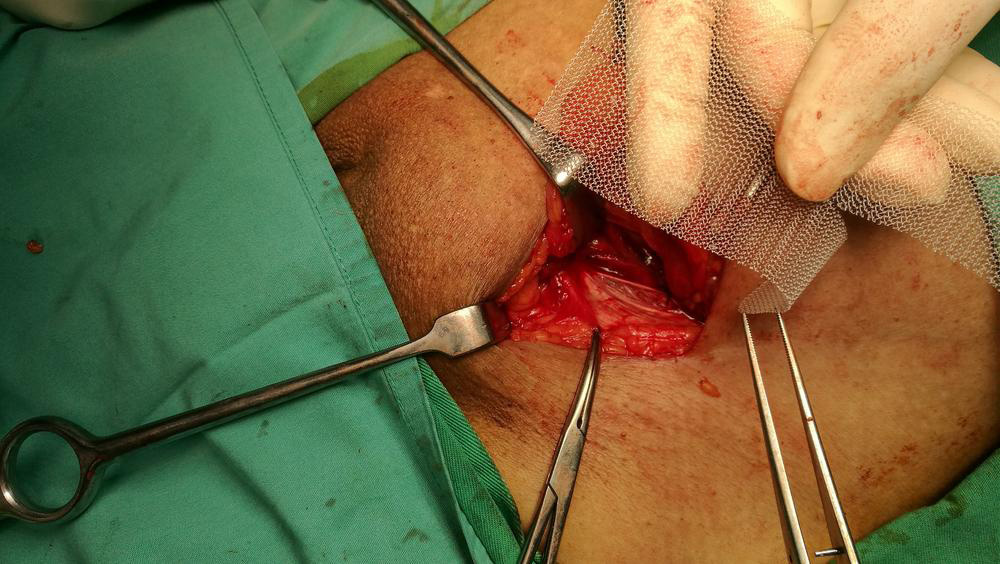
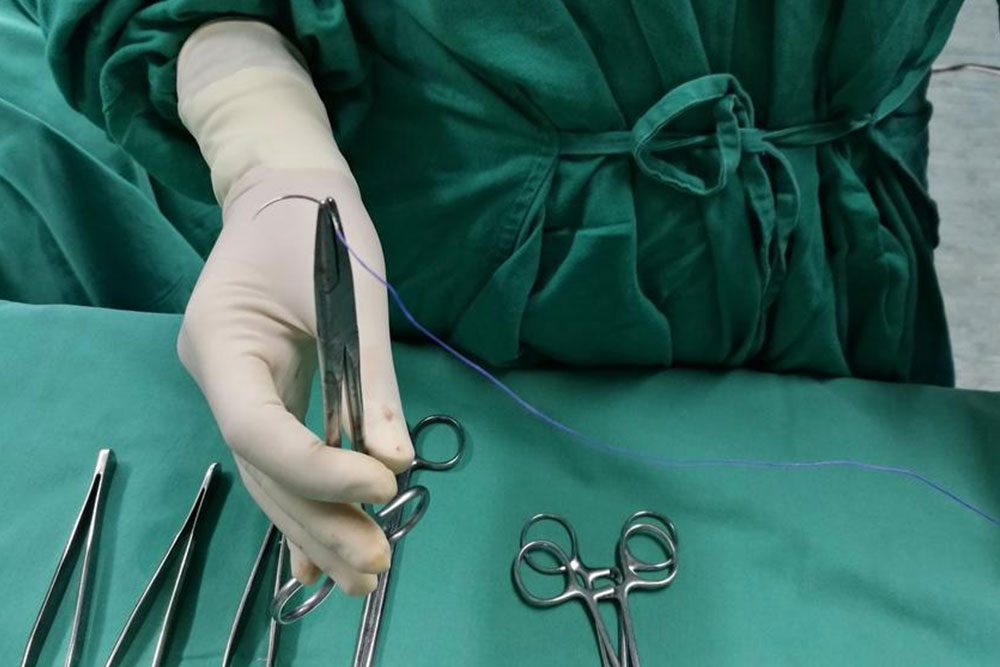
Surgical Interventions: Surgery is often necessary when hernias cause significant pain, enlarge, or pose risks of complications. The two main surgical procedures include:
Open Hernia Repair: Involves making an incision near the hernia site, pushing the protruding tissue back into place, and suturing the weakened muscle wall. Mesh reinforcement is commonly used to strengthen the repair and reduce recurrence risk.
Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery: A minimally invasive technique using small incisions and a camera-guided approach. It allows quicker recovery, less post-op pain, and often results in a lower chance of hernia recurrence.
The Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Timely diagnosis and management of hernias are critical to prevent complications such as incarceration (where tissue becomes trapped) or strangulation (where blood flow is cut off), which can be life-threatening. If you suspect a hernia, seeking immediate medical attention ensures the right treatment strategy is implemented promptly.
Always consult a qualified healthcare professional to discuss your symptoms and determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific condition. Do not attempt to self-treat or delay seeking medical advice, as untreated hernias can lead to serious health issues.