Comprehensive Insights into How Hepatitis C Affects Your Body and Overall Health
Hepatitis C significantly impacts liver health and can cause systemic issues affecting digestion, neurological function, and circulation. Early detection and modern antiviral treatments have improved outcomes, making awareness crucial for prevention and management of this persistent infection.

The Impact of Hepatitis C on Your Body and Well-Being
Hepatitis C, commonly known as hep C, is a contagious viral infection that primarily targets the liver, leading to inflammation and potential long-term damage. This disease is transmitted mainly through contact with infected blood, such as sharing needles, unsterilized tattoo equipment, or blood transfusions before screening protocols were improved. Understanding hepatitis C comprehensively is essential for early detection, management, and prevention. In this detailed guide, we will explore how hepatitis C impacts various bodily functions, the symptoms to watch for, and the most effective ways to address this persistent health threat.
How Hepatitis C Affects the Human Body
Many individuals infected with hepatitis C may remain asymptomatic for years. However, despite the lack of symptoms, the virus can cause significant damage over time. Recognizing the effects of hepatitis C on different organs and systems in the body is crucial for timely intervention.
This comprehensive guide delves into the primary effects of hepatitis C on the body, shedding light on how this virus influences health and what you can do to mitigate its impacts:
Liver Damage and Disease Progression: The hepatitis C virus primarily infects liver cells, leading to inflammation and, over time, chronic liver disease. The early stages may go unnoticed, but persistent infection can cause liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer). The destruction of healthy liver tissue impairs the liver's ability to perform its vital functions, which affects overall health.
Disrupted Bile Production and Digestive Issues: The liver produces bile, a substance essential for digesting fats. Hepatitis C-induced liver damage can impair bile synthesis, leading to problems digesting fatty foods. This can result in symptoms like diarrhea, bloating, and malabsorption, ultimately affecting nutritional health.
Impact on Toxin Filtration and Central Nervous System: The liver's role in detoxifying the body is compromised by hepatitis C. When the liver can't effectively filter toxins from the bloodstream, these toxins may accumulate, leading to neurological symptoms such as forgetfulness, confusion, difficulty concentrating, and in severe cases, hepatic encephalopathy—a decline in brain function due to liver disease.
Blood Flow Disruptions and Circulatory Problems: As hepatitis C progresses, it can cause increased pressure in the veins that carry blood from the liver, known as portal hypertension. This condition can lead to varices (enlarged veins), which are prone to rupture and bleeding, posing serious health risks. Also, impaired circulation can cause swelling and other complications in various parts of the body.
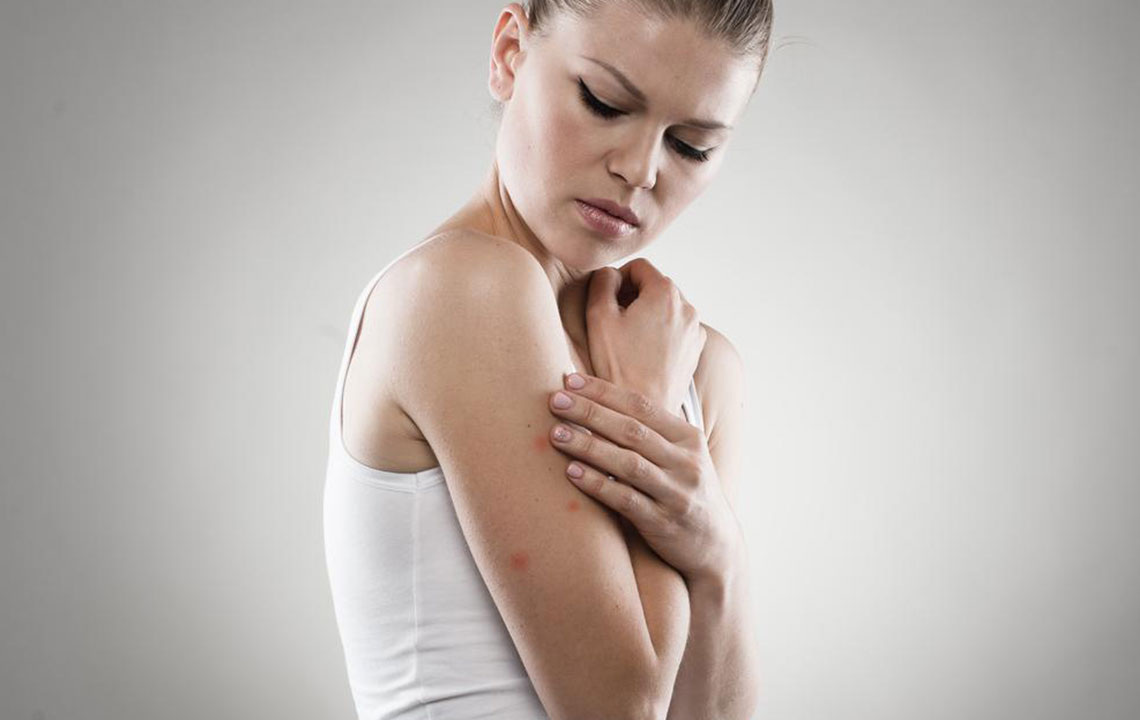
Skin, Hair, and Nail Changes: The systemic effects of hepatitis C may manifest in skin problems like rashes, pigmentation changes, or itching. Hair thinning or hair loss and brittleness of nails can also occur, signifying a broader impact on health.
Recognizing these effects underscores the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment strategies for hepatitis C. With advancements in antiviral therapies, the prognosis has improved significantly, making it possible to cure the infection and prevent severe health complications.
In conclusion, hepatitis C is a serious viral infection with far-reaching effects beyond the liver. Its progression can lead to life-threatening conditions if left untreated. Maintaining awareness of its symptoms and risk factors, coupled with timely medical intervention, can help manage the disease effectively and improve long-term health outcomes.